Lec 30 - VFs Bacterial Toxins Flashcards
(12 cards)
Give the 2 subtypes of toxins & explain them briefly
EXOTOXINS
- soluble proteins
- heat labile
- secreted/released during cell lysis
- found in both Gram +/-ve bacteria
ENDOTOXINS
- LPS component in OM of Gram-ve
How are exotoxins named and do they have one specific cell type they affect?
- named based on species they come from, activity, cell type attacked
- can affect one single type of cells or more of a broad range
What are the 3 main types of exotoxin?
- AB toxins
- membrane disrupting toxins
- superantigens
Give 3 examples of AB toxins and state the 2 types of AB toxins that can be found (draw a diagram of these 2 types)
DIPTHERIA TOXIN
CHOLERA
BOTULINUM (BoNT/Botox)
- simple / compound
- disulfide bridges hold the 2 components together following proteolytic cleavage

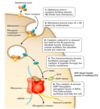
Describe the diptheria toxin , draw a diagram summarising this process
- simple
- produced by lysogenic phages under conditions of low Fe (body)
- A part ADP ribosylates EF2 at dipthamide resiue
- results in no translocation on the ribosome and therefore no protein synthesis
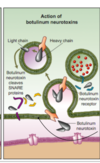
Describe the Botulinum toxin
- simple
- release of the A subunit following endocytosis and escape from endosome, works to cleave SNARE proteins
- this means that acetylcholine vesicles can’t fue @ the membrane of the neuromuscular junction & no acetylcholine neurotransmiiter released
- muscle paralysis
Describe the cholera toxin
- compound
- endocytosis (normally) then when reaches Golgi A1 subunit released into cytosol
- ADP ribosylates GSa protein
- stops hydrolysis of GTP
- build up of GTP
- activates adenylate cyclase
- more cAMP
- activates protein kinase A
- P CFTR protein leading to efflux of Cl- ions
- results in massive loss of water from lumen of the gut
Describe the 2 forms of membrane disrupting toxins & briefly describe them
PORE FORMING
- protein aggregates @ cell membrane
- no enzyme activity
- results in pore formation and loss of ions&metabolites
- eg staphyloccocal a toxin binds to cholesterol molecules in membrane
ENZYMES
- eg phospholipases
- hydrolyse head groups @ varying positions
- major membrane disruption and strucutural failures
Describe superantigens and give an example of where a superantigen is involved in disease
- superantigens create unnatural associations between MHC II receptors (on APC) and T cell receptors of T cell
- leads to overrelease of cytokines from T cell
- organ failure due to increase in cytokines
Eg = Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin first identified in tampon use from S. aureus
Draw a diagram to illustrate how superantigens bind APCs and T cells together

Draw the structure of LPS and state the function of the core polysacchardie
core polysacchardie confers solubility

Which part of LPS is the most toxic and what occurs when it is released into the bloodstream?
- Lipid A = most toxic
- stimulates cytokine release leading to septic shock
- Lipid A mediated cytokine release also leads to complement and coagulation cascade
- leads to coagulation of blood in peripheral vessels > ORGAN FAILURE
- leads to low blood pressure (hypotension) > CELL DEATH


