images/histology - julia Flashcards
1
Q

A
- bacterial endocarditis
- little irregular blue things = inflammatory cells
- bottom right corner = fibrin
- smudgy blue material = masses of bacteria
1
Q

A
- liver with malaria
- breakdown products of Hb in Kupfer cells
2
Q

A
- inflammation in appendicitis
- way too many cells throughout
- epithelial surface being destroyed
3
Q

A
- bacterial endocarditis
- blue smudges = inflammatory cells or bacteria
- lighter pink = fibrin
- darker pink = collagen
3
Q

A
- cytomegalovirus
- cells become enlarged with huge intranuclear inclusions and cytoplasmic inclusions
4
Q

A
- acute pyelonephritis
- collecting tubule is the long thin thing full of PMNs in the middle/right of the image
- acute inflammatory infiltrate on right side
5
Q

A
normal small bowel
5
Q

A
* measles pneumonia
* interstital process
* airways don’t fill with inflammatory cells
* multinucleated giant cells scattered through the intestitum = typical marker of measles pneumonia
* most cells in the interstitium are lymphocytes, with some macrophages
5
Q

A
- amebic colitis in bowel
- higher magnification of edge of ulcer
- can see individual amebi
- look sort of like macrophages - round cells
6
Q

A
- biopsy of esophageal mucosa
- infected with CMV
enlarged endothelial cells with prominent intranuclear inclusions - stained by specific antibodies for CMV
- owl’s eye formation in center of enlarged cells
7
Q

A
- granuloma in lung due to TB
- can see langerhans giant cell in center of granuloma
8
Q

A
- serosal inflammation (right) and mucosal ulceration (left) in appendicitis
- superficial epithelium being sluffed off - mucosal ulceration
- too many little blue cells in serosa - inflammatory response
9
Q

A
- pneumonia
- alvolar wall thickening
- edema/fluid in alveoli
9
Q

A
- parasitized RBCs in small vessels of brain
- due to malaria
- each little dark dot = RBC full of malaria
10
Q

A
- aspergilis infection in lung vessels
- aspergilis is vasotropic, occludes and destroys walls
11
Q

A
- pneumonia
- cells with irregular nuclei = PMNs (they’re in the white space in the center)
- pink clumps (pale) = fibrin
- dark red = congested vessels
11
Q
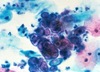
A
- pap smear of patient with herpes
- inclusion bodies indicate herpes
11
Q

A
- HSV in lung or trachea
- big red inclusions
12
Q

A
- bowel
- mucosa at edge of ulcer due to amebic colitis
- mucosa being destroyed
12
Q

A
- lung
- respiratory syncytial virus
- cuase formation of syncytia = large groups of cells merged together
13
Q

A
- influenza pneumonia
- lung - large respiratory bronchial
- lymphocytes in the bronchial submucosa
- loss of superficial epithelium and fibrin in lumen
- epithelium sluffing off
- fibrin becuase there’s edema
- fibrin adhering to the airway - not filling up the air spaces
14
Q

A
- lung biopsy
- patient with mononuclear inflammation in interstitium
- too many nuclei in walls
- foamy material in airways = protein, pathogen, no inflammatory cells
15
Q

A
- liver
- most hepatocytes appear normal, but ducts dilated and have brown material in them
- bile has backed up into them
- due to swelling of pancreus => common bile duct gets compressed => back up of bile
16
Q

A
- lung infected with pneumocystis
- interstitial inflammation with foamy exudate in alveoli
17
Q

A
normal skin
17
Q

A
- peribronchial caseation
- caseation is on the left side - bland pink area
- due to granulomas joining, loss of blood supply
- later stage of continued infection of lung
18
Q

A
- lung with abscess/empyema
- area of fibrin with mononuclear cells and micro-colonies
- dark purple dots = chronic inflammatory infiltrate
19
Q

A
- adrenal gland disfunction due DIC
- hemorrhagic adrenal glands
- normal = tan yellow
20
Q

A
- granulation tissue
- skin
- wound healing
- early stage
- loose watery material in background (pinkish material) = ECM = fibrin, fibronectin, collagen
- lots of inflammatory cells
- many tiny, thin-walled blood vessels
- big blue “angry looking” cells = highly activated fibroblasts- producing lots of ECM and laying down collagen
21
Q

A
- bacterial endocarditis
- smudgy groups = bacteria (in top left corner)
- more distinct dark purple = PMNs = below bacteria and in large clear cleft
22
Q

A
- caseation necrosis and fibrosis
- can’t tell that this is lung (but was)
25
Q

A
normal kidney
26
Q

A
- RBCs infected with malaria
- ring form = condensed nuclear mass with ring of blue cytoplasm
27
Q

A
- resolution of pneumonia
- restoration of archetecture by macrophage cleanup or inflammatory infiltrates
- in middle, most of cells are macrophages
- more or less normal archetecture of alveolar space
28
Q

A
- keloid, skin
- dense collagen, lots of fibroblasts
- huge ropey-like fibers of collagen diffusely through the tissue
- will be a firm lesion
30
Q

