Introduction to Dermatology Flashcards
What is the largest organ in the body?
Skin
What are some skin adnexal structures?
Hair
Nails
Glands
Sensory structures
What are important functions of the skin?
- Protection
- Homeostasis
- Transmission of sensation
What are the layers of the skin from superficial to deep?
Epidermis
Dermis
(then below but not part of the skin is the hypodermis)

What are the layers of the skin from superficial to deep (invidividual layers)?
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale

What forms the stratum corneum?
Dead cells with a hard protein envelope
Cells contain keratin and are surrounded by lipids

What forms the stratum lucidum?
Dead cells lie within despersed keratohyalin
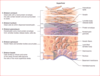
What forms the stratum granulosum?
Keratohyalin and a hard protein envolope
Lamellar bodies release lipids
Cells die

What forms the stratum spinosum?
Keratin fibres and lamellar bodies accumulate

What forms the stratum basale?
Cells divide by mitosis and some of the newly formed cells become the cells of the more superficial streta

What within the skin releases lipids?
Lamellar bodies
What is A?
Hyponychium
What is B?
Nail plate
What is C?
Lateral nailfold
What is D?
Nail bed
What is E?
Lunula
What is F?
Cuficle
What is G?
Proximal nailfold
What is H?
Nail matrix
What are the 3 different stages of the hair cycle?
Anagen
Catagen
Telogen
What is the anagen phase of hair cycle?
Active growing phase
What is the catagen phase of hair cycle?
2-3 week phase growth stops/follicles shrink
What is the telogen phase of hair cycle?
Resting phase for 1-4 months
How long does the telogen phase of hair cycle last?
1-4 months
How long does the catagen phase of hair growth last?
2-3 weeks
During what phase of the hair cycle is most hair in?
Anagen (80-90% hair)
Telogen (up to 10% of hair)
Categen (1-3% of hair)
What are some functions of the skin?
- Thermoregulation
- Insulation, heat transfer
- Skin immune system
- Innate and adaptive functions
- Barrier
- Protects against mechanical, chemical, microorganisms, UV light
- Keep in water and electrolytes, macromolecules
- Sensation
- Temperature, touch and pain
- Vitamin D synthesis
- UV light converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholecalciferol
- Interpersonal communication
- Physical appearance, smell, self-identity
The skin acts as a barrier to protect against what?
Mechanical, chemical, microorgasms and UV light
What kinds of sensations does the skin transmit?
Temperature
Touch
Pain
How does the skin perform vitamin D synthesis?
UV light converts 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholecalciferol
How much of skin disease is skin cancer/lesions?
50%
Why is skin disease important?
- Disfigurement
- Discomfort
- Disability
- Depression
- Death
What are some causes of skin disease?
- External
- Temperature
- Cold injury
- Frostbite, chilblains
- Skin necrosis
- Cold urticaria
- Cold injury
- UV
- Called photosensitivity
- Commonly caused by medications
- Exposed sites affected
- Can be sensitive to UVA, UVB, visible light or a combination
- Chemical
- Infection (allergen or irritant)
- Trauma
- Dermatitis artefacta (skin lesions solely produced by patients own actions)
- Temperature
- Internal
- Systemic disease
- Genetics
- Drugs
- Think of OTC drugs
- Infection
- Autoimmune
- Bullous pemphigoid
What can cold injuries to the skin cause?
Frostbite, chilblains
Skin necrosis
Cold urticaria
What are chilblains?
Small lesions caused by inflammation of small blood vessels due to exposure to cold air
What is cold urticaria?
Disorder where hives (urticaria) or large red welts form on the skin after exposure to a cold stimulus
What is a skin lesion solely produced by patients own actions called?
Dermatitis artefacta
What is an example of an autoimmune skin disease?
Bullous pemphigoid
What is the morphology of a skin lesion?
Appearance of a skin lesion
How big is a “small” skin lesion?
Typically means less than 5mm
What are some descriptive words for skin lesions?
- Macule
- Small circumscribed area
- Patch
- Larger circumscribed area
- Papule
- Small raised area
- Plaque
- Larger raised area
- Vesicle
- Small fluid filled
- Bulla
- Large fluid filled
- Pustule
- Small pus filled
- Abscess
- Large pus filled
- Erosion
- Loss of epidermis
- Ulcer
- Loss of epidermis and dermis
What is a macule?
Small circumscribed area
What is a patch?
Larger circumscribed area
What is a papule?
Small raised area
What is a plaque?
Larger raised area
What is a vesicle?
Small fluid filled lesion
What is a bulla?
Large fluid filled lesion
What is a pustule?
Small pus filled lesion
What is an abscess?
Large pus filled lesion
What is an erosion?
Loss of epidermis
What is an ulcer?
Loss of epidermis and dermis
What is a lesion?
A region in an organ or tissue which has suffered damage through injury or disease
What does distribution of a lesion refer to?
How skin lesions are scattered or spread out
What are the different kinds of distributions of lesions?
Isolated or multiple
What is used to describe skin lesions?
Morphology
Distribution
What are some examples of common skin conditions?

What are some examples of general conditions that can have cutaneous signs?
- Erythema nodosum
- Sarcoidosis
- Vasculitis
- Malignancy
- Auto-immune conditions
What does cutaneous mean?
Relating to or affecting the skin
What is a skin sign of hyperlipidaemia?
Eruptive xanthoma
What is acanthosis nigricans?
Brown to black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin
Hyperkeratosis and hyperpigmentation
What is acanthosis nigricans associated with?
What investigations should be done if bacterial infection is suspected for a skin condition?
- Charcoal swab
- Ask for MC&S
- Microscopy
- Culture
- Sensitivities
What investigations should be done if viral infection is suspected for a skin condition?
- Viral swab for PCR
- Can swab vesicle/bulla if vesicular eruption
- If systemic illness, can take throat swab
What investigations should be done if bacterial infection is suspected for a skin condition?
- Skin scraping
- Nail clipping
- Hair sample
- Fungal cultures
What is a simple way to take a skin biopsy?
Punch biopsy


