Large Bowel Flashcards
Facts about the caecum
Blind pouch just distal to the ileocecal valve - larger in herbivores
Facts about the appendix
Thin, finger like extension of the caecum - not physiologiclaly relevant in humans
What are the principal functions of the large bowel
Reabsorption of electrolytes and water
Elimination of undigested food and waste
1.5m long 6 cm diameter
Differen parts of the colon
Asencding colon runs from caecum to hepatic flexure
Transerse colon runs from hepatic flexure to spelnic flexure, hangs off the stomach - attached by a wide band of tissue called greater omentum
Descending colon - splenic flexure to sigmoid colon
Sigmond colon runs from descneding colon to rectum
Blood supply of colon
Supplied with blood by the middle colic artery (branch of superior mesenteric artery)
Distal third of colon perfused by inferior mesentric artery
Region between two is sensitive to ischemia
What is taenia coli used for
Large intestine motility
What are teh nodules of lymphoid tissue
Small intestine - peyers patches
Large intestine - solitary nodules
What causes haustra
Taenia coli shorter than small intestine
Colon function
Colon absorbs electrolyes and water
Na and Cl absorbed by exchange mechanisms
Water follows by osmosis
K moves passively into lumb
Large intestine can reabsobre 4.5 litres - above this threshold results in diarrhoea
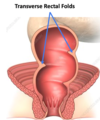
How is the rectum different to the colon
Transverse rectal folds in submucosa and absence of taenia coli
What is the mucosal organisation of large bowel
Mucosa appears smooth at gross level because no villi
Enterocytes have short irregular mcirovilli with reabsorption of salts
Crypts dominated by goblet cells
Goblet cells in large bowel
Mucus - facilitates passage of increasingly solid colonic contents
Acetylcholine - stimulates goblet cell secretion
Difference between large bowel and small bowel
No paneth cells and enteroendocrine cells
Glycocalyx do not contain digestive enzymes
What are the muscle layers of the large bowel
Circular muscles segmentally thickened
Logitudinal laeyrs concentrated in three badns -taenia coli
Between taenia longitudinal layer is thin
Bundles of teniae coli penetrate circular layer at irregular intervals
Is movement of large bowel more or less complicated than small intestine
More complicated


