lab exam Flashcards
This lung tissue from a pig is described as multifocal red areas (acute inflammation) what is an MDX, possible agents, and what type of route of entry into this system?

MDX: embolic pneumonia
Agent: bacteria fungal can show sim lesions
Route: hematogenous
This lung tissue is from a pig has a lesion in the caudal-mid lung lobe on the cranial side. Hint looks like Manhemiosis in cattle*** What is the description, EDX, dz name?

Description: fibrinous hemorrhagic necrosis
EDX: Actinobacillous pleural pneumonia
Dz name: Porcine plueral pneumonia
This is the thorax of a rabbit. There is evidence of pulmonary actolectisis whicch compress and decreases the expansion of lungs. What is the MDX, Etiology?

MDX: chronic suppurative pleural pneumonia (pyothorax 2ndary to ruptured abscess)
Etiology: Pasturella “Snuffles”
Lung from a steer lesion is fibrinous pale necorsis and dark which is indicative of hemorrhage in the cranioventral lobes. What is MDX, DiffDX, Dz name, Etiology?

MDX: fibrino necrotizing hemorrhagic pneumonia
DiffDX: emphysema
Dz name: Shipping Fever/ Pneumotic Manheimiosis
Etiology: Manheimia hemolytica
Larynx/trachea from a steer that presented with signs of severe respiratory distress. What is MDX, Etiology, Diff dx?

MDX:necrotizing ulcerative fibrinous laryngitis
Etiology: IBR
Diff DX: Fusobacterium would be more necrotizing cassous more in larynx
Trachea-tongue of foal that presented with severe resp distress after a sx!!!
What happened?

Iatrogenic (vet induced) during tx or diagnostics. Nasogastric tube wrong place aspiration pneumonia
Lung tissue from a horse, that has been traveling to shows during the summer season. distrubution in the right lung indicative of this!!! What is MDX

Cause is shipping with a halter prevents dust from being cleared from the nostril so horses aspirate material into right lung (cranioventral)
MDX: focal pneumonia subacute suppurative
Cricoarytenoid muscle from a horse is atrophied after the horse presents with roaring and collapse. MDX/Dz name?

MDX: unilateral atrophy of the dorsal lateral cricoarytenoid m.
Dz name: laryngeal hemiplasia
Tissue from a young horse! Your MDX is multifocal to coalescing pyogranulomatous pneumonia. What is the Etiology and EDX?

Etiology: Rhodococcus equii
EDX: Rhodococcal pneumonia
Another horse from the same farm as the previous foal with Rhodococcus has died… is it another case or another pathogen?

Same pathogen because its multfocal pyogranulomatous pneumonia from Rhodococcus
Head of a sheep what is the MDX, Agent?

MDX: catarrhal sinositis
Agent: oestrus ovis
What is in the dorsal nasal turbinate of this sheep?

Oestrus ovis
This is the thorax of a young growing pig that was showing signs of panting and respiratory distress then it died in the holding pen in St kitts. There are whitish foci!!! What is going on and why?

interstitial pneumonia
Toxin!!!
This is the serosal surface of the pig that died in St. Kitts what is the MDX?

MDX: severe diffuse interstitial fibrino necrotizing pneumonia
These are HE stains of the lung of the pig who died in St Kitts. What is the predominant inflam cell seen in these cases?

macrophages with zooites

This is another slide of the pig that died in St. Kitts, true or false this is caused by Toxoplasmosis alone.

False
Toxo does not usually cause clin dz in pigs alone. It is usually in conjunction with PCV2
This is the thorax of a dog with metastatic pulmonary carcinoma what is the route of malignancy?

transcolomic
What is the MDX?

Atrophic rhinitis
This pig has……

atrophic rhinitis
This is a femur from a calf is it normal or abnorm?

NORMAL
young are hematopoietically active bone marrow with uniform consistency dark red
This is the abdomen of a dog. It shows signs of icterus/jaundice \ and splenomegaly (esp. in the fat) Looking at the bloodwork there was an increase in bili. What can cause the this increase in bili? What type of jaundice could this suggest? If there is an increase in the amount of macrophages in the spleen is it bloddy or meaty?

increase in serum bili could be a product of hemolytic anemia
This could be pre/post hepatic jaundice
The spleen is a MEATY big spleen
This is a lesion in a puppy, there was evidence of 2ndary bact infections in other areas of the body. What is the agent that caused this? What other body samples could you collect to determine the cause?