A
- ulceration and necrosis in appendicitis
- inflammatory infiltrate and destruction of tissue and necrosis
31
Q

A
- consolidated lung (white area)
- lower lobe dense and not spongy
- due to pneumonia
32
Q

A
- lung granuloma
- due to TB
- giant cell with multiple nuclei in center of granuloma
- lymphocytes = dark staining cells around boarder
- patch of epithelioid cells in bottom left of the granuloma (they’re slightly darker pink) - these just look like epithelial cells - were originally of monocyte/macrophage origin
32
Q
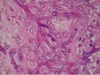
A
- zygomycosis
- note wide angle branching
- irregular, broad, nonseptate hyphae
33
Q

A
- early scar on left, late on right
- trichrome stain - blue = fully formed collagen
- collagen in early not fully organized yet so doesn’t stain blue
- so granulation tissue has only a few little wisps of blue
- also lots of dilated capiliareis in granulation tissue
33
Q

A
- bowel with schistosome eggs and chronic inflammation
- villa nicely preserved
- on right, can see white spots = eggs
33
Q

A
- lung with HSV infection
- thickend alveolar walls, but alveolar spaces still open
- lots of lymphocytes in walls - indicates that you’re probably looking at something viral rather than bacterial
34
Q

A
- india ink can’t get into yeast (can’t get through capsule)
- so can use to stain for yeast - yeast will be clear/white while everything around it will stain black
34
Q

A
- gram stain of pseudomembrane
- contains budding yeast and pseudohyphae
- infected with candida albicans
- when this is in the oropharynx = thrush
- oval - budding yeast forms
- tubular structures are pseudohyphae
35
Q

A
normal myocardium
36
Q
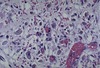
A
- heart, 3-4 days after MI
- scaring process
- neutrophils virtually all gone
- macrophage predominant cell type
- some fibroblasts but “not in full swing of producing collagen yet”
- few little capillaries form
37
Q

A
- * measles pneumonia
* interstital process
* airways don’t fill with inflammatory cells
* multinucleated giant cells scattered through the intestitum = typical marker of measles pneumonia
* most cells in the interstitium are lymphocytes, with some macrophages
39
Q

A
- early pneumonia
- pink in alveolus = edema/serum
- all pink fluid came from endothelial vessels - begining to pull apart
- thin alveolar walls but thickening
40
Q

A
- mononuclear inflammation of bowel wall due to thyphoid
- intracellular bacteria (though can’t see them)
41
Q

A
- kidney of patient with kidney failure due back pressure
- back pressure causes them to atrophy
- have chronic inflammation, fibrosis, glomeruli sclerosis
- renal tubules dilated, full of protein
42
Q

A
- cervix of patient with herpes
- inclusion bodies indicate herpes - darker purple, larger spots
43
Q

A
- interstitial pneumonia
- way too many cells
- many infammatory - expanding interstitium
- interstitial inflammation - results in “fluffy” inflitrates in xray
43
Q
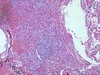
A
- lung in patient with DIC and fungal infection and pneumonia
- doesn’t look anything like lung
- hemorrhagic necrosis = lots of cellular debris, fibrin, dead cells, branching mold
44
Q

A
- brain with melanin stain (left) and silver impregnation techinque (right)
- cryptococcus makes tryptophan into pigement that’s brown, very much like melanin
- on left, can stain for melanin to detect yeast
- can also use silver stain - silver molecules impregnate cell wall - will stain walls of any yeast
- can also see budding - identifies these cells as yeast
46
Q

A
normal liver
47
Q

A
- skin with purpuria
- fibrin platelet thrombi in small vessels
48
Q

A
- brain
- necrosis of neurons and microgilal cells
- toxoplasma gondii encephalitis
- tiny dots = intracellular parasites (can’t see well at this magnification)
50
Q
what is this (connective tissue)?

A
- collage type I
- EM image
- most abundant type of collagen
- periodicity - lots of long extended cables - each cable made of three molecules wound together
51
Q

A
- lung
- respiratory syncytial virus
- cuase formation of syncytia = large groups of cells merged together
52
Q

A
- gram stain, lower respiratory sputum, pneumonia
- see PMNs (have mulitlobed bright red nuclei - in middle of image)
- pneumococci - little blue dots
53
Q

A
- typhoid nodule in liver
- normal hepatocytes on boarders
- aggregation of mononuclear cells in center = typhoid nodule
- no neutrophils (doens’t involved chemokines that bring in neutrophils)
54
Q

A
- lung with HSV infection
- thickend alveolar walls, but alveolar spaces still open
- lots of lymphocytes in walls - indicates that you’re probably looking at something viral rather than bacterial
55
Q

A
- base of bowel ulcer due to amebic colitis
- high magnification so can see amebi
55
Q

A
- brain of infant with HSV
- hemorrhage
55
Q

A
- skin infected with pseudomonas folliculitis
- get lesion in hair follicle - microabscesses that consist of masses of neutrophils
57
Q

A
- amebic colitis in bowel
- edge of ulcer - can see normal mucosa but at base all of the mucosa is gone, tissue being destroyed under the submucosa
58
Q

