Lec 3 - Hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds Flashcards
Draw out the RNA backbone including which phosphodiester bonds are going to be cleaved also give the names of the carbon groups where cleavage occurs
Raff 3 pg 2 3’ and 5’

What type of reaction is the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bonds
SN2 substitution nucleophillic bimolecular
Draw out the general scheme for the hydrolysis of nucleic acids for an SN2 nucleophillic attack
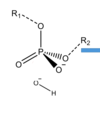
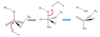
Draw out the associative and dissociative SN2 mechanisms involving the P group
Raff 3 pg 5

Under what conditions can the phosphodiester bond self cleave? Draw out this mechanism

alkaline

Are nucleases separate enzymes or part of larger complexes?
can be both separate and part of larger complexes - eg DNAP has a nuclease domain as a checking mechanism
Describe the general mode of action of REases
- nonspecific binding to DNA - linear diffusion - by either a scanning mechanism or jumping - increase in no. specific interactions @ target site creates fold in DNA - metal ions act as cofactors - hydrolysis - release of products
Give 2 examples of Type II REases and give the residue sequence of the common motif found in their AS
EcoRV EcoRI - PD…D/ExK
Give examples of metal ion cofactors found in REases
- Mg2+, Mn2+ (less common because rare) - Ca2+ most likely to be used as an inhibitory compound
Give the 3 uses that metal ion cofactors have
- stabilises the double -ve charges of the pentavalent TS - promotes formation of OH- nucleophile by a base eg Lys/Glu - stabilises the 3’ Oxyanion leaving group
How are the metal ions stabilised in the AS
- Asp/Glu residues
Why is Mg2+ a popular metal ion used in REases?
high charge density and can coordinate H20 molecules
Where is at least one metal ion positioned w/in the AS
near the scissile P group which fills the space when the p group leaves
Describe the one metal ion mechanism
substrate assisted cleavage
- O- group from nearby P is used to generate attacking OH- nucleophile

Which compound and why was it used to identify this one metalion mechanism
methylphosphonate no -ve charge on O- therefore no nucleophile could be generated
Describe the 3 functions of the Mg2+ ions in a 2 metal ion catalysis
- together stabilise pentavalent TS negative charges (need to be 4A apart for this) - one promotes the formation of the nucleophile - one positions a H20 molecule to attack as H+ donor to stabilise the 3’ oxyanion group
Describe the HNH family nucleases
uses His residues to promote the formation of the OH- nucleophile uses Mg2+ to stabilise the TS intermediate
Give the name of a HNH type nuclease and name a couple of metal ions that can be used as cofactors
E7 colison His molecules (as well as generating nucleophile) stabilise the positioning of Zn2+, Mg2+
Describe the 2 pathways that can be followed to remove the ssDNA flaps from the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand
RNase H dependent - RNase H then cleavage by FEN1 (humans) RNase H independent - just cleavage by FEN1

Describe how the T5 phage FEN breaks the flap ssDNA
helical arch structure where the flap ssDNA is passed through allows the 3 metal ions in its AS to be in close proximity to the P backbone the metal ions (Mg2+) stabilise the TS intermediate and promote the formation of the attacking OH- nucleophile


