Investigative Techniques Flashcards
In a 70kg human, what percentage of their body is water?
How many litres is that?
60%
42 L
In a 70kg human, 60% water, how much of this is INTRACELLULAR?
2/3 of 42 L = 28 L
In a 70kg human, 60% water, how much of this is EXTRACELLULAR?
1/3 of 42 L = 14 L
In a 70kg human, how many litres of INTERSTITIAL water do they have?
11 L
In a 70kg human, what is their circulating blood volume?
How much of this is plasma and how much is red cells?
5 L
3 L plasma, 2 L red cells
What is haematocrit?
What is the haematocrit value for males and females according to UHL?
Red blood cells
Males 40-54%
Females 37-47%
What is the cardiac output at rest?
Rate x stroke volume
e.g. 70 bpm * 70 ml
= 4900 mls/min = 5 L/min
HOW MUCH and HOW FAST
How long does it take for the total blood volume to circulate once?
1 minute.
I want to view some cells with a light microsope. What are the three processes I must carry out to prepare the sample?
Preserve with formalin
Slice it thinly after setting in paraffin
Stain with Haematoxylin and Eosin
Which structures stain with haematoxylin?
Nucleus
Which structures stain with eosin?
Cytoplasm
ECM
I want to create a frozen section. Why and how?
E.g. in surgery for quick analysis
Frozen -20-30deg C
Cryostat (cold microtome)
Stain H&E
I think my patient has gout. How might I distinguish this from pseudogout?
Polarised light microscopy
Gout: Monosodium urate: needle shaped, yellow; more common in big toe
Pseudogout: calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate: rod/rhomboid, blue; more common in knee
I want to give my patient an ultrasound. What do I need to ensure a good resolution?
High frequency, short wavelength
What is this?
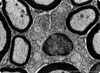
Transmission electron microscopy image
What is this?

Scanning electron microscopy image


