Lab Exam 1 pt. 2 Flashcards
(342 cards)
1
Q

A
Coronal suture
2
Q

A
Parietal bone
3
Q

A
Squamous suture
4
Q

A
Lambdoid suture
5
Q

A
Occipital bone
6
Q

A
Temporal bone
7
Q

A
Zygomatic process
8
Q

A
Occipitomastoid suture
9
Q

A
External acoustic meatus
10
Q

A
Mastoid process
11
Q

A
Styloid process
12
Q

A
Condylar process
13
Q

A
Mandibular notch
14
Q

A
Mandible
15
Q

A
Mental foramen
16
Q

A
Alveolar process
17
Q

A
Maxilla
18
Q

A
Zygomatic bone
19
Q

A
Nasal bone
20
Q

A
Lacrimal fossa
21
Q

A
Lacrimal bone
22
Q

A
Ethmoid bone
23
Q

A
Sphenoid bone
24
Q

A
Frontal bone
25

External occipital protuberance
26

Internal acoustic meatus
27

Sella turcica of sphenoid bone
28

Pterygoid process of sphenoid bone
29

Palatine bone
30

Palatine process of maxilla
31

Incisive canal
32

Vomer
33

Crista galli
34

Frontal sinus
35
Where is the abdominal region
The midsection
36
Where is the axillary region
edge of the chest, under the armpit
37
Where is the brachial region
The bicep and tricep area
38
Where is the buccal region
It is your cheek area
39
Where is the calcaneal region?
The heel of the foot
40
Where is the carpal region
The wrist
41
Where is the cephalic?
The head
42
Where is the cervical region?
The throat and back of neck
43
Where is the coxal region?
The hip
44
Where is the digital?
Fingers and toes
45
Where is the frontal region?
The forehead
46
Where is the gluteal region?
The butt cheeks
47
Where is the inguinal region?
The groin
48
Where is the lumbar region?
Lower back
49
Where is the mammary region?
Men and womens nipples
50
Where is the manus region?
The hand
51
where is the mental region?
The chin
52
Where is the nasal region?
The cheekbones, nasal sinuses
53
Where is the occipital region?
Back of the head
54
Where is the oral region?
The mouth
55
Where is the orbital region
The eyes
56
Where is the otic region?
The ears
57
Where is the pelvic region?
Right above the groin area
58
Where is the plantar region?
Bottom of the foot
59
Where is the popliteal region?
Back of the knee
60
Where is the pubic region?
The genitalia
61
Where is the sacral region?
Right above the butt crack
62
Where is the thoracic region?
The chest area
63
Where is the umbilical region?
Belly button area
64
Where is the vertebral region?
Middle of the back
65
What is another name for the frontal plane?
Coronal plane
66
Define the frontal plane
Lies vertically
67
How does the frontal plane divide the the body
Anteriorly and posteriorly
68
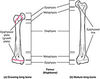
Define the median plane
exactly in the midline
69
How does the medial plane divide the body?
Right and left parts
70
Define sagittal plane
Vertical plane
71
What is another name for a horizontal plane?
Transverse plane
72
Define transverse plane
Runs horizontally from right to left
73
How does the transverse plane divide the body
Superiorly and inferioraly
74
Where is the cranial cavity?
The skull
75
What does the cranial cavity hold?
The brain
76
Where is the thoracic cavity?
The chest
77
What does the thoracic cavity hold?
Heart and lungs
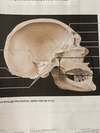
78
What does the abdominal cavity hold?
The digestive system
79
Where is the mediastinum?
Upper chest
80
What does the mediastinum hold?
The heart, and surround the esophagus and trachea
81
What does the pelvic cavity hold?
Urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and the rectum
82
What does the pericardial cavity hold?
The heart
83
What is the peritoneum
The tissue that lines your abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in your abdomen
84
What does the pleural cavity hold?
The lungs
85
What does the vertebral cavity hold?
The spinal cord
86
What is another name for inferior
Caudal
87
What is another way of saying superior?
Cranial
88
Define deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
89
Define distal
Farther from the origin of a body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
90
What is another way of saying posterior?
Dorsal
91
Define inferior
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a stucture or the body; below
92
Define lateral
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of
93
Define medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of
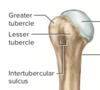
94
Define proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
95
Define superficial
Toward or at the body surface
96
Define superior
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
97
What is another way of saying anterior?
Ventral
98
Define anterior
Toward or athe front of the body; in front of
99
Define abduction
the movement of a limb away from the midline.
100
Define adduction
The movement of a limb toward the body midline
101
Define cicumduction
Moving a limb in a circle
102
Defien depression
Moving an elevated part inferiorly
103
Define dorsiflexion
Lifting the foot so that its superior surface approaches the shin
104
Define Elevation
Lifting a body part superiorly
105
Define eversion
The sole of the foot faces laterally
106
Define extension
Movement along the sagittal plane that increaes the angle between the articulating bones and typically straightens a flexed limb or body part
107
Define flexion
The bending movement of a joint that decreases the angle
108
Define hyperextension
extension of body part beyond the anatomical position
109
Define gliding
When one flat bone surface glides or slips over another
110
Define lateral rotation
Turning of a bone around its own long axis
111
Define opposition
The saddle joint in the hand that allows movement within the thumb
112
Define plantar flexion
Pointing the toes
113
Define pronation
Rotating the forearm medially and the palm faces posteriorly or inferiorly
114
Define supination
When the forearm roates laterally so the palm faces anteriorly or superiorly
115
Define protraction
Jutting out your jaw
116
Define retracting
Pulling your body part back in
Moving your jaw back
117
Where is simple squamous epithelial tissue found?
Kidneys and lungs
Found where filtration or the exchange of substances by rapid diffusion is a priority
118
Where is simple columnar epithelium found?
Lines the digestive tract
119
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium found?
Forms the walls of ducts of glands and kidney tubules
120
Where is psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium found?
Lines the respiratory tract
121
where is stratified squamous epithelium found?
Forms the external suface of the skin and every body opening
122
Where is stratified columnar epithelium found?
Pharynx, mare urethra, and glandular ducts
123
Where is stratified cuboidal epithelium found?
sweat glands and mammary glands
124
Where is transitional epithelium found?
Forms the lining of hollow urinary organs
125
What is the role of endocrine glands?
They produce hormones
126
Where are endocrine glands found?
Digestive tract lining and in the brain
127
What is the role of exocrine glands?
Secrete products onto the skin
128
What are exocrine glands?
The liver, the pancreas, mucous, sweat, oil, and salivary glands
129
Define holocrine glands
accumulate their products within them until they trupture
130
What are holocrine glands?
Sebaceous oil glands
131
Define merocrine glands
Secrete their products by exocytosis as they are porducts
132
What glands are classified as merocrine glands?
The pancreas, sweat glands, and salivary glands
133
Define apocrine glands
The cell pinches off, releasing the secretory granules and a small amount of cytoplasm
134
What is an example of apocrine glands?
The mammary glands
135
Define goblet cells
Individual cells that produce mucus
136
Define cilia
Tiny, hairlike projections of a cell; may move in a wavelike manner to propel substances across the exposed cell surface
137
Define microvilia
Tiny projections on the free surfaces of some peithelial cells; increase surface area for absoprtion
138
What is connective tissue made up of
extracellular matrix
139
Where does connective tissue come from?
The mesenchyme
140
What are the types of loose CT
areolar
adipose
reticular
141
Define areolar connective tissue
Most widely ditributed connective tissue
142
What is the role of the areolar tissue
supporting and bidnging other tissues
holding body fluids
defending against infection
storing nutrients as fat in adipoctyes
143
Define adipose tissue
Made up of fat cells- adipocytes
Areolar connective tissue modified to store fat; a connective tissue consisting chiefly of adipocytes
144
What is the role of adipose tissue?
Shock absorber
insulation
energy storage site
145
Where can you find adipose tissue?
Subcutaneous tissue
146
Define reticular tissue
Connective tissue with a fine network of reticular fibers that form the internal supporting framework of lymphoid organs
147
Where is reticular tissue found?
Lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow
148
Define dense regular connective tissue
It creates flexible structures with great resistance to tension
149
What does dense regular connective tissue make?
Tendons
Aponeuroses
Ligaments
150
Define aponeuroses
Flat, sheetlike tendons taht attach msucles to other muscles or to bones
151
Define dense irregular connective tissue
Collagen fibers are thicker than regular
152
Where is dense irregular connective tissue found?
Skin in the dermis
firbrous joint capsules
fibrous coverings that surround some organs
153
Where is elastic tissue found?
In the walls of large arteries
154
Define erythrocytes
Red blood cells
155
Define neutrophils
Most abundant type of white blood cell
156
Define lymphocyte
Agranular white blood cell that arises from bone marrow and becomes functionally mature in the lymphoid organs of the body
157
Define monocytes
Large single-nucleus white blood cell; agranular leukocyte
158
Define eosinophils
Granular white blood cell whose granules readily take up an acid stain called eosin
159
Define basophils
White blood cell whose granules stain puplish-black with basic dye
160
Define platelets
A cell fragment found in blood; involved in clotting
161
Define lymph
Protein-containing fluid transported by lymphatic vessels
162
Define hyaline cartilage
The most abundant cartilage in the body
163
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
The ends of long bones, absorbs compression at joints
Supports the tip of the nose
Connects the ribs to the sternum
Supports most of the respiratory system
Makes up the embryonic skeleton before the babies bone forms, it is also in the growth plates during childhood
164
Define elastic cartilage
Has more elastic fibers than hyaline cartilage
165
Where is elastic cartilage found?
External ear
epiglottis
166
Define fibrocartilage
Rows of chondrocytes alternate with thick collagen fibers
167
Where is fibrocartilage found?
interverebral discs
spongy cartilages of the knee
168
Where is nervous tissue found?
Brain
spinal cord
nerves
169
Define neurons
highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses
170
What is the role of neurons
Respond to stimuli
Transmit electrical impulses over suvstantail distances
171
Define axon
Neuron process that carries action potentials away from the nerve cell body; effernet process; the conducting portion of a nerve cell
172
Define dendrites
Branching enuron process that serves as a receptive, or input, region; transmits an electrical signal toward the cell body
173
Define synapse
Fucntional junction or point of close contact between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell
174
Define neuromuscular junction
Region where a moton neuron comes into close contact with a skeletal muscle cell
175
Define skeletal muscle
It is voluntary
They have banded or strieted appearance
Packed by connective tissue sheets
176
Define cardiac muscle
Contains intercalated discs
Only found in the heart
177
# Define smooth muscle
No striations
Found in hollow organs
178
What are the layers of the epidermis?
Stratum corneum
Stratum licuidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
179
What are layers of the dermis?
Papillary
Reticular
180
What is the function of the eccrine sweat gland?
Temperature control
antibacterial properties
181
Where are eccrine glands found?
Everywhere
But especially hands and feet
182
What is the function of apocrine sweat glands?
May act as sexual scent gland
183
Where is the apocrine sweat gland found?
Axillary and anogenital regions
184
What is the function of the sebaceous gland?
Lucricate skin and hair
Help prevent water loss
Antibacterial porperties
185
Where is the sebaceous gland found?
Everywhere except palms and soles
186
Define keratinocytes
Deepest part of the pidermis , they form our epidermis
187
What is the role of keratinocytes
Produces keratin, which gives the epidermis its protective properties
188

