L5 - Etiology Flashcards
Etiology refers to: A. Cause of a disease B. Disease C. Gross appearance or lesion
A. Cause of a disease
Who was the “1st to give documented definitions for etiology” ? A. Robert Koch B. Edward Jenner C. Marcus Terentius Varro D. Louis Pasteur
C. Marcus Terentius Varro
Who “gave experimental support for the concept of infectious disease” ? A. Robert Koch B. Edward Jenner C. Marcus Terentius Varro D. Louis Pasteur
A. Robert Koch
Etiology can be split into 2 major classes of factors causing disease, what are they ?
- genetic 2. acquired
Can you think of an etiology for this lesion from a horse?

Etiology here would be trauma
Note: Etiological Dx: Traumatic fracture, scapula
Can you think of an etiology for this lesion from a horse?

Cause: Trauma to the back of the skull as from a backward fall onto the occiput (the back of the head or skull)
Note: Morphological Dx: Ventral fractures of the skull
Cryptococcosis, thalamus, cerebellum, and mesencephalon, transverse sections, cat. What is the etiology here ?
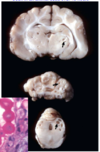
Etiology: Cryptococcus neoformans
What is the name of this single gene disorder disease ?

Spider lamb chondrodysplasia (spine) Note: Single base change in the tyrosine kinase II domain of FGFR3
Which of the following is NOT a syndrome associated with vitamin E deficiency and excess intakes of polyunsaturated fatty acids.
A. Encephalomalacia
B. Pancreatic fibrosis
C. Muscular degeneration
D. Dermatitis
D. Dermatitis
What is this image an example of ?

Hepatosis dietetica (nutritional hepatic necrosis) Deficiency of Vitamin E and/or Selenium
Gastric ulcer (pars esophagea) in the stomach of this pig is caused by:
A. Ingestion of finely ground grain or pelleted feed
B. Possible vitamin E deficientcy
C. Fermentation of sugars in the feed
D. Stress of confinement rearing
E. All of the above

E. All of the above
Animals dying of sepsis, toxemia, aspiration of gastric contents, and pancreatitis lead to which condition ?
A. Pulmonary edema
B. Hepatic necrosis
C. CNS disorders
D. Anemia
A. Pulmonary edema
Squamous metaplasia, esophagus, parrot
Name the etiology

Cause: Avitaminosis A
Nutritional
When birds don’t get enough vitamin A
Embolic nephritis, kidney, horse
Name the etiology

Cause: Actinobacillus equuli
Microbial
Localized bacteria in the glomeruli; known to have a descending infection
Bones, Cows, cut surfaces
Morphologic DX: Congenital porphyria
Name the etiology

Cause: Defect in heme synthesis caused by a deficiency in uroporphyrinogen III cosynthetase
Genetic
Chronic passive congestion (nutmeg liver), liver, cow
Name the etiology

Cause: Ingestion of hepatotoxin (i.e. Wedelia glauca etc) or right sided heart failure
Toxins
Mainly due to heart failure or ingestion of toxins
Globoid cell leukodystrophy, dog (a type of Lysosomal storage disease)
Name the etiology
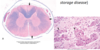
Cause: Defect in an enzyme (galactosylceraminidase)
Genetic
Bovine, Nasal epithelium
MDx: Acute allergic rhinitis with secondary plant foreign body
Name the etiology

Cause: Type I hypersensitivity reaction –plant allergen
Immune mediated
Bovine abomasal lymphoma
Name the etiology

Cause: Bovine Leukemia Virus
Microbial ?
Ulcerated area of lymphoma
Epithelial plaques, papular stomatitis, hard palate mucosa, calf
Name the etiology

Cause: Parapoxvirus
Microbial
can infect small ruminants
_________ means of unknown cause or spontaneous origin
Idiopathic
Epilepsy, renal amyloidosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, canine polyarteritis, pulmonary fibrosis, laryngeal hemaplasis are all examples of what ?
Idiopathic diseases
Multifocal locally -extensive chronic granulomatous pneumonia
Name the etiology

Cause: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Microbial
FYI

Multifocal to coalescing, granulomatous vasculitis/nephritis, kidney, cat




