Lab 4 Visual pathway and vestibular system overview Flashcards
(22 cards)
What do sensory receptors do and how does this occur?
Convert a sensory stimulus into neurobiological activity. (transduction). A stimulus causes a change in membrane permeability Which leads to a receptor potential. This causes an action potential in a neuron which is carried to the CNS.
What is the retina?
A sheet of nerve and glial cells that lines the posterior globe .
Where does the retina terminate?
It terminates anteriorly at the ora Serrata.
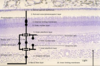
Label these parts of the retina.

What are the two types of photoreceptors and what vision are they involved in?
Rods = Scotopic; low light level high sensitivity
Cones =Photopic; high acuity but low sensitivity
Where are visual pigments found in photoreceptors?
The outer segment of photoreceptors contain a disc in which the membranes contain visual pigments.
What are visual pigments made from?
Chromoproteins. - these comprise of chromophore and proetin.
The 4 visual pigments have retinal as their chromophore and opsin as their protein.
What determines the spectral nature of each visual pigment?
The protein determines the spectral nature of each visual pigment.
When adapted to the dark what happens to the photopigment?
The retinal is bent 11-cis configuration and is bound to the opsin within a ‘binding pocket’ formed by the opsin helices.
What is photoisomerisation?
The visual pigment chromophore can exist in a number of different isomeric forms.
When in dark-adapted form what happens when a visual pigment encounters a photon?
The absorption of a photon isomerises the chromophore to the ‘straight’ all trans form.
The all-trans isomer no longer fits into the opsin binding pocket and the opsin and retinal separate
The visual pigment bleaches.
Label this diagram


Via what, does the visual system reach the CNS?
Via the second cranial nerve which passes from the retina to the brain by the optic canal.
What is the vestibular system involved in?
balance and acceleration
Via what, does the V111 th nerve pass from the ear to the brain?
By the internal auditory meatus

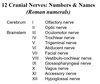
label the cranial sections.

What are the 12 cranial nerves and their respective number?

What does damage to the II optic nerve cause?
Specific visual field loss (anopia)
Where does the II optic nerve of each eye cross over?
The optic chiasm

How can a tumour of the pituitary affect vision?
Pituitary Gland sits directly below the optic chiasm
Tumours in the gland (adenomas) tend to grow upwards
Cutting the Nasal axons from both eyes as they cross in the chiasm.
Leading to bi-lateral loss of the temporal half-fields
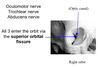
Where does the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve and abducens nerve enter the orbit from?
The superior orbital fissure.