Cause: Canine Parvovirus 2
this causes immunesuppression because it depletes the lymphoid of the bone marrow. This causes immunesuppression which accounts for the 2ndary bact infections. You can collect mesenteric LNs, spleen, bone marrow to check for Ag of CPV2
Dog passes away and you find this dark pigmented lesion in the bone? What is a poss diff DX?

Melenoma
This red tumor like growth is found in the bone and associated muscle of a horse. What is a poss diff DX ?

Muscle hemangiosarcoma invading the bone/bone marrow
A llama tests positive for TB and you find this serous atrophy of fat in the long bones. What is the MDX?

MDX: Multifocal granulomatous osteomyelitis
This is one of the most common neoplasms of goats. Describe the lesion and provide a poss dx

Lesion is yellow at the epiphysis and it is displacing the red and white marrow to the medulla.
Lymphoma/lymphosarcoma
This is very indicative of a cow with _____ _______.
Mdx: serous atrophy of fat

chronic emaciation
This dog presents with osteolytic punch out lesions in the spinal processes and in the long bones. The bloodwork shows an increase in Ca, cytopenia, and monoclonal gammaopathy. The urinalysis shows Bence Jones proteinuria. What neoplasm is this?

Multiple Myleoma effects plasma cell
This is a histo taken out of an enlarged spleen. What type of inflamation is this? What cell predominates in this slide? What can that tell you about the dz process?

Lymphadenitis
Neutrophils predominate
This alludes to an acute dz process

What inflam cell predominates during a fibrous chronic dz process
macrophages
A horse presents with bilateral retropharyngeal suppurative inflam. What is the MDX, Etiology, and Dz name?

MDX: acute suppurative lymphadenitis
Etiology: Strep. equi ssp. equi
Dz name: Equine Strangles
This is a characterisitic sheep finding for what etiology? what is the MDX?

Etiology: Corny. pseudotuberculosis
MDX: chronic casseous lymphadenitis
Can you eat a cow when you find this LN with granulomatous lymphadenitis? What Dz is this?

No can’t eat.
M. bovis TB
What is the horseshoe structure in the square if this sample is taken from an ox?

giant cell
This slide should be stained with silver stain to provide an accurate dx. What do you think the cow has?

Mycobacterial infxn
John’s Dz
This white/yellow neoplasm can form anywhere in the body and probably spread through the mediastinal LN’s. It is _______

lymphoma (lymphosarcoma)
This giant jaw mandibular LN abscess on a pig is indicative of ______

Strep. porcinus
This fatty looking infiltrate in the cow spinal cord is extending into the epidural space. Poss diff dx?

lymphoma (lymphosarcoma)
This is a canine popliteal LN aspirate. Name the dz.

Leishmaniasis not histoplasma
This cat has enlarged LNs that is diffuse granulomatous lymphadenitis. What type of organism do you think it could be?

fungal
Cryptococosis (Cryptococcus gattii)
A goat presents with diffuse granulomatous (casseous) lymphadenitis what is the etiology?

Cornybacterium pseudotuberculosis
MDX of this ox lesion

MDX: Fibrino necrotizing lymphandenitis
This dog shows evidence nodular hyperplasia and ___ ____

siderotic plaque
Dog lesion: What is the pigment (brown on HE stain and blue with the Perl’s Prussia blue rxn [+ stain for iron])

Hemosiderin
What are some poss diff dx for this dog spleen?

histiocytic sarcoma, lymphoma, plasma cell tumor, mast cell tumor, splenitis, amyloidosis
Both of these are lesions on the spleen with infarcts (arteries) The top exemplifies a(n) _____ process. The bottom exemplifies a(n) _____ process. The pale growth on the bottom spleen is an example of _____ and is an incidental finding.

acute
chronic
lymphoid hyperplasia
You find a dead pig in Africa and think WTF ill take a look at the spleen. Describe what you see and what Dz do you think it could be?

Diffuse severe splenic congestion
African Swine Fever
You determine that these 2 lesions in a dog are of the same dz origin which alludes to a metastatic form of _______

hemangiosarcoma
This chicken is suffering from multiple yellow lesions. You ask to see samples of the eye and sciatic nerve and find that they are normal. Why would you want the other samples, what do you suspect? Finding them normal what is your definitive dz?

