Intro to Pharmacodynamics Flashcards
What kind of curve are you going to get when you plot a drug dose arithmetically?
Hyperbolic Curve

What kind of curve are you going to get when you plot a drug dose as a logarithm?
Sigmoidal Curve

The maximal effect that can be produced by the drug is ___________.
Emax
The does of drug that produces 50% of its maximal effect is ___________.
ED50
Which question does a Graded Response answer?
What is on the “y-axis”?
“How much?”
Effect of the drug is on the “y-axis”
- i.e. Arterial Pressure Change
Which question does a Quantal Response answer?
“Binary” Responses
All or non / Yes-no
“Does the response occur or not?”
“In how many?”
Requires a Pre-Defined Response: Death falling asleep, 10% reduction in blood pressure
What is the name of the curve that measures the number or % of individuals responding at a dose of a drug and only at that does?
Non-Cumulative Quantal Dose Response Curve

What is the name of the curve that measures the number or % of individuals responding to a dose of a drug AND at all doses lower than that dose?
Cumulative Quantal Dose Response Curve

How do you calculate the Therapeutic index?
What does that value tell you?
TI = TD50 / ED50
The Higher the TI, the SAFER the drug
TD50 - Median Toxic Dose
The range of doses of a drug or of its concentration in a bodily system that provides for the safe and effective therapy is referred to as __________ .
Therapeutic Window
Differentiate between narrow and wide therapeutic windows.
Wide: Not expecting to seem many Adverse Side Effects
Name the three parameters that describe the interaction of a drug with a receptor.
- Affinity
- Selectivity
- Intrinsic Activity
What does the affinity of a drug with its receptor tell you?
High Affinity –> Good drug-receptor interaction; LESS drug is needed to produce a response
Low Affinity –> Poor drug-receptor interaction; MORE drug needed to produce a response
What does the selectivity of a drug with its receptor tell you?
A more selective drug would affect FEWER targets over a specific concentration range
What does the intrinsic activity of a drug with its receptor tell you?
Agonists and Antagonist
Antagonists –> Block the response so that it DOES NOT have intrinsic activity
Describe the different types of Agonists.
- Full Agonists
- Partial Agonists (Emax is lower here than in FULL agonists)
- Inverse Agonists
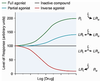
Action at the SAME receptor as the endogenous ligands is what type of Actagonism?
Pharmacologic (Receptor) Antagonism
Can have Agonist AND Allosteric Site Binding
What type of antagonism is present when chemical antagonist makes the other drug unavailable?
Chemical Antagonism
What type of Antagonism occurs between endogenous pathways regulated by different receptors?
Physiologic Antagonism
How do you control the drug effects when beneficial and adverse effects are mediated by the same receptors/signal transduction pathway on the same cell types?
TIGHT dose control
Ex: Insulin and DM1
How do you control the drug effects when beneficial and adverse effects are mediated by the same receptors/signal transduction pathway on different cell types?
AVOID systemic administration
Ex: B2 agonist acts on Bronchi, Blood Vessels and the Liver
How do you control the drug effects when beneficial and adverse effects are mediated by different types of receptors?
HIGHLY selective drugs are going to have LESS side effects
Which axis will you look at to get the ED50 measurement? What does ED50 tell you?
X-AXIS
Tells you how potent the drug will be! Lower ED50 means the drug will be MORE potent
Describe the relationship between KD and Affinity.
INVERSE
(Low KD = High Affinity)


