Language of Anatomy Flashcards
What is the anatomical position and what does it look like?
Reference position to describe all comparative and some absolute terms to navigate around the body
Standing erect, eyes looking forwards, body over the hips and so a perfect line of balance, feet together, arms by the side, palms facing forwards

What is meant by the terms:
Bilateral
Unilateral
Ipsilateral
Contralateral
Bilateral - two of the same structure on either side of the body e.g. eyes, ears, upper limbs etc.
Unilateral - one of that structure e.g. spleen
Ipsilateral - a structure is on the same side of the body as another structure
Contralateral - a structure is on the opposite side of the body as another structure
What is meant by the terms: superior, inferior, posterior, anterior, medial, lateral, external and internal?
Superior - above
Inferior - below
Posterior - back / behind
Anterior - in front / ahead
Medial - towards the middle of the body
Lateral - towards the side of the body
External and internal tend to refer to the surfaces of the same structure:
External - on the outside
Internal - towards the inside
What is meant by the terms: superficial, deep, distal, proximal, dorsal, ventral, rostral and caudal?
Superficial - towards the surface / shallow
Deep - further away from the surface / more into the body
Distal and proximal tend to be used to describe limbs:
Distal - further away from the centre of the body in the anatomical position
Proximal - towards the centre of the body in the anatomical position
Dorsal - relating to the back of a structure
Ventral - relating to the front of a structure
Rostral - situated towards the oral / nasal region
Caudal - situated towards the hind region
The following set of terms are used to describe movement, typically of the limbs
What is meant by the terms:
Flexion
Extension
Flexion - a movement that results in a reduction in the angle between the two bones (a joint)
Extension - a movement that results in an increase in the angle between the two bones (a joint)

What are the set of terms that are used to describe the movement of the upper limbs only?
Pronation
and Supination
What is meant by the terms:
Pronation
Supination
These two positions are to do with the radius and ulnar bones in the arm
The anatomical position lies in the supinated position, with the palm facing forwards
Supination - palm facing forwards
Pronation is when the radius is rotated around the ulnar so the thumb lies closer to the middle of the body
Pronation - dorsum of the hand facing forwards

These terms are used to describe movement of the limbs
What is meant by the terms:
Medial rotation
Lateral rotation
Medial rotation - also referred to as internal rotation, rotational movement towards the midline e.g. humerus of the arm rotating inwards towards the body
Lateral rotation - also referred to as external rotation, rotational movement away from the midline e.g. humerus of the arm rotating outwards away from the body

What is circumduction?
A combination of movements e.g. abduction and lateral rotation
Which regions of the trunk can have lateral flexion? Describe the movement:
The cervical and lumbar regions
Cervical spine - placing your ear on your shoulder is lateral flexion of the cervical region
Lumbar spine - bending at the waist towards one side is lateral flexion of the lumbar region

Can there be rotation of the spine and how would this be possible?
Rotation of the head on the cervical spine
If the chin is brought as laterally far as possible i.e. chin above the shoulder

What is meant by the terms:
Elevation
Depression
Where are elevation and depression commonly tested clinically?
Elevation - movement in the superior direction
Depression - movement in the inferior direction
The elevation and depression of shoulders

What is meant by the terms:
Protrusion
Retrusion
To which part of the body are these terms generally restricted to?
Protrusion - movement straight ahead / forwards
Retrusion - movement straight behind / backwards
Usually used to describe the movement of the mandible e.g. during chewing

What is meant by the terms:
Protraction
Retraction
To which body part are these movements in relation to?
Protraction - movement of the shoulder (usually) in the anterior direction e.g. reaching forward to grab something
Retraction - shoulder moving posteriorly and medially towards the vertebral column
Scapula around the thorax (scapula = flat triangular shaped bone typically known as the ‘shoulder blade’ found in the upper thoracic region)

What is the palmar surface of the hand?
What is the dorsum / dorsal surface of the hand?
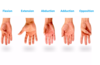
What are the 4 movements of the fingers?
Palmar - palm facing upwards
Dorsum / dorsal - back of the hand facing upwards
Flexion and extension
Abduction and adduction - based around the middle finger, so spreading the fingers is abduction, putting the fingers close together so they touch, is adduction

What are the 5 movements of the thumb and describe them?
Abduction - thumb movement away from the palm at a right angle
Adduction - thumb movement towards the palm at a right angle
Extension - thumb movement away from the palm on the same plane as the hand
Flexion - thumb movement towards the palm on the same plane as the hand
Opposition - thumb and little finger touching at their tips
What is the dorsal surface of the foot?
What is the plantar surface of the foot?
What are the 2 movements around the ankle joint?
What are the 2 movements around the subtalar joint?
Dorsal - top of the foot
Plantar - underneath the foot, the surface you stand on
Ankle joint:
Dorsi flexion - movement of the top of the foot up towards the shin
Plantar flexion - movement of the top of the foot away from the shin
Subtalar joint (found beneath the ankle joint):
Inversion - movements that tilt the sole / plantar surface of the foot towards towards the midline
Eversion - movements that tilt the sole / plantar surface of the foot away from the midline of the body

What are the 3 anatomical planes and describe them?
Axial - also known as horizontal or transverse, at 90 degrees to its long axis of the body, going up and down
Saggital - along the long axis of the body, going from left to right
Coronal - along the long axis of the body, going from front to back



