inherited metabolic disorders Flashcards
(29 cards)
what is tested in the uk newborn blood screen?
- CF -PKU -SCD- sickle cell disease - MCAD- medium chain acetyl co a dehydrogenase - MSUD - maple syrup urine disease
what are the criteria for a newborn blood screen?
- common problem - importan problem - reliable test - there should be facilities for diagnosis and treatment of disease - cost effective
what are common characteristics of metabolic disorder?
- under diagnosed - normal at first - become symptomatic later as a result go diet or illness - presentation mimics sepsis - can lead normal life if diagnosed early and there is no damage to organs
what is the inheritance pattern for most metabolic inherited diseases?
autosomal recessive- due to consanginty
what is the common mechanism of IMD?
there is a block from precursor to product, so there will be no negative feedback and the precursor will continue to increase bc precursor can’t go to product it will build up and go via alternative pathways to make toxic products
what are the minimum screening tests for IMD?
- plasma ammonia - blood gas - urine for metabolites
what specific tests can you do for imd?
blood test tissue sampling
what defieiceny do you have in PKU?
phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB) deficiency–> is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
Encoded on chromosome 12

what is management of PKU?
Diet (don’t drink fizzy drinks as contain aspartame which includes phenylalanine!)
L-DOPA, 5HT
BH4
- early treatment reduces neural impairment from 80-90% to 6-8%
how does PKU present?
- initialy normal
- gradual neurophysiology problems
- microcephaly
- low iq
- seizures
- tremors
- impaired myelination
- blonde hair
- musty odor
which toxic products build up during urea cycle defect?
Glutamine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, glycine
- they are a prduct of protein catabolism
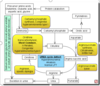
what are the effects of a urea cycle defect?
Soon after birth; if untreated, fatal
Lethargy, poor feeding, seizures, coma, death
High ammonia- ammonia intoxication
how to treat urea cycle defects
- removal of dietary protein intake
- removal oexcess ammonia- using levulose
- removalof urea cycle precursors that buld up and are toxic
- na bezoate- remove glycine
- naphenylbutyrate- remove glutamate - replacement of intermediates to force enzymes o work at their max for urea synthesis
- cirtruline
- arginine - liver transplant
wha are examples of amino acid disorders?
transport disorders
- dibasic amino acids- cystinuria
- neutral amino acid disorders- hartnup disease- affects absorption of non polar amino acids like tryptophan
metabolism disorders
- phenylalanine (pku)
- urea cycle defect
what happens in cystinuria?
- defective cystine transporter
- crystalises and stones form
how do you manage cystinuria?
water- to prevet stone formation
lithotripsy
chelation
what are carbohydrate disorders?
- GSD1 - glucose 6 phosphate deficiency
- GAL1PUT deficieny- galactosemia
what happens in gsd1 deficincy ?
- glycogen storage disease (von gierke’s disase)
- mutation in glucose 6 phosphatase gene on chromosome 17
- so glycogen cant be broken down into glucose in the liver
what are signs of GSD1?
- hypoglycaemia
- lactic acidosis
- lipidemia
- hepatomegaly
- uricaemia
- neutropenia
- bruising
- renal disease
how can GSD1 present?
- in 3-6 month old here is:
lethargy
weakness
seizure- because of not enough glucose reaching the brain
what is the management of GSD1?
- continuous corn starch feed bc of its slow absorption
- limit other sugars- fructose, galactose, sucrose maltose
- inhibi uric acid production- allopurinol
- hive cholesterol for hig statins
- liver transplant
wha happens in galactoseamia?
- Galactosemia is a rare autosomal recessive genetic metabolic disorder that affects galactose metabolism.
- Galactosemia results from a deficiency in one of the enzymes responsible for galactose degradation, usually galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase
- results in toxin accumulation in the liver, eyes, and brain.
there is currently no screening for this in the uk
what si the effect of galactosemia?
- prolonged jaundice
- cataracts
- poor weight gain
- hepatomegaly
what are examples of lipid and fatty acid organic disorders?
maple syrup uring disease
- MCAD- medium chain acetyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency



