Lab Flashcards
(15 cards)

1) Yellow – this is the anterior commissure (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 2)
2) Violet – Suprachiasmatic nucleus (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 15)
3) Pale green – interventricular foramen (of Monroe) also known as the hypothalamic sulcus (Ventricles lecture – slide 17 and 18)
1) I believe it is mammillothalamic tract (Thalamus lecture – slide 26; Hypothalamus lecture – slide 33)


1) Salmon – this is the fornix and it communicates with the mammillary nucleus (connects this with the hippocampus) (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 8)
1) The fornix divides (and hence passes through) the hypothalamus into the medial and lateral regions (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 11)
2) Dark blue – This looks like the mammillary body (inferior) and possibly the thalamus
1) Was not sure what was being asked, but projections of the mammillary body to the thalamus via the mammillothalamic tract for the Papez circuit associated with memory and emotion


Most likely answer: C (lots of references from multiple labs; Coronal Brain Sections was major contributor).
Reasoning: we can first determine the picture is more anterior than posterior due to the shape of the lateral ventricles (head = butterfly, body = hawk). This helps with eliminating A and B as well as E and F. After that, you can look at the temporal lobe to notice that there is a slight bit of a ‘scroll’ like figure which could be the hippocampal complex just caudal to the amygdala. This would help eliminate H. All that is left is C, D, and G. Notice the small rounded bulges just lateral and inferior to the 3rd ventricle. This should be the optic tracts. This would indicate that the slice should be posterior to the optic chiasm. Hence, the only one that now fits is ‘C’.


1) Blue – 3rd ventricle (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 10)
2) Rust – fairly certain it is the optic tract (Reference this website: http://www.neuroanatomy.ca/cross_sections/sections_coronal.html)
Algae – this space will eventually be occupied by the pons (Reference this website: http://www.neuroanatomy.ca/cross_sections/sections_coronal.html


1) Stimulation of fuchsia would increase desire to eat; this is the lateral hypothalamus which is involved in appetite control (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 27).
2) Algae – This is the pituitary gland (specifically it should be the posterior pituitary); axons in this structure are derived from supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 39-41)
1) Axons transport: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 41 and 42)
2) Veins here carry hormones to the neurohypophysis (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 41)


1) Pale green – Anterior commissure (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 2)
2) Red brown – Supraoptic recess (Reference: http://radiopaedia.org/articles/supraoptic-recess-2)
3) Yellow – Massa intermedia (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 2)
4) Blue – Optic chiasm (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 2)


1) Yellow – This area is the hypothalamus (yeah, I know) and the fiber bundle dividing this region mediolaterally is the fornix.
2) Violet is pointing to the mammillary body whereas the green is pointing to the thalamus. The mammillothalamic tract ascends into and through the thalamus to reach the anterior thalamic nucleus which is involved in the limbic system (emotion and memory (Papez circuit)) (Thalamus lecture – slide 26)
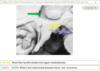

1) Icy blue – area involved in response to heat (regulates mechanisms of heat dissipation; Hypothalamus lecture – slide 30)
2) Flame orange – area involved in response to cold (heat production via vasoconstriction and shivering; Hypothalamus lecture – slide 31)


1) Violet – Optic nerve (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 4)
2) Green – Optic tract (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 4; if only they were this easy on the exam)
3) Orange – Crus cerebri (Netters p. 107)
4) Blue – posterior perforated substance (Netters p. 107 and Hypothalamus lecture – slide 4 and 50)


1) Yellow – nerve tract found here is the supraopticohypophyseal tract that runs in the infundibulum (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 41)
2) Green – median eminence (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 4)
3) Blue – limbic system (Hypothalamus lecture – slide 8)
1) Main input comes from – hippocampus
2) Structure that brings it’s input – fornix (large, myelinated limbic fiber bundle that connects hippocampus to the mammillary nucleus)


1) Orange – sphenoid bone (Wikipedia, sorry)
1) Fossa Latin name – Sella Turcica
2) Blue – sphenoid sinus
3) Red – Internal carotid
1) 2 brs. – the superior and inferior hypophyseal brs.


1) Violet – olfactory tract (Neuroanatomy book – p. 22)
2) Green – optic chiasm (Neuroanatomy book – p. 22)
3) Orange – uncus (Neuroanatomy book – p. 22)
4) Blue – pyramid (Neuroanatomy book – p. 22)


1) Blue – anterior pituitary, adenohypothalamus, pars distalis
1) Arterial branch – superior hypophyseal a. (br. of Internal carotid)
2) 2 principle hypothalamic nuclei – preoptic and arcuate nuclei
3) Veins: hypothalamohypophyseal portal vv.
●


1) Green – posterior pituitary, neurohypothalamus, pars nervosa
1) 2 hormones: oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
2) Hypothalamic nuclei: Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
3) Along what tract: supraopticohypophyseal tract
4) What artery: inferior hypophyseal a. (br. of internal carotid)


1) Violet – 3rd ventricle
2) Red – pituitary stalk
3) Orange – internal carotid a.
4) Green – pituitary
1) 2 vessels supply green: inferior and superior hypopheal a.
2) Origin of these 2 vessels is the internal carotid a.
3) Secretion effects what physio. functions: regulation of other glands; pituitary is ‘master gland’



