INDE Flashcards
Why is melena black?
The iron in blood is oxidized as it passes through the bowels. Melena generally signifies an upper GI bleed whereas hematachezia generally signifies a lower GI bleed. According to wiipedia it takes ~14 hours for the oxidation.
What is the difference between tendons and ligaments?
Ligaments attach bone to bone Tendons attach muscle to bone
What is a bursa?
A flat pouch of synovial fluid that usually cushions joint movement, but can become inflammed and cause pain
What is the main bursa to be aware of in the shoulder?
The subacromial bursa
What are the three main shoulder problems?
Pain Instablity Decreased range of motion (remember: referred pain possible…)
Important associated MSK symptoms
clicking (crepitus), stiffness, weakness, swelling
What’s the general flow of MSK exams?
Look Feel Move (flex, extend, abduct, adduct, internal and external rotation) Special Tests Neurovascular
What structures are you feeling for in the shoulder?
Bony: clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula, medial border of scapula Muscles: teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, deltoids
What is shoulder impingement? What movements are painful?
compression of soft tissues between the acromion and the greater tuberosity of the humeral head. Elevation +/- internal rotation Pain when reaching overhead or behind the back Stiffness in the morning
What are the special tests for shoulder impingement?
Painful arc (abduct arms, most painful between 70 and 120 degrees) Drop arm test ( examiner abducts arm up to shoulder level, then tells pt to smoothly lower arm. pain or ratcheting are positive) Hawkins Sign Neer’s sign
What is the sulcus sign?
grab around the acromial clavicular joint, pull the arm down. a sulcus around the glenohumeral joint is indicative of joint laxity/instability
Differentiate between features of OA and rotator cuff tear in the shoulder
OA: uncommon in shoulder, deep ache and stiffness, develops over years, bone-on-bone feeling limits ROM Rotator cuff tear: preceded by trauma or repetitive movement, painful with specific movements, can have associated impingement, pain/weakness limits ROM
Common elbow complaints
fractures/dislocations medial and lateral epicondylitis (tennis and golfers elbow) Olecranon bursitis Inflammatory arthritis Instability Ulnar nerve injury
What is the common flexor and extensor origin of the elbow (wrist?)?
Flexor: medial epicondyle Extensor: lateral epicondyle
What are the common names for medial and lateral epicondylitis?
Medial: golfer’s elbow Lateral: tennis elbow
What are the active and passive provocation tests for lateral and medial epicondylitis?
Passively extend/flex the wrist and fingers (passive provocation) Have patient resist your attempt to flex or extend (active provocation)
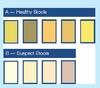
What are healthy and unhealthy stool colors for neonates?
What is Broselow tape?
A pediatric tape measure with quick reference values on it (e.g. BP, HR, med dosages)
Can pyloric stenosis be palpated?
Yes- olive shaped. May also see a visible peristaltic wave after eating
What will the DRE elicit in a child with acute appendicitis?
tenderness anteriorly and to the right
What is VACTERL and what is the clinical significance?
AKA VATER syndrome: a group of congenital anomalies that tend to occur together. The finding of one of these should prompt the clinician to evaluate the patient for the rest.
Vertebral
Anal atresia
Cardiac defects
Tracheo-
Esophageal
Renal
Limb
What is gastrochisis? What is omphalocele?
Both are congenital anomalies where the bowel protrudes through the anterior abdominal wall. They have different pathogenesis. Omphalocele has clear membrane around it and may contain liver
What is the CAGE screen?
Have you ever felt you need to cut back
Has anyone annoyed you by criticizing your drinking
Have you ever felt guilty about drinking
Have you ever had to drink first thing in the morning to get rid of a hangover or steady your nerves (eye-opener)?
GI history alarm symptoms
nocturnal symptoms
involuntary weight loss
intereference with daily functioning
What are the two phases of swallowing? Are they voluntary or involuntary? What is the difference between dysphagia and odynophagia?
- Transfer/oropharyngeal: voluntary
- Esophageal: involuntary
Dysphagia: difficulty swallowing
Odynophagia: pain swallowing (e.g. due to esophagitis)…feels like a razor blade
Dysphagia with regurgitation, choking and coughing would be suggestive of dysfunction in which phase of swallowing?
The oropharyngeal phase
Dysphagia with solids but not liquids is suggestive of what? What are possible causes?
Something structural as opposed to a mobility issue.
- esophageal ring (concentric..e.g. Schatzki ring) or web (eccentric)
- esophageal stricture
- esophageal cancer
- mediastinal compression (e.g. enlarged hilar node, goiter)
differentiate poor appetite and early satiety
- don’t feel like eating vs. getting full early
nausea and vomiting that improves when fasting suggests what kind of etiology
something GI related
How to assess for volume depletion?
- urine output
- mentation
- postural Sx
- cap refill
- skin tugor
- JVP
- peripheral pulses
Hematemesis or coffee ground emesis suggests bleeding from which anatomic part of the GI tract? What is the differential?
Proximal to the ligament of Trietz:
What can turn stool black?
- iron
- peptobismol
- blood



