L5 - Synapses and Neural Integration Flashcards
1
Q
Neuron Signals:
A
-
Electrical Signals
- Within-neuron: Action Potential, electrical signal from axon hillock, along axon, to pre-synaptic axon terminal
-
Chemical Signals
- Between-neurons: Neurotransmitter signal across synapse

2
Q
The Synapse:
A
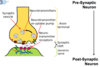
3
Q
Neurotransmitters:
A
Amino Acids
- Glutamate: Excitatory – used in 90% of synaptic transmissions
- Gamma-aminobultyricacid: Inhibitory – used in 9% of synaptic transmissions
Monomines and Acetylcholine (the other 1%)
-
Cholinergic System
- Uses Acetylcholine (Striatum)
- Important for arousal, vigilance and memory
- Reduced activity implicated in Alzheimer’s
-
Dopaminergic System
- Uses Dopamine (Substantia Nigra)
- Important for motor control
- Reduced activity linked to Parkinson’s
-
Noradrenergic System
- Uses Norephinephrine (Locus cerelus of the brainstem)
- Important for attention and executive control
- Reduced activity implicated in ADHD
-
Serotonergic System
- Uses Serotonin (Raphe Nuclei of the brainstem)
- Important for sleep, aggression and memory
- Reduced Activity implicated in depression
4
Q
“Lock and key” - neurotransmitter receptors:
A
- Each receptor only binds to a specific type of neurotransmitter
- Neurotransmitters only “activate” their specific type of receptor
- Important for drug effects
- Drugs can act on specific receptors to cause specific effects (eg. L-DOPA for Parkinson’s disease replaces dopamine in the brain)

5
Q
Anti-Depressant Drugs - Serotonin
A

6
Q
Ligand-Gated ion channels:
A
- Neurotransmitter receptors open ion channels when neurotransmitter binds
- Different neurotransmitters bind to and open different ion channels (Na+, K+,Cl-) to change membrane potential in different ways
-
Receptor binding:
- Can cause depolarisation (less negative) e.g. Na+ flows in
- Can cause hyperpolarisation (more negative) e.g. K+ flows out or Cl- flows in

7
Q
Excitatory and Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potentials:
A
- Excitatory (EPSP) and inhibitory (IPSP) post synaptic potentials feed into the dendrites of a neuron
- The influence of EPSP and ISPS vary depending on the strength of the synaptic connection between the neurons
-
Graded potential: The resulting potential at the axon hillock determined on the sum and timing of inputs (EPSPs and IPSPs).
- Depolarisation: Less negative and closer to 0 (and the AP threshold) - Excitatory
- Hyperpolarisation: More negative and further from 0 - Inhibitory
- If enough excitatory inputs occur together close enough in time, membrane potential will exceed AP threshold level and the neuron will fire an AP
- Neural integration: The summation of all sensory or higher inputs to determine motor output