You want to look at the eye to rule out Mereks dz. the eyes would be affected and the sciatic nerve roots would be thickened. Knowing these are normal you suspect lymphoma
This cat has a Thymus covered with yellowish lesions, what do you suspect?
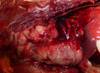
thymic lymphoma
Describe the lesions in this cow thymus?

Multifocal petechial to echymotic hemorrhage in the thymus
This cat liver is pale enlarged rounded edges and floats in solution. The cat has a history of brief anorexia. What is your dx?

diffuse hepatic lipidosis
A young pig presents yellow after scalding at slaughter. the young pig carcass was condemned. What does this pigment suggest?

jaundice icterus
The condemned pig has a change in color it is enlarged dark with some fibrin on the serousal surface indicating an acute process. What are some poss MDX’s of this liver? What is the Dz process? What other samples would you look for to confirm your suspecisions?

MDX: massive hepatic necrosis
MDX: panlobular hepatic necrosis
Vit E/Se deficiency
Look for skeletal m. necrosis and heart lesions
A dog presents with this liver. It has a history of primidone (anticonvulsant) therapy. The hyperplasia is nodular and the liver is diffusely pale with evidence of fatty change. What are 2 poss MDX’s?

MDX: hepatic chirrosis (end stage liver failure)
MDX: chronic hepatitis with post necrotic scarring and nodular regeneration
This cow liver has dark discoloration on the surface. Black is indicative of hemorrhage, necrosis, or melanin. You find that the pigemnt is + for iron/porphyron. What is your dx?

Fluke pigment
Fasciloides magna in parenchyma
What is the MDX and EDX of these cystic lesions that are fibrous and have evidence of eosinophillic granulomatous inflamation.

MDX: chronic necrotizing hepatitis
EDX: Parasitic hepatitis
Fas. hepatica attacks what part of the body?
bile ducts
cholangitis
These adult liver flukes causing Platysomiosis effect what part of the body (in St Kitts)

gall bladder and bile ducts
These thickened cat bile ducts can occur when a cat eats ____ and transmits Platysnosomum fastosum

LIZARDS
The metacercaria of P. fastosum obliterate the bile ducts causing hyperplasia. The eosinophilica inflamation infiltrate and cause _____
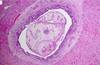
cholecystitis, cholangitis, pericholangitis
This dog came in after being HBC. After humane euthanasia you found a hemoabdomen and the liver looked like so. What caused the bleed into the abdomen?

Liver fractures
What dz process can predispose an animal to liver fractures other than trauma?
Primary liver amyloidosis
This is a very common passive sequel to right sided congestive heart failure. The liver is large, bloody, nodular, and has fibrosis which is evidence of a chronic process.

Nutmeg liver
cardiac chirrosis
What is the MDX of this rabbit liver?

chronic proliferative cholangitis hepatitis
The rabbit’s histo was evident of chronic proliferative cholangitis hepatitis. What is a poss EDX? Etiology?

EDX: coccidial hepatitis
Etiology: Eimeria stieda
This is a dog stomach. The dog presented with dark feces (melena), vomiting, hemorrhage. What is the MDX, poss causes for a dog

MDX: ulcerative necrotizing gastritis
Case: NSAIDs/steroids, mast cell tumor(histamine release), stress, Helicobacter
If a horse presents with ulcerative necrotizing gastritis what is a possible cause and where else might you see lesions?
NSAIDs can cause this damage. You may also see damage in the right dorsal colon, kidney papillary crest necrosis
What is the pathogenisis of ulcerative necrotizing gastritis?
There is an interference of bloodflow from a decrease in prostoglandins –> vasoconstrxn –> ischemic necrosis
If a pig presents with ulcerative necrotizing gastritis what is a probable cause?
Finely ground food, increased PUFA in food
This dog has a brown gut (jejunum) which is discolored by ceroid indicative of intestinal lipofusion. What are some poss causes for this? What is the name of the syndrome?

Vit E/Se def, PUFA ingestion, associated with exocrine pancreatic dz, chronic enteric dz
Brown Bowl Syndrome
This is a dog not a puppy what is going on with the teeth?

