Joint Pathology Flashcards
Normal Joint
Architecture
Components of Cartilage:
- Chondrocytes
- Water
- Collagen
- Proteoglycans

Osteoarthritis
Overview
“Degenerative Joint Disease”
- See deterioration and loss of articular cartilage
- Takes place over the course of many years
- Affects weight bearing joints
- Pathogenesis: biomechanical and biochemical theories
-
Clinical course: insidious with progressive pain and disability
- No constitutional signs, differential from RA
- No specific preventative or maintenance therapy (as of now)

Osteoarthritis
Morphology
- Loss of cartilage
- Exposure and eburnation of subchondral bone
- ± Subchondral cyst formation
- Osteophytes aka “Joint mice”
- Heberden’s nodes

Osteoarthritis
Symptoms
- Joint pain associated with movement
- Limitation of motion
- Stiffness after periods of rest
- Referred pain

Osteoarthritis
Clinical Manifestations
- Changes in shape of the joint
- Malalignment
- Limitation of motion
- Instability
- Spasm or atrophy of surrounding muscles
- Fine crepitation on joint motion

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Overview
Systemic, relapsing, chronic destructive synovitis
- Etiology unknown, course unpredictable
- Women affected 3x more than men
- Diagnosis by physical exam and lab studies
- Shortened life expectancy, often due to complications of therapy
- Variants: juvenile RA, Felty’s syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Morphology
-
Irregular, hypertrophied synovial membrane
- ‘Villiform’ structure
- Lymphoid inflammation
- Can contain lymphoid follicles
- Chronic inflammation
- Pannus formation (scarring @ edges of joint space)
- Fibrous and bony ankylosis (bone fusion)

Felty’s Syndrome
Constellation of sx:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Splenomegaly
- Neutropenia
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Pathogenesis
Believed to be autoimmune disease.
(Theory that process can be initiated by a virus)

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Course
Disease can follow various courses:
- Single episode followed by sustained remission
- Initial episode followed by complete remissions and exacerbations
- Acute illness with intercurrent milder disease activity
- Sustained disease activity
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Intra-articular Manifestation
- Joints inflamed
- Progressive stiffness and ankylosis (fusion of the bones)
- Hand becomes claw-like with ulnar deviation

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Extra-articular Manifestations
-
Subcutaneous and subperiosteal nodules
- Fibrin core surrounded by palisading histiocytes
- Constitutional sx (malaise, fatigue, diffuse pain, fever)
-
Organs and Tissue involvement:
- Pulmonary
- Cardiac
- Ocular
- Neurological
- Vascular
- RA pts often have Sjogren’s syndrome

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Pulmonary Involvement
- Pleuritis
- Pleural effusion
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Parenchymal rheumatoid nodules
Caplan’s Syndrome
Peumoconiosis and rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Vascular Involvement
-
Digital Arteritis
- Focal ischemic areas with pitting
- Digital gangrene
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Leg ulcers
-
Necrotizing systemic vasculitis
- Mesenteric
- Renal
- Coronary

Suppurative (Septic) Arthritis
- Destructive non-specific acute inflammatory reaction
- Hematogenous or direct spread to single large joints
- See Gonococci, Staph, Strep, Gram negative bacilli

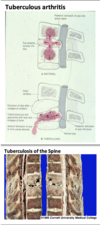
Tuberculous Arthritis
- Caseating granulomas similar to those seen in TB elsewhere
- Causes ankylosis, skin sinuses, or damage to spinal cord
- Insidious chronic disease in children
- Affects the spine, hip, etc
- Early diagnosis essential
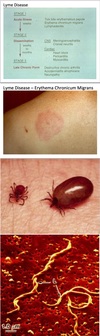
Lyme Disease
- Spirochetal infection
- Transmitted by deer ticks
-
Progression:
- First stage: skin lesion
- Second stage: cardiac and nervous systems affected
- Third stage: chronic disabling arthritis in 10% of cases
- Serologic diagnosis
- Abx therapy essential
Gout
Overview
- Hyperuricemia
- Recurrent acute arthritis following asymptomatic intervals
- Deposition of tophi
- Renal impairment may occur
- Few with hyperuricemia develop gout
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia does not require treatment
- 95% of cases in adult males, usually in great toe

Gout
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis relates to production and excretion of uric acid:
-
Primary Gout
- Due to overproduction of uric acid
- Cause of overproduction generally unknown
-
Secondary Gout
- Can be due to reduced excretion
- Glomerular or tubular defect or due to certain drugs
- Lead poisoning of the kidneys in Victorian England
- Can be due to increased production
- Chemotherapy
- Can be due to reduced excretion
Gout
Morphology
-
Acute arthritis due to precipitation of urates in joint fluid
- Birefringent crystals phagocytized by neutrophils and MΦ ⇒ release of harmful products
- Attack ends when crystals go back into solution
- Chronic arthritis is due to progressive precipitation of urates into synovium ⇒ destruction and ankylosis of joint
- Tophus: inflammatory mass of urates, pathognomonic
- Renal involvement by gout can include stones or urate deposits

Gout
Clinical Phases
- Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
- Recurrent acute gouty arthritis
- Chronic gouty arthritis
Diagnosis important because treatment is available
Pseudogout
“Calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition disease”
- Get precipitation of crystals in menisci and intervertebral discs
- Deposits can enlarge and rupture into the joint
- Produces inflammation
- Often asymptomatic
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Reactive arthritis
- Enteropathic arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
Ankylosing Spondylitis
“Bechterew disease”
-
Rare type of arthritis that causes pain and stiffness in the spine
- Most often affects sacroiliac joints
- Lifelong condition
- Seen in adolescent males
- 90% have HLA B-27
Reactive Arthritis
“Reiter syndrome”
-
Triad of:
- Arthritis
- Non-gonococcal urethritis or cervicitis
- Conjunctivitis
- 80% are HLA B-27
- Autoimmune reaction to GI or GU infection
Enteropathic Arthritis
- Induced by GI infection with Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter
- Often HLA B-27
Psoriatic Arthritis
- Form of arthritis that affects some pts with psoriasis
- Type of inflammatory arthritis
- Affects DIP joints of hands and feet and large joints
- Symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling
- Tx includes antiinflammatories, steroid injections, or joint replacement surgery
Ganglion Cyst
Fluid-filled sac arising from an adjacent joint capsule or tendon sheath
Most common mass that develops in the hand

Nodular Tenosynovitis
- Common
- More frequent in women
- Usually seen on hands and feet, more often proximally and on flexor surfaces
- May erode contiguous bone by pressure
- Pathogenesis: Controversial, some view as reactive, others see it as neoplastic (but usually benign)
-
Gross appearance:
- Single mass, usually 1–3cm diameter
- Fairly well-defined capsule
- May be somewhat lobulated
- Varies in color from whitish gray to yellowish brown
- Microscopic: dense, cellular tissue



