Lab Practical 1 Flashcards
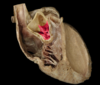
identify the blue structure

Pulmonary trunk
What is this rhythm called?

Long QT syndrome
What is the normal Percentage of normal Lymphocytes?
15-40%
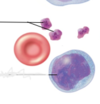
Name the White blood cell

Band neutrophil
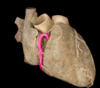
identify the structure in pink

left common carotid artery
Identify the red structure

Right atrium
What is the part of the wave labelled purple

ST segment
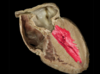
Identify the red structure

Right AV valve (tricuspid)
If a person has blood type A, which antigens and antibodies do they have?
A- Antigens
B- Antibodies
Identify the blue structure

Brachiocephalic vein
If a person has type AB blood. Which antigens and antibodies do they express?
A and B antigens
no antibodies
Identify the pink structure

right common carotid artery
Name the White blood cell

Eosinophil
Identify the red structure

right auricle
What is ventricular fibrillation?
ventricular fibrillation is a dangerous type of arrhythmia or irregular heartbeat. It affects your heart’s ventricles
How full should the capillary tube be?
2/3 full
What is the normal Percentage of Basophils?
0-2%
High band neutrophils suggests
acute bacterial infection
Name the white blood cell

Atypical lymphocyte
When using a hemoglobinometer, does the card insert first or the blood go on the card?
Insert card
Wait for blood drop symbol on the screen
Put sheep blood in the well of the card
Identify the blue structure

subclavian veins
Identify the pink structure

Right subclavian artery
Identify the red structure

Left atrium
Identify the pink structure

superior mesenteric artery