Dental calculi (plaque)
This horse has some flies around its face and these bean things in its stomach what is the MDX, what is this thing?

MDX: Ulcerative gastritis
agent: Gastrophilus parasite
This equine jejunum is hyperplastic and the histo has lots of macrophages… What type of inflamation does this indicate? Could it be lymphoma?

chronic granulomatous enteritis
probably not lymphoma is usually ulcerative
This is a wildly abnormal cat esophogus ? Just kill it!!!

JK JK
this is a normal aboral close to the stomach part of the esophagus. classic herringbone pattern
You can tell this is a horse stomach because of the glandular and nonglandular stomach. There are probably not many clinical signs from this even though there is gastric hyperplasia. What is the EDX?

Trichostrongylus multifical ulceration
The horse duodenum is infiltrated with neutrophils and some macrophages. There is also a hemorrhagic necrotic ring around the lesion what is the MDX, etiology?

MDX: intestinal purforation
Peritonitis rupture
This horse has parasitic enteritis. Where will you find larval stage? MDX? Agent? Poss sequel?

Larval stage in lungs
MDX: catarrhal enteritis
Agent: Ascarids parascara sarcorum
Obstruction poss with Tx
Horse has lesion in the nonglandular stomach what is the MDX/ what is a poss cause?

MDX: ulcerative gastritis
Squamous cell carcinoma
This is a crazy ass alpaca stomach right?

nahhh its normal 3 compartment stomach
Look at this funky dog intestine….. MDX/Name???

MDX: necrotizing segmental enteritis
Name: canine parvoviral enteritis
Cow has ulcerative necrotizing glossitis and esophagitis what is the Etiology?

BVD
The reticulum of this cow looks like it has a yellow white growth… what is this and why might it have grown?

lymphoma from BLV
Adult cat necropsy. Can see fibrin with this lesion sometimes. What is the etiology? MDX?
What could it be if this was a young kitten…..

Etiology: FIP coronavirus
MDX: multifocal granulotamous vasculitis/peritonitis
If young could be coccidia or panlukemia
This dog is suffering from either proliferative inflam or neoplasia. It seems to be malignant what are some diff dx?

Oral melenoma
squamous cell carcinoma
fibrosarcoma
This pigs ileum and spiral colon are seen. The pig had watery diarrhea that is fibrinonecrotizing. What is the name of the dz and the agent?

Swine dysentary
Brachyspira hyodisenteriae
This lamb has hemorrhagic enteritis what is an EDX/Diff dx?

EDX: coccidial enteritis
Diff dx: clostridium, E coli
this dog has ______

intestinal intusseception
What is this?
What is a common complication….

palatoschisis
trauma complication bronchopneumonia aspiration ingesta
This is a characteristic lesion of what dz on the ventral surface of the tongue. It is bilateral and symmetrical glossitis.
Why does the lesion happen?
Where else will you see lesions?

Renal fail because ammonia increases in blood urea nitrogen and the bact in the mouth use this and cause glossitis
other lesions may be in mineralization in the stomach or heart. Also lung pneumocytis is poss
What are some lesions associated with uremia and renal fail are secondary to?

These are made of hair what are they called? If they were made of plants what would they be called?

Trichobezoars (hair)
Phytobezoars (plant)
Is this megaesophagus congential or aquired?

acquired because its the whole esophagus
Is this acquired or congenital

congenital not whole esophagus just the cranial portion
persistent right aortic arch PRAA
This dog is young and has a history of parvo which immunosuppressed him. What is going on?

papillomatosis
Papiloma virus
can spont regress
This6 month old cow still has milk teeth. It has erosive ulcerative virus. Diff dx?

Mucosal dz (BVD), FMD, Malig Catarrhal Fever (MCF)
This puppy is immunsuppresed and has segmental hemorrhagic enteritis. What can cause this?

CPV2
canine parvo enteritis
also may see tongue epithelium inclusion bodies
This dog has an ouchie testicle and jejunum. There is a venous infarction. What is going on?

Jejunal inguinal hernia incarceration
Abdomenal cavity inguinal hernia
What is this nasty horse stomach suffering from?

squamous cell carcinoma
What is the MDXfor this canine ?

catarrhal enteritis
This can be caused by ischemia, sx, etc…..

stenosis, stricture
This pig small intestine causes proliferative illeitis what is the name of the agent?