Cortex
189

Medulla
190

cuticle
191

Hair bulb
192

Root
193

Sheath
194

Arrector pilli muscle
195

Reticular layer
196

Epidermis
197

Papillary layer
198

Dermis
199

Adipose tissue
200

Hair root
201

Sebacous oil gland
202

arrector pilli muscle
203

Eccrine sweat gland
204

Dermal papillae
205

Hypodermis/Subcutaneous tissue
206

Epidermis
207

Dermis
208

Reticular dermis
209

Dermal papillae
210

Appocrine sweat gland
211
Define langerhans cells
They ingest foegin substances and are key activators of our immune system
212
Where do langerhans cells come from
Bone marrow and migrate to the epidermis
213
Define melanocyte
Epithelial cells that synthesize the pigment melanin
214
Define meissner's corpuscles
AKA tactile corpuscles
Small receptors
Found in the dermal papillae
A lot is the nipples, fingertips, soles
They are receptors for discriminative touch
215
Define pacinian corpsucle
AKA lamellar corpuscles
Found in the dermis and suvcutaneous tissue
They respond only when pressure is first applied
Monitor vibration
216
Define merkel cells
AKA tactile epithelial cells
Assocaited with a disclike sensory nerve ending
It is a sensory receptor for touch
217
Define free nerve endings
They are light touch receptors that detect bending of hairs
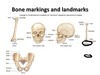
218
Define a process on a bone
Any bony prominence
219
Define tuberosity

