L3 GI Organs Flashcards
(31 cards)
The digestive system consists of the following stuctures:
- oral cavity
- pharynx
- esophagus
- stomach
- small intestine
- large intestine

The accessory digestive organs are:
- liver
- gallbladder
- salivary glands
- pancreas

The oral cavity opens to the:
Pharynx

muscular tube & common chamber (shared by digestive & respiratory system)
The ____ to the ____ is located within the abdomen
distal esophagus; sigmoid colon

The esophagus enters the abdominal cavity through:
The diaphragm at T10

Anterior vagal trunk comes from the _____ nerve; Posterior vagal trunk comes from the _____nerve
left vagus nerve; right vagal nerve

The esophagus receives blood from which two arteries?
- Left gastric (celiac trunk)
- left inferior phrenic (abdominal aorta)

What is the function of the upper esophageal sphincter?
What is the function of the lower esophageal sphincter?
- Prevent the entrance of air during respiration and reflux of gastric contents
- which guards against gastro-esophageal reflux

Name the 4 parts of the stomach.
- Cardia/cardiac region
- Fundus
- Body
- Funnel-shaped pyloric part

Where is the pyloric sphincter located?
within the pyloric constriction
Surrounds the distal portion of the stomach, the pyloric orifice.

Define “angular incisure”
A bend on the lesser curvature of the stomach

What is the start and end of the small intestine?
pylorus to the ileocecal junction

What are the three surface modifications that increase surface area in the small intestine?
- circular folds/plicae circulares of mucosa-sumucosa
- Vili
- Microvili

What is the most frequent location for peptic ulcers?
Duodenal cap
(imaging: x-ray w/barium swallow)

Where does the duodenum receive the bile and pancreatic enzymes?
Hepatopancreatic ampulla at the major duodenal papilla.
site for gallstone impaction

What is the junction between upper GI bleeding and lower?
duodenojejunal junction

The jejunum is the proximal ____ of the small intestine is located in the ______ quadrant?
2/5; left upper (LUQ)

The ileum forms the distal _____ of the small intestine and is located mainly in the _____ quadrant.
3/5; lower right (LRQ)
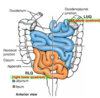
Describe the blood supply of the jejunum.
few arterial arcades
long vasa recta
little fat

Describe the blood supply of the ileum.
many arterial arcades
short vasa recta
laden with fat

Ileum opens into large intestine at the _____.
Ileocecal junction
(may have embryonic remnant: ileal diverticulum (Meckel’s))

The large intestine consists of:
- Cecum
- appendix
- Colon
- Ascending
- Transverse
- Descending
- Sigmoid
- Rectum
- Anal canal
List the 3 features that distinguish the large intestine from the small intestine.
- Omental appendices: small fatty projections
- Teniae coli: longitudinal smooth muscle
- Haustra (sacculations)
Where is the appendix located? (which structure of the GI)
cecum (inferior to ileocecal junction)