Lawsonia intracellularis
What causes these punch out lesions, intervertebral disc dz, anchylosis

multiple myeloma
Testicular tumor diff dx?

Sertoli tumor, Leydig (interstitial cell) tumor, Seminoma
Is this cow tissue norm or lesion?

norm Follicle and CL
Is this cow tissue norm or a lesion?

lesion
Follicular cyst
thin walled and estroge prod so it prolongs estrus/anestrus
Is this cow ovary normal or a lesion?

lesion
Follicular cyst
Is this tissue from a cow normal or a lesion?

lesion
Luteal cyst (inside CL)
thick walled progesterone prod
This is tissue from a cow is it norm or a lesion ?

lesion
Granulosa cell tumor
characterisitc hemorrhage
Is this cow tissue normal or a lesion

lesion
teratoma (literally any cell type)
Is this tissue from a cow norm or a lesion

lesion
uterine torsion –> gangrene/dead fetus
predisposed by tein dystocia
Is this ouchie cow a normal ochie or a lesion ouchie

lesion
retained placenta
This is a rare neoplasm of the uterus smooth muscle, but if you didnt know that what are some poss diff dx?

leiloma
diff dx lymphoma, lymphosarcoma, BLV
This is tissue from a dog is it norm or lesion? MDX?

endometrial cysts
MDX: cystic endometrial hyperplasia
What is this LESION in a MONKEY

endometriosis
Is this norm or lesion tissue from a horse?

normal
Endometrial cups
Is this normal or lesion tissue from a cow

normal
amnionic plaques incidental not pathological
Is this normal or lesion tissue from a horse

normal
cervical star (NOT A DYSTOCIA)
Is this normal or a lesion tissue from a cat? Owner says that the cat is not doing well and is distended

lesion
PYOMETRA puss filled uterus
Septicemia : Ecoli, gram (-), endotoxin
This cat has what type of lesion?

Prolapse uterus
This is from a a dog or a cat is it normal or a nasty lesion

zonary placenta
Tissue from a dog that is bleeding what is going on?

placenta subinvolusion
This is tissue from a cow is it normal or a lesion

normal
Adventitia placentation
incidental caruncles and cotyledons
This is tissue from a cow is it normal or a lesion

lesion
retained placenta in the uterus
This is tissue from a ruminant is it normal or a lesion?

normal
caruncle on mom side
cotyledons on fetus side
together they make a placentome
This is tissue from an alien… jk a cow what happened?

mummified fetus (dry/dehydrated)
Macerated fetus has bact

PYOMETRA
This is a purulent lesion in a mare. It causes infertility. What is it? Do you test the mares that have the symptoms? Is it reportable?

CEM
Taylorella equigenitalis
test stallions
reportable
What is this leathery bat cow abortion spawn from?

Fungal infxn
Aspergillus fumigatus
Leptospira borgpetersenii causes late term abortion?
no usually early embryonic death
This liver is from an equine fetus what is the MDX and likely etiology?

MDX: multifocal necrotizing hepatitis
Etiology: Equine herpes virus 1
This is tissue from a cow what is going on?

Amorphous globosus
Mento lesion
What is a freemartin?
twins one male and female
male hormone prod first makes the female sterile
this hyperplastic vulva on a pig happens because of what???

hyperestrogenism from moldy corn can lead to prolapse vagina
See this on a rat think _________

MAMMARY FIRBROADENOMA
is this bull penis normal or lesion?

lesion
MDX: multifocal penis inflam
Bovine Herpesvirus 1
This is a nasty awful deathy cancer on a young cat right????

nope
its Fibroadenomatous hyperplasia
This is just a really healthy ram right?

probs not
dermatitis on scrotum could be from Brucellosis need to rule this out first because zoonotic
Is this a lesion or a normal?

lesion
Cryptorchid
This epididymis gets nasty when a sheep is infected with ______

Brucella ovis
An inflammed epididymis

epididymitis
What are these donut lesions on an ovine fetus from?

campylobacter
This tissue from a sheep is what happens when infected with what zoonotic dz? You would confirm it with PCR or histopath of protozoa

toxoplasma
This brain is from a bovine fetus. what is the lesion and how would a cow get it? if this was a cat how would they get it?