Large rounded projection; may be roughened
220
Define tubercle
Small rounded prjection or process
221
Define crest

Narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent
222
Define spine
Sharp, slender, often pointed projection
223
Define ramus
Branch of a nerve, artery, or bone
224
Define a line of bone
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
225
Define trochanter
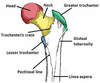
Very large, blunt, irregularly shaped process
226
Define a protuberance
A bony outgrowth or protruding part
227
Define fossa

Shallow, basinlike depression in a bone, often serving as an artivular surface
228
Define fovea

A pit
229
Define groove
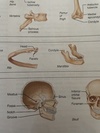
Furrow
230
Define notch

indentation at the edge of a structure
231
Define cavity
A hollow space within a bone
232
Define sulcus
A furrow on the brain, less deep than a fissure
233
Define foramen

Round or oval opening through a bone
234
Define canal

A tubular passage or channel which connects different regions of the body
235
Define sinus
Cavity within a bone, filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
236
Define duct
a bodily tube or vessel especially when carrying the secretion of a gland
237
Define meatus

Canal-like passageway
238
Define Head

Bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
239
Define condyle

Rounded articular projection; often articulates with a corresponding fossa
240
Define trochlea
a structure resembling a pully, groove at the end of the humerus, forming the elbow joint
241
Define facet

Smooth, nearly flat articular surface
242

Inferior turbinate bones
243

Malleus
244
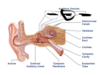
Incus
245

Stapes
246

Perpendicular plate
247
Palatine bone
248

Nasal crest
249

Horizontal plate
250

Lacrimal bone
251

Zygomatic bone
252

Inferior nasal conchae
253

Vomer
254

Hyoid bone
255

Coastal cartilage
256

Xiphoid process
257

Body of the sternum
258

Manubrium
259

Jugular notch
260

Calvicular notch
261

True ribs
262

False ribs
263

Floating ribs
264

Head of the rib
265

Neck of rib
266

Tubercle of rib
267

Angle of rib
268

Axis
269

Atlas
270

Median sacral crest
271

Lumbar vertebra
272

Thoracic vertebra
273

Cervical vertabra
274

Inferior articular process
275

Transverse foramen
276

Superior articlar process
277

Body of the vertebra
278

Coccyx
279

Intervertebral foramen
280

Transverse process
281

Spinous process
282

Coronoid process
283

Head of ulna
284

Ulnar styloid process
285

Radial notch of ulna
286

Trochlear notch
287

Olecranon process
288

Coronoid process
289

Lateral epicondyle
290

Medial epicondyle
291

Olecranon fossa
292

Capitulum
293

Trochlea
294

Lesser tubercle
295

Greater tubercle
296

Head of humerus
297

Infraspinous fossa
298

Supraspinous fossa
299

Spine
300

Coracoid process
301

Acromion
302

Glenoid cavity
303

Scapula
304

Clavicle
305
Number 9

Obturator foramen
306
Number 8

Ischial tuberosity
307
Number 5

Ischial spine
308
Number 16

Superior ramus of pubis
309
Number 19

Inferior ramus of pubis
310
Number 7

Head of the femur
311
Number 8

Neck of the femur
312
Number 1

Greater trochanter
313
Number 9

Lesser trochanter
314
Number 12

Medial condyle
315
Number 5

Lateral condyle
316
Number 11

Medial epicondyle
317
Number 4

Lateral epicondyle
318
Name the bone

Tibia
319
Number 4

Medial condyle
320
Number 1

Lateral condyle
321
Number 2

Tibial tuberosity
322
Number 5

Medial malleolus
323
Name the bone

Fibula
324
Number 1

Head of the fibula
325
Number 3

Lateral malleolus
326
Number 1

Calcaneus
327
Number 2

Cuboid
328
Number 3

Lateral cuneiform
329
Number 4

Metatarsals
330
Number 8

Talus
331
Number 9

Navicular
332
Number 10

Intermediate cuneiform
333
Number 11

Medial cuneiform
334
Number 12

Metatarsal
335
Number 13

Phalange
336
Number 11

Pubic symphysis
337
Number 15

Acetabulum
338
Number 7

Ulnar notch
339
Number 2

Radial tuberosity
340
Number 4

Styloid process
341
Number 1

Head of the radius
342


