Introduction and Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Flashcards
What 4 main components is the urinary system made up of?
Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra
Functions of the urinary system?
Filters blood of metabolic waste Regulates electrolytes and BP via RAAS Helps stabilize pH Reabsorption of small molecules Makes erythropoietin
What vertebral level are the kidneys at and explain how they are they peritonised?
T12-L3 Retroperitoneal - partially peritonised by the organs around her
Name the posterior relations of the kidneys.
12th rib
Subcostal nerve
Right kidney
Iliohypogastric nerve
Ilioinguinal nerve
Structures of the kidney from outer to inner?
Cortex Medulla - Pyramid, papilla, minor then major calyx, pelvis then ureter
Name the possible constriction sites of the ureter.
1st - ureter passes over inferior renal pole 2nd - Ureter crosses over the external iliac vessels 3rd - ureter traverses the bladder wall
What is the order of vessels that enter the renal hilum from anterior to posterior?
VAP Vein, Artery, Pelvis
Explain the blood supply of the kidneys.
Renal arteries branch off the aorta Then they split into 5 segmental arteries inside each kidney Then into interlobar Then Arcuate which arcs round the circumference Then interlobular branches which end up supllying each individual nephron
Explain the blood drainage of the kidneys.
Renal veins drain into IVC
Where does lymph drain into from kidneys?
Lateral aortic lymph nodes
What is the nerve supply for the kidneys?
Sympathetic - T10 to L1 spinal nerves Sensory afferent - T11 to L2 spinal nerves
What is the median umbilical ligament a remnant of and where is it found?
Embryonic Urachus On the bladder
What is found at the medial umbilical folds?
Occluded umbilical artery
What is found at the 2 lateral umbilical folds?
Inferior epigastric vessels
What are the parts of the urethra in males in order of start to finish? What general area they found
Preprostatic - before prostate Prostatic - at the prostate Membranous - In between prostatic and spongy, is small Spongy - penile urethra
What is the bladder walls made from muscle wise?
detrusor smooth muscle
What epithelium does the bladder have?
Transitional epithelium
What does the prostatic urethra receive?
Ejaculatory duct
Which nerve supply constricts detrusor muscle during micturition?
Parasympathetic - rest and digest
Which nerve constricts internal urethral sphincter during ejaculation?
Sympathetic nerve
Which is the narrowest part of the urethra in male?
Membranous
Transpyloric plane passes through which vertebral level?
L1
What is a uriniferous tubule?
Nephron plus a collecting duct
What is a nephron?
Renal corpuscles + renal tubules
What is a renal corpuscles?
Glomerulus + bowmans capsule
How does the purified blood go back into circulation?
Renal veins
Name some common clinical urinary cases.
UTIs Glomerulonephritis Kidney stones/renal calculi Kidney failure and dialysis Urinary incontinence
What are some important markers of kidney disease?
High protein/albumin in urine - proteinuria GFR Increased level of serum creatinine/urea
What does this show?

Kidney cortex
What sort of epithelium is the proximal and distal convoluted tubules and the collecting tubules?`
Cuboidal
What is this?

Kidney medulla
What epithelium is the loop of henle made from?
Squamous
What is this

Ureter
What epithelium is the ureter
Explain the musclular layout of the ureter
Transitional epithelium
A star shaped lumen with inner longitudinal smooth muscle and outer circular smooth muscle
What is this? What epithelium is it? Explain the musclulature.
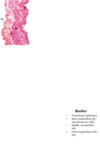
Bladder
Transitional
Inner longitudinal, middle circular and outer longitudinal SM


