L14: Airway management Flashcards
What are the 2 causes of inadequate airways?
- Impaired Laryngeal reflexes
- Weakness or flaccidity eg
- CVA, head injury
- Guillian Barre
- Weakness or flaccidity eg
- Obstruction eg
- tumour
- secretions
- Mucosal inflammation and thickening
- Chronic reactions
- Acute reactions
- Laryngospasm
- Anaphylactic reaction
- Diphtheria
- Burn injury
- Acute respiratory failure
Whayt are the 6 indications of upper airway obstruction?

What are the 6 different major indications of upper airway obstruction?
- Congenital
- Infective
- Trauma
- Neoplasm
- Foreign body
- Vocal cords
What are 8 signs of inadequate airway?
- Voice alteration, hoarseness
- Tachycardia, Tachypnea, sweating
- Anxiety, confusion, lethargy
- Gurgling
- Drooling
- Choking, gagging
- Inspiratory stridor, crowing
- Hypercarbia and hypoxaemia
Upper airway transmitted sounds, inability to cough
What are the 7 methods of maintaining clear airway?
- Positioning – upright side lying
- Jaw position
- Nebulized Adrenaline (laryngospasm)
- Suctioning
- Oropharyngeal/nasopharyngeal airway
- Endotracheal tube
- Tracheostomy
- cricothyroidectomy
- percutaneous
- surgical
- minitracheotomy
What are the 3 characteristics of positioning?

What are 5 artificial airways?
- Oropharyngeal/Guedels
- Nasopharyngeal
- Endotracheal/Nasotracheal
- Tracheostomy
- Minitracheotomy
What are 7 characteristics oropharyneal or “guedels” airways?
- Short plastic tube - to pharynx only
- Keeps airway patent
- Facilitates suction
- Inserted by medical, nursing or PT staff
- Can cause patient to gag, vomit
- Pt in side lying - gag reflex
- Care with loose teeth, bite reflex

RULE: IF PATIENT CAN TOLERATE IT THEY NEED IT
What are the methods of insertion- upside down and then twist?

What are 4 characteristics of nasopharyngeal airway?
- Soft silastic tube to pharynx
- Inserted with lubricant
- Changed several times a day
- Usually changed once every 24hrs
- Inserted by medical, nursing or PT staff
Once it is in –> not irritating (except for getting it in)
What are 4 precautions of nasopharyngeal airways?
- Nasal/facial fractures, CSF leak, torn dura (For people with head injuries)
- Coagulopathy (Bleed easily –> might have a severe nose bleed)
- Anticoagulant therapy
- Hypotension

What are 6 characteristics of intubation? What are 2 considerations?
- “Definitive” or formal airway ie
- Nasotracheal/Endotracheal
- Tracheostomy
- Tube to just above carina
- Inserted by medical staff/advanced paramedics (very hard to intubate)
- Only access to ventilation
- Often require sedation to tolerate it
- Condition must be reversible
- If someone had terminal cancer –> could not be appropriate
This is the only airway (must make sure equipment is safe)
Considerations:
- Unable to talk (think about QoL)
- must be intensive care –> beds are scarce (need to know have good prognosis)

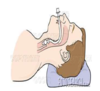
What is the position of endotracheal tube?

What are the 7 indications for “intubation”?
- Airway obstruction
- Inadequate oxygenation
- Inadequate ventilation
- Elevated work of breathing
- Airway protection ie protection from oral or gastrointestinal secretions
- Facilitation of tracheobronchial suctioning
- Facilitation of mechanical ventilation
What are 2 types of tubes?
- Endotracheal/nasotracheal
- Tracheostomy-
- Surgical
- Minitracheotomy
- Percutaneous tracheostomy
- Cricothyroidectomy
What are 4 types of tracheostomy tubes?
- Surgical
- Minitracheotomy
- Percutaneous tracheostomy
- Cricothyroidectomy
What are 4 characteristics of Endtracheal tube?
- Larger tube
- Less well tolerated by patient
- Tube occlusion by biting
- Damage to patients teeth
What are 4 characteristics of Nasotracheal tube?
- Oral hygiene easier
- Easier to insert
- Smaller tube, but easier to block with secretions
- Sinus infections, nose bleeds
What are the 4 grades of airways?

What are some predictors of a difficulty airway?

What are 4 functions of cuff in tubes for intubation?
- Prevents aspiration of gastrointestinal contents
- Provides good seal for ventilation
- Prevents movement/holds tube in
- Low pressure, high volume
What does a cuff and uncuffed tube look like?

What are the 4 indications of a cuffed tube?
- Unconscious
- Unable to swallow
- Requires full mechanical ventilation
- Can potentially cause trauma to vocal cords
- If tube is removed –> cuff must be not be inflated = can damage larynx…etc

What are the 4 indications of an uncuffed tube?
- Awake or able to swallow
- Pediatric use
- Patient able to speak with uncuffed tube
- Uncuffed tube may cause ↑ secretions due to irritation and movement