cerebellar hypoplasia
BVD in cow
panlukopenia, feline parvo cat
A neonatal puppy would get this lesion from…….

canine herpes virus
This yellowish tumor prod testosterone what type of tumor is in this testicle of a dog

interstitial cell tumor
This testicle tumor prod estrogen what is it?????

sertoli cell tumor
This tumor is white and fatty lipoma looking in a male dog…..

seminoma
These prostates are huge because of ……

prostatic hyperplasia
This dog is suffering from what type of lesion

hypospadia
Describe this skin lesion from a dog

crust, alopecia, ulceration, hyperpigmentation
What is the MDX?

calcinosis cutis
What endocrine abnormality could cause this?

hyperadrenocorticism
Hyperadrenocorticism can cause skin lesions and lesions in what other tissues?

pyoderma, bilateral symetrical alopecia, potbelly, PU/PD, adrenal hyperplasia, adenoma
What is the MDX for this big adrenal gland?

MDX: adrenal cortical hyperplasia
What is the cause of this lesion if there is increased ACTH corticotrophs in circulation

Pituitary adenoma
What is the dz name for a pituitary adenoma induced hyperadrenocorticism

secondary Cushings
Adult female dog has a history of wt gain eating the same amount of food as in the past and lethargy. It also has a distended abdomen, hyperpigmentation, and alopecia what is the MDX?

MDX: cutaneous myxedema
What is this face an example of ???

tragic face
The eyes of this dog have a mucopurulent exudate conjunctivitis from a secondary bact infection. What anatomical lesion caused this?

inverted eyelids
all the fat around the thyroid leads to what lesion in the thyroid?

thyroid atrophy

This thyroid has a lot of lymphocyte infiltration. There are not many follicles and there is a decrease in the colloid because of the atrophy. What is the status of the thyroid hormone? What is the MDX:

decreased thyroid hormone
MDX: lymphocytic thyroiditis
Slightly raised blood vessels also known as…..

coronary atherosclerosis
Uneven thickening of blood vessel walls on the heart shows evidence of cellular foaming, mineralization…. What does this mean for the levels of cholesterol

hypercholesterolemia
cholesterol deposited in vessel walls damage to vessel walls
14 yr old cat enlarged bilaterally thyroid. it is T4 producing and nodular. What is the MDX?cause?

Nodular bilateral hyperplasia
Adenoma
When T4 is increased it injures the heart causing cardiac biventricualr hypertrophy, decreasing the fxn and thrombi can form. True or false

true
decreased thyroid can cause kidney infarct via thrombi from an overworking failing heart

false
increased T4
PTH gland from an adult cat both proliferating what does this do to Ca in the bone? in the blood? Where else would you see lesions?

Ca in the bone will decrease
Ca in the blood will increase
other lesions in the kidney poss
This tumor can lead to _____ hyperthyroidism. If there wasnt a tumor what three things could you check?

secondary hyperthyroidism
if no tumor check history of diet, renal in a PM or blood for renal involvement
What is the pink pigment?

amyloidosis
This nasty adrenal gland from a horse is probably what type of dz process…..

neoplasm
Pheochromocytoma (red), adrenocortical aenoma, adenocarcinoma (tan)
This ferret liver has what MDX:

insulinocarcinoma or islet cell carcinoma
What does this lesion due to serum glucose levels?

hypoglycemia
This cat came in for a PM what do you think the MDX, EDX if you just have access to this sample?

MDX: multifocal (bilateral) ulcerative necrotizing glossitis
EDX: uremic glossitis
What is the pathogenisis of this uremic glossitis on a Shae Pei and why might this be a difficult lesion to dx?

Pathogenisis: mouth bact use urea (ammonia) to grow and they destroy the oral epithelium esp under the tongue
Difficult to dx because Shar peis have colored tongues
What is the circled area on this tongue histo?

fibrin
which sometimes forms as a sequel of uremic glossitis
This sample is from a dog, it is nodular whitish mineralization. it is a common sequel of what dz in dogs? What is the EDX?

common result of uremia (renal fail)
EDX: uremic endocarditis
What is the specific location for uremic endocarditis from renal fail in dogs?

