lab practical 1 Flashcards
fungi reproduce…
asexually
the three shapes of bacterial cell walls
bacillus (rod-shaped), coccus (spherical) and spirillum (spiral)

penicillium
fungi
phylum: ascomycota
multicellular free-living heterotrophic
appearance: clear rings, sort of square
have one flagellum, most primitive protozoans and are parasitic as well as free-living heterotrophs
flaggellates
Ex. trypanosoma (cause african sleeping sickness)

rhizopus
fungi (bread mold)
phylum: zygomycota
multicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
Reproducing: bulbs with stems on two ends mass: fuzzy with dots
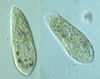
paramecium
protist
phylum: cilophora
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic, protozoan
Swimmy when alive, ovals w/ distinct nucleus looking inside circle
How large is a tryanosome relative to Amoeba?
Much smaller
Archaebacteria that are survivors of ancient lines that have persisted in habitats similar to those present when bacteria first evolved
extremophiles
pigments of cyanobacteria
chlorophyll a, phycocyanin an phyocoerythrin
Free-living in freshwater. One of the most studied and undergoes reproduction through conjugation.
paramecium (ciliate)
segmention of the body for reproduction
transverse fission
derive their energy from photosynthesis or the oxidation of inorganic molecules
autotrophic
The three main domains of organisms
Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya
Eukaryotes
has membrane-bound organelles

saccharomyces
fungi (yeast)
phylum: ascomycota
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
appearance: little purple/pink circles
slime mold that live alongg the damp forest floor in a mass of brightly colored protoplasm
plasmodium
when do fungi reproduce sexually?
When hyphae of two genetically different individuals of the same species encounter one another.

amoeba
protist
phylum: rhizopoda
unicellular, free-living, heterotrophic, protozoan
appearance: spongebob background clouds with center dot
Stains pink
Gram Negative
when fungi’s nuclei fuse
karyogamy
How do daughter colonies exit Volvox?
They are released when the parent cell disintegrates
Prokaryotes
lacks cell membrane bound organelles,
four major phyla of fungi
chytridiomycota, zygomycota, ascomycota and basidiomycota

volvox
protist
phylum: chlorophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
appearance: orbs with little orbs in them
What is the function of the eyespot of Euglena?
It detects light
Domain that includes fungi, plantae and animalia
Domain Eukarya

coprinus
fungi
phylum: basidiomycota
multicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
appearance: thin clear horseshoe crab shape
movable extenison of cytoplasm used for locomation and gathering food
pseudopods

euglena
protist
phylum: euglenophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
appearance: little swimmy guys but algae too

diatom
protist
phylum: chrysophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
appearance: beautiful, distinct shapes
Are the filaments of Spirogyra branched?
Yes
Bacteria reproduce asexually via…
Binary fission

patch of millions of bacterial cells that produce the look of a single cell on agars surface
colony

cladophora
protist
phylum: chlorophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
appearance: branching stems, green

lichen
fungi with a symbiotic relationship with algae
phylum: ascomycota
multicellular, free-living, hetero/autotrophic
appearance: Thick line, w/ 2 sides. One thick and bumpy, the other sort of clear
stains purple
Gram positive
What are the advantages of conjugation in Paramecium?
Exchange of genetic material
Would you expect lichens to grow best in rural or urban environments?
Rural because they are susceptible to air pollution
types of asexual reproduction in fungi
budding and fragmentation
How is the structure of yeast hyphae different from that of molds?
They are round while others form linear structures
“shelled amoebas” marine organisms that are stiff pseudopods with a test made of CaCO3
foraminiferans
when food is engulfed and a food vacuole is formed
phagocytic

geaster
fungi
phylum: basidiomycota
multicellular, free-living, heterotrophic
appearance: mushroom flower
a long appendage that helps for movement in a cork-screw like motion.
flagellum
two types of nuclei in ciliates
micronuclei and macronuclei

plasmodium
protist
phylum: apicomplexa
unicellular, parasitic, heterotrophic, protozoan
Parasites INSIDE blood cells
What is the adaptive significance of spores forming on ends of upright filaments rather than closer to the protective substrate?
It makes it easier for them to spread

spirogyra
protist
phylum: chlorophyta
unicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
Appearance: stick stem segments, green
What are the tiny spheres inside the larger sphere of Volvox?
Daughter colonies
mycelium and hyphae absorb nutrients making fungi..
absorptive heterotrophs
slender filament of cytoplasm and nuclei enclosed by the cell wall.
hypha
derive their energy from organic molecules made by other organisms
heterotrophic
Under what environmental conditions would a zygote not undergo meiosis immediately?
During unfavorable environmental conditions
transformation of atmospheric nitrogen into other nitrogenous compounds that can be used as nutrients by plants.
nitrogen fixation

escherichia coli
Kingdom: eubacteria
mass of hypha make up an individual organism called..
mycelium
when haploid cells from two mating fungi strains fuse their cytoplasms
plasmogamy

fucus
protist
phylum: phaeophyta
multicellular, free-living, autotrophic, algae
Kelp
Some bacteria have genetic recombination via… That all or seom parts of the genetic material is transferred from one bacterium to another bacterium
conjugation

slime mold
protist
phylum: apicomplexa
multicellular, free-living, heterotrophic, protozoan
appearance: blotchy under slide, not under slide I know it

allomyces
fungi
phylum: chytridiomycota
multicellular, parasitic, heterotrophic
appearance: stems with dots on them
How does movement of Paramecium compare with that of Amoeba?
Paramecium uses cilia

trypanosoma
protist
phylum: sarcomastigophora
unicellular, parasitic, heterotrophic, protozoan
parasites among the blood cells


