Lab 4 Flashcards
(91 cards)
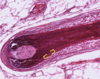
Skin layers - epidermis, dermis (Papillary Layer: Loose CT, Reticular Layer: Dense irregular CT), hypodermis

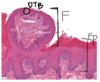
Epidermis (E). Papillary layer of dermis (P), reticular layer of dermis (R). Hypodermis (H)

Dermal papillae, epidermal ridge or interpapillary peg

Eccrine sweat glands in reticular layer of dermis
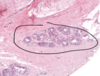
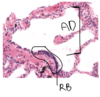
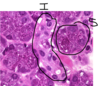
Pacinian corpuscle at border between hypodermis and dermis – detects vibration and pressure lower down in the skin. There are layers of Schwann cells with fluid filled spaces in between, and centre has an axon

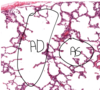
Meissner’s corpuscle in papillary layer of dermis - have barrel shape that have unmyelinated axon and groups of schwann cells that form layers. The nuclei on the outer edge of meissner is schwann cell nuclei, there are some fibroblasts too.
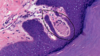
Basement membrane under epidermis (wrong), points to granulosum layer

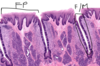
Layers of epidermis
Stratum corneum has keratin (no nuclei, has some holes). Stratum basale (forms stem cells that divide, mitosis occurs here, has merkel cells). Stratum spinosum (cells with nice nucleolus and lots of euchromatin, prickle areas between adjacent cells where desmosomes bind the intermediate filaments from one cell to the next cell). Stratum granulosum (keratohyalin granules, 2-3 cell layers thick, cells make proteins that cross link the keratin). Stratum lucidum (cells from stratum granulosum that died, has keratin flakes).

Thin skin characteristics
Epidermis with thin keratin layer (stratified squamous keratinized epithelium), papillary layer of dermis, reticular layer of dermis. Sweat glands, hair, sebaceous glands. Arrector pili muscle (smooth muscle that attaches to hair follicle, causes goose bumps, if the muscle contracts then it squishes the sebaceous gland to release sebum for hair lubrication)

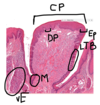
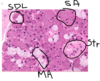
Thin skin - thin epidermis (due to thin stratum corneum and thin stratum spinosum), adipose tissue at hypodermis. Reticular layer of dermis. Papillary layer of dermis (Lighter collagenous layer). Eccrine sweat glands. Hair follicle.
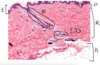
Thin skin – thin stratum corneum, stratum basale (cells with brown pigments, melanocytes with white halo due to golgi apparatus making melanosomes)

Thin skin – bundles of elastin within reticular layer of dermis (elastin changes with age, decreases with age)

Scalp is thin skin – lots of hair follicles in cross section. Sebaceous glands, sweat glands.

Hair follicle – hair bulb, dermal papilla. Hair matrix cells. Hair shaft (inside to out: medulla, cortex, hair cuticle), internal root sheath (inside to out: internal root sheath cuticle, Huxley layer, Henle layer), external root sheath (continuous with epithelium)

Hair follicle cross section

Scalp – hair follicles in hypodermis; hair shaft, internal root sheath, external root sheath (multicellular layer), glassy membrane (is basement membrane continuous with epidermis). Arrector pili muscle

Hair shaft longitudinal – hair bulb, dermal papillae, matrix cells, hair shaft, cuticle, internal root sheath, external root sheath, glassy membrane
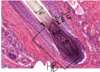
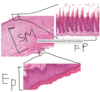
Sebaceous gland
big grouping is one sebaceous gland
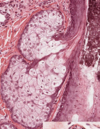
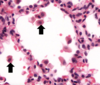
Sweat gland, Simple tubular eccrine sweat gland
Sweat glands in clumps, Simple tubular eccrine sweat gland is lighter colored and encircled with black outline

Eccrine sweat gland of Thick skin with resorptive duct and secretory coil – 2 profiles: darker stained is duct portion (modifies secretions), lighter stained is secretory portion (secretes components of sweat: proteins, electrolytes, ammonia, urea). Darker stained duct portion has STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL epithelium with lumen (2 layers of cells). Lighter stained secretory portion has PSEUDOSTRATIFIED EPITHELIUM around the gland and also a ring of darker eosinophilic cells called MYOEPITHELIAL cells on the outside.

Scalp – sebaceous gland (branched acini) around hair follicle.
Holocrine secretion occurs in sebaceous gland: cells at basal part are on basement membrane and are a bit basophilic due to protein and lipid production. Basal part cells divide and daughter cells are pushed to centre of sebaceous gland, filling with lipid droplets. After cells are filled up, apoptosis occurs, releasing oil to hair follicle.
Merocrine secretion is exocytosis of secretory vesicles in eccrine sweat glands and apocrine sweat glands. Apocrine secretion is in mammary glands and some male reproductive glands.

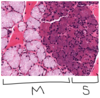
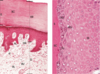
Left: Human thick skin, x132. Right: Monkey thick skin, x540.
Abbreviations: BV: Blood vessels; D: dermis; DR: dermal ridges; E: epidermis;
ER: epidermal ridges; KG: Keratohyalin granules; PL: papillary layer; RL: reticulum layer; S:squames; SC: stratum corneum; SG: stratum granulosum; SS: stratum spinosum; Tc: transitional cells; d: duct of sweat gland.
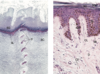
Human thick (left, x132) and thin (right, x270) skin sections. Abbreviations: CF: collagen fibre; CL: capillary loops; D: dermis; SB: stratum basale; SC: stratum corneum; SG: stratum granulosum; SL: stratum lucidum; SS: stratum spinosum; sDR: secondary dermal ridges; d:duct of a sweat gland.
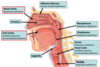
Epithelium of Nasal Cavity, conchae, Oral Cavity, epiglottis, Olfactory Mucosa, Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Larynx, Vocal Cords, Trachea
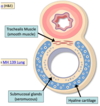
Respiratory epithelium is pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells