L8 - K Okkenhaug - T cells Flashcards
(68 cards)
what does the T cell receptor bind / response to?
fragmented antigenic peptides bound to MHC molecules.
describe a class 1 CD8 cytotoxic T cell
CD8 cytotoxic

describe a class 2 helper T cell

how are TCRs and antibodys closely related?
what structure do they share in commen?
The TCR is closely related to a single antibody Fab fragment

how is TCR variability generated?
VDJ recombination - much like antibodies
describe TCRs peptide structure?
two polypeptide chains each containing a constant and a variable region.
4 differences between TCR and antibodies
TCR is:
- monovalent
- membrane bound - no secreted counterpart
- no somatic hypermutation
- solely used for antigen recognition
- not linked to effector function
where do T cells mature
thymus
do you understand how VDJ recombination works?

____ is the most variable region in TCR and is focused on the VDJ junctions.
CDR3 is the most variable region in TCR and is focused on the VDJ junctions.
CDR3s role in the TCR is
CDR3 makes the major contact with peptide present in the MHC groove.
Only abou X% of
double-positive (CD4+ /CD8+) thymocytes survive selection.
Only about 1-2% of
double-positive (CD4+ /CD8+) thymocytes survive selection.
in T cell selection, whats the purpose of negative selection?
Negative selection helps prevent autoimmunity by deleting autoreactive cells.
in T cell selection, whats the purpose of Positive selection?
Positive selection ensures that peripheral T cells will be useful since cells that cannot recognise self MHC cannot become activated.
CD8+ T cells are selected for by MHC X molecules. CD4+ T cells are selected for by MHC X molecules
CD8+ T cells are selected for by MHC I molecules. CD4+ T cells are selected for by MHC II molecules
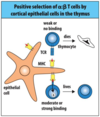
Pictuer to help understanding of T cell selection

is positive selection unique to T cells
yes
T cell undergo positive and negative selection in the ____
T cell undergo positive and negative selection in the thymus
where does positive selection take place?
cortical epithelium in thymus
explain positive selection in the cortical epithelium in the thymus for t cells
Newly rearranged T-cell receptors are tested against self peptide/MHC complexes expressed on cortical epithelial cells.
TCRs with a “moderate affinity” for self MHC/peptide receive a positive signal to continue maturation.
Lack of interaction results in death by neglect.
Expression of CD4 and CD8 co-receptors is altered to match MHC restriction.
Cells that survive will be CD4+ single positive if selected against MHC class II/peptide or CD8+ single positive if selected against MHC class I/peptide.
thymus organisation picture
where does negative selection occur
thymus medulla
where do mature t cells travel to after the thymus
secondary lymph tissue
describe negative selection
- potentially autoreactive thymocytes expressive TCRs with high affinity for MHC/self peptides
are eliminated from the repertoire by programmed cell death (apoptosis).
- Negative selection can not eliminate T cells with receptors recognising MHC/peptide combinations that are not expressed in the thymus. These are dealt with by mechanisms that operate in the periphery.
why are macrophages important in the thymus
Macrophages are important for removing thymocytes that fail to mature.










