Lec 1 - Fatty acid biosynthesis 1 Flashcards
Why, in biological applications, can borohydride (BH4-) not be used as a reductant? What alternative is used for biological systems?
v powerful reductant B is toxic to the cells - NAD(P)H
Give the full name of NADP
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (P)
Draw a rough outline of the NADP structure

In which form, NADH or NAD+, do we get a planar e- ring structure and why?
NAD+ - only 1 H at C4 therefore planar 2 Hs @ C4 means that 1 H is pointing above the plane and one is pointing below
Draw a generalised mechanism of an NADH cofactor and an acyl group being reduced

What are the 2 key things that correct H- transfer has to have in order to achieve perfect stereospecificity?
cofactor and substrate have to be at correct angle and distance for H- efficent transfer
What is the normal distance between NADH and its substrate for H- transfer to occur?
VDW distance (3.5A)
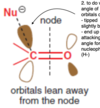
Regarding the orbitals of the C in a C=O bond, which direction/angle are they in in order for nucleophilic attack to occur?
orbitals are pointing away from the node
Name the enzyme system that carries out fatty acid (FA) biosynthesis
Fatty acid synthetase enzyme (FAS)
Name the types of FAS and state which organisms they are present in
FAS I - vertebrates, yeast, some bacteria FAS II - plants, most bacteria (eg E. coli, M. tuberculosis)
Describe Type I / II FAS systems
Type I - one/two polypeptides w/ catalytic domains Type II - multiple polypeptides each catalysing a single step
Draw the fatty acid elongation cycle


Describe the FA elongation cycle (in general terms)
addition of 2C units to an S-acyl primed ACYL CARRIER PROTEIN
Describe the structure of an E. coli ACP
ACP - phosphopantetheine arm - Ser - covalently linked acyl groups
What happens to the binding pocket of ACP during FA elongation? What also happens to the phospopantetheine arm and and FA chain?
the binding pocket expands to accommodate the growing peptide chain - adopt a number of different binding modes and configurations
Draw out the reaction mechanism that is catalysed by Beta Keto ACP reductase (BKR)

What 2 key residues are in the AS of BKR?
Lys and Tyr
Describe the BKR structure
- tetramer
- NADPH dependent
- Rossman fold