Left atrium endocardium
What is a possible misdx of uremic endocarditis?
Jet lesions from turbulence due to bad valves
This mineralization of the intercostal muscles, what is the MDX/Etiology?

MDX: multifocal intercostal subpleural mineralization
Etiology: chronic renal fail (uremia)
Would you see this mineralization in the intercostal spaces with hypercalcemia of malignancy?

no not usually seen here so we can rule that dx out
This dog stomach is ouchie… what is the MDX/EDX? What organ will you see this damage in a large animal?

MDX: hemorrhagic ulcerative gastritis
EDX: uremic gastritis
Will see this lesion in the colon not so much in the stomach
This is a up close and personal ______ of the stomach rugae

mineralization
This is a histo of a 2 yr old Shih-Tzu. The blood chem has abnormally high urea and crea what is the probable cause

renal fail
these dogs are prone to this
The histos of the shih-tzu stomach would be easier to interpret as calcification if they used what stain?

von kossa stain
The MDX and the dz name are the same for this dog…..

Fibrous osteodystrophy
The paranasal sinus bones are replaced with soft CT. what is going on????

secondary hyperparathyroidism which can be from a renal or dietary source
This radiograph shows a decrease in the amount of alveolar bone and a decrease in density of the ramus portion of the mandible. (osteopenia) What clin signs might the patient present with?

loose teeth, lost teeth, or teeth that are not properly aligned
What is the common name of this lesion?

rubber jaw
true or false
Animals that die from renal fail usually die from: insufficient kindeys, electrolyte imbalance, metabolic acidosis, cardiotox (increased serum K), and pulm edema
false
not usually from kidney dsyfxn
9 month old female rottwiler pup presents with a week and a half of lethargy, not eating, foul smelling vomit/diarrhea. Over the last couple months present with lethargy, not eating, bloody diarrhea, anemia. Treated for hookworms and with IV fluids but it died. What is this sample illistrating, and what is the pathogenisis of this lesion?

The conjunctva is pale = anemia
Pathogenisis: lack of prod of EPO in the kidney which is needed for the prod of RBC. Another contributing factor is the bloody diarrhea/vomit which contributes to lood loss and anemia
The right kidney of the rottweiler puppy is nodular and thickened over the parenchyma. it is small and firm indicative of a chronic or acute process?

chronic
Kidneys of the rottwiler


The rottweiler lungs look enlarged, have rib impressions, and some signs of edema what is the EDX?

EDX: uremic pneumonitis
These frothy enlarged lungs are classic of what process ____

pulm edema
The stomach of the rottweiler give a description….

areas of hemorrhage, edema
What is the widespread calcification of the kidney called?

nephrocalcinosis
The enlarged/mineralized alveolar septae and evidence of edema is classic of ______. What dz will show a similar lesion in the lungs of dogs?

uremic pneumonopathy
Dogs with cushings (hyperadrenocorticism)
This multiorgan mineralization of the rottweiler helps us determine the three final dx what are they?

1) Juvenile progressive nephropathy
2) Uremic gastritis
3) Uremic pneumonitis (pneumonopathy) with severe pulm edema
Rottweilers are prone to familial renal fail
Tissue collection for histology may be representative or may contain lesions, what percent buffer soln should the sample be placed in right away?
10% neutral buffer formalin
What is the circled area and can it be diagnostic?

no it is autolysis not diagnostic but the right picture is still diagnostic
____ stops autolysis by bact enzyme agents, if not done properly the tissues may not stain well, this changes the refractive index of tissue which allows for contrast, most commonly done with 10% NBF, requires a minimum 10:1 formalin to tissue ratio, and the process happens at a rate of 1 mm/hr
fixation
What is the minimum formalin to tissue ratio for fixation
10:1
what is the rate of fixation?
1 mm/hr
What is the recommended fixation time period? And what can you use to harden autolyzed or nueral tissue?
24 hrs
Bouin’s or Davidson’s
In big organs or samples what should you do to them to increase the surface area and promsote proper fixation?
breadloaf them
or open gut and empty contents
When a pathologist is trimming masses she uses ink?
no only the surgeon uses ink to show sx margin
Ideal thickness of tissue for in cassette
3 mm
In order to facilitate cutting a tissue what should you put the sample on?
ice
DEAR GAWD WILL WE PASS THIS LAB FINAL
HELL YEAH


