anatomy Flashcards
What are the landmarks that surround the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamic sulcus
anterior sulcus
lamina terminalis
chismatic cistern
optic chiasm
interpeduncular cistern
mammillary body
midbrain mass intermedia

What does the 3rd ventricle seperate?
what is the floor of the hypothalmus?
walls of the hypothalmus

The floor of the hypothalamus includes the tuber cinereum and median eminence
What are the medial/lateral amd anterior/posterior of the hypothalmus?
medial/lateral- optic tracts
anterior-optic chiasm
posterior- posterior perforated substance

hypothalmus with nuclei and tracts?

What descends the hypothalmic grey?
the fornix (circled in green)

What doe sthe fornix connect?
a large, myelinated limbic fiber bundle that connects hippocampus to mammillary nucleus

optic tracts

What is a major landmark of the hypothalamus?
Optic Chiasm
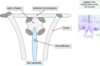
What does the fornix divide the hypothalamus into?
medial zone
lateral zone
periventricular zone is adjacent to the 3rd ventricle

What is lateral to the lateral hypothalamus?
What does it include?
Lateral to lateral hypothalamus is the substantia innominata (part of the general area called the basal forebrain)
Area includes nucleus basalis of Meynert, a major player in cortical function

What passes rostrocaudally through the lateral hypothalamic zone?
Medial forebrain bundle

What is the hypothalamic nuclei subdivided into?
What lies between the 3rd ventricle and the fornix in the medial hypothalamic zone?
anterior (preoptic)
middle(tuberal)
posterior (mammillary)
Between 3rd ventricle & fornix column are 10 nuclei named for position or shape

What nuclei lie in the anterior zone?
5 nuclei: 3 anteriormost named in relation to the optic system
Preoptic nucleus
suprachiasmatic nucleus
supraoptic nucleus
anterior nucleus
paraventricular nucleus

What nuclei lie in the middle zone?
3 nuclei
Ventromedial
dorsomedial
arcuate

Which nuclei lie in the posterior zone?
2 nuclei
posterior
mammillary

Which tract ascends out of the mammillary nucleus?
mammillothalmic tract

How does the lateral hypothalmus send and receive fibers?
What is the cousre of the medial forebrain?
Lateral hypothalamus sends and receives fibers via medial forebrain bundle (MFB) as do other parts of the hypothalamus.
MFB courses from forebrain rostrally through brainstem caudally.

What is the tubermammillary nucleus of the LHA function for the brain?
part of the brain’s sleep-wake circuitry and is involved in wakefullness (cortical arousal).

Where is the only source of orexineergic nuerons in the CNS?
what is the role of orexin?
where does orexin neurons output to?
Lateral hypothalamus is the only source of orexinergic neurons in the CNS.
Neurotransmitter orexin plays a primary role in wakefullness.
Orexin neurons output to other neurotransmitter systems involved in arousal.

What is the affect of dysregulatin orexin?
Dysregulation or degeneration of LHA orexin neuron circuits is implicated in excssive sleepiness (hypersomnolence), cataplexy (loss of muscle tone), and narcolepsy (sudden wake to REM sleep-like state).
What type of regulation is the lateral hypothalmus involved in?
What is the affect of stimulating the lateral hypothalmus?
What do lesions in the lateral hypothalmus produce?
Lateral hypothalamus is involved in appetite control (regulation of food intake)
stimulation causes hyperphagia
lesion produces anorexia

What is the function of the Ventromedial hypothalmus?
What does stimulation of the ventromedial cause?
What does lesions of the ventromedial hypothalmus cause?
LHA in regulation of food intake
Considered a satiety center (deciding when to stop eating)
stimulation inhibits eating (anorexia)
lesion causes overeating (hyperphagia)

How does leptin(anorexigenic) and ghrelin (orexigenic) molecules gain acces to the hypothalamic feeding regulation nueral network?
qprobably through the median eminence, one of the leaky-capillaried circumventricular organs (CVO)

What is the anterior hypothalamic nucleus regulate?
What does the anterior (preoptic) area have for this regulation?
Anterior hypothalamic nuc. is involved in temperature regulation
anterior (preoptic) area has both cold and heat sensitive neurons (thermostat)
at high blood temperature, regulates mechanisms of heat dissipation


















