Intracellular Accumulations and Pathologic Calcifications Flashcards
1
Q
4 Main Pathways of Cellular Accumulation
A
- Abnormal Metabolism (Steatosis/Fatty Liver)
- Defect in Protein Folding/Transport (Mutated forms of alpha 1 anti trypsin)
- Lack of Enzyme (Storage Disorders)
- Ingestion of Indigestible Materials (Carbon/Silica)
2
Q
Steatosis/Fatty Change
A
- Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells
- Liver (main), heart, muscle, kidneys
- caused by: toxins, protein malnutrition, diabetes mellitus, obesity, anoxia, alcoholic liver disease
3
Q

A
Steatosis
4
Q
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Esters
A
- metabolism tightle regulated
- used for synthesis of cell membranes
- no intracellular communication
- will see intracytoplasmic vacuoles if accumulated
5
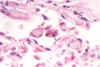
Q
Atherosclerosis
A
- Smooth muscle cells and macrophages in surface/wall of arteries filled with lipid vacuoles
- mostly cholesterol and cholesterol esters
- Aggregates of foam cell in surface/wall give yellow appearance of atheromas
- some may rupture releasing lipids into extracellular space
- will see cholesterol clefts-cholesterol esters crystallized as long needles
6
Q

A
Atherosclerotic lesion
7
Q
Xanthomas
A
- intracellular accumulation of cholesterol
- Xanthomas=groups of foamy macrophages found in connective tissue of skin and in tendons
- can be seen in non hyperlipidemic states
8
Q
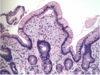
A
Gastric Xanthoma
9
Q

A
Cholesterolosis of Gallbladder
10
Q
Neimann-Pick Disease, Type C
A
- lysosomal storage disease
- mutations in enzyme involved in cholesterol trafficking
- cholesterol accumulates in multiple organs
11
Q
Renal Tubule Reabsorption Droplets
A
- Seen in kidney conditions that have protein loss in the urine
- increased reabsorption of protein into vessicles
- protein has a appearance of pink hyaline droplets within cytoplasm of proximal tubular cells
- reversible
12
Q

A
Renal tubule reabsorption droplets
13
Q
Russel bodies
A
- plasma cells actively synthesizing immunoglobulins may show russel bodies
- ER becomes hugely distended: large eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions
14
Q

A
Russel bodies
15
Q
Alpha 1 anti trypsin deficiency
A
- mutation in protein slows protein folding
- causes build up of partially folded intermediates that aggregate in liver cells
- resulting deficiency causes emphysema of the lungs
16
Q

A
Alpha 1 anti trypsin deficiency
17
Q
Accumulation of cytoskeletal proteins
A
- certain injuries cause aggregation of keratin filaments and neurofilaments