A
- heart 24 hours after MI
- early scaring
- necrotic myocytes
- vast influx of neutrophils
- neutrophils themselves breaking down and degenerating as they release proteolytic enzymes, collagenases, etc. => digestion and removal of tissue
59
Q

A
- lung on left - normal
- redish area = granulation tissue - used to be single layer of pleural cells
- purple area = cavity full of lymphocytes and inflammation cells
60
Q

A
- base of ulcer in bowel due to amebic colitis
- mucosa and submucosa shredding
61
Q
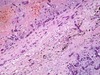
A
- aspergilis infection in lung vessels
- aspergilis is vasotropic, occludes and destroys walls
62
Q

A
- septal renal infarct
- dark clump in center = bacteria
- dark blue dots = inflammatory infiltrate
- this was once an artery
- blocked by something carrying bacteria = infected infarction
62
Q

A
- acute inflammation in pneumonia
- recruitment of PMNs - cells with irregular nuclei
- some cells with a little more cytoplasm - probably macrophages
- vessels very congested - huge numbers of RBCs in what should be very thin walls
- granular pink stuff = serous fluid has fibrinogen - being activated by coagulation cascade and forms clumps of fibrin
62
Q

A
- aspergillosis (fungi)
- note 45 degree branching
- can see septate = little walls
- these differentiate this from zygomycosis, which won’t have visible septae
64
Q
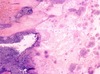
A
- lung abscess and empyema
- liquefied cavity = dark purple in bottom left corner
- right region = fibrin, bacteria, inflammatory cells
65
Q

A
- heart, mature scar tissue after MI
- trichrome stain
- can see collagen between myocytes
- after many months
66
Q

A
- trachea with HSV infection
- mucosal epithelium has been lost
- cells where it has been maintained have cytopathic effect due to virus
68
Q

A
- granulation tissue - skin
- wound healing, early stage
69
Q

A
- aspergilis infection in lung vessels
- aspergilis is vasotropic, occludes and destroys walls
71
Q

A
- dense dermal scar tissue in skin
- late stage of scar formation
- no inflammation
- virtually no blood vessels
- everything linear, nicely polymerized collagen
- very few and quiescent fibroblasts
- can take months to years
72
Q

A
- small bowel of patient with typhoid
- inflammation that goes all the way through the bowel wall
- mononuclear inflammation within peyer’s patches
72
Q

A
- edge of emypema with granulation tissue and inflammatory cells
- on left, new vessels and fibrous tissue
- on right, dense chronic inflammation - mononucelar cells, plasma cells
72
Q

A
- was once normal liver
- marked fribrosis surrounding schistosome granuloma
- all the pink stuff around the outside is collagen
- fibrosis has replaced the normal archetecture especially surrounding the veins, since that’s how the eggs came in
74
Q
A
normal lung
76
Q

A
- pseudomembranous colitis associated with C. Diff
- form of nectritizing inflammation
- bowel
- with marked inflammation
- lesion like appearance of volcano
- pink stuff in pseudomembrane = fibrin
- also lots of inflammatory cells
- also bacteria there, but they’re too small to see at this mag
77
Q

A
- lung in patient with DIC and fungal infection and pneumonia
- doesn’t look anything like lung
- hemorrhagic necrosis = lots of cellular debris, fibrin, dead cells, branching mold
78
Q

A
- lung in patient with DIC and fungal infection and pneumonia
- doesn’t look anything like lung
- hemorrhagic necrosis = lots of cellular debris, fibrin, dead cells, branching mold
- can see broad fungal hyphus in middle of image (dark purple and sort of wispy)
79
Q

A
- cytomegalovirus
- cells become enlarged with huge intranuclear inclusions and cytoplasmic inclusions
81
Q

A
- pseudomembrane
- pile of cellular debris, with bacteria, dead cells, fibrin
- due to C. diff
82
Q

A
- granulation tissue - skin
- wound healing - early stage
- punch biopsy
- pit has become filled - lots of inflammatory cells, lots of very activated fibroblasts
83
Q

A
- schistosome egg in bowel wall
- acute inflammation with eosinophils
84
Q

A
- brain
- toxoplasma gondii encephalitis
- purple dots = intracellular parasites
85
Q

A
- aspergilis infection in lung vessels
- aspergilis is vasotropic, occludes and destroys walls
86
Q

A
- skin biopsy of lesion with infection
- only acute immune reaction because patient lacks neutrophils
- lots of gram negative rods - can see in the middle
88
Q
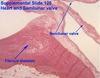
A
normal heart valve
90
Q

A
- acute inflammatory infiltrate in pneumonia
- macrophages have kidney shaped nucleus, a little more cytoplasm
- some RBCs, nucleus paler than the PMN nucleus
- PMNs = cells with the really dark blue irregular nuclei
91
Q
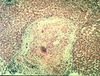
A
- hepatic lesion
- granuloma and fibrosis
- schistosomia egg in middle
- light pink cells around it = epitheliod cells
- resembles TB granuloma (but develops differently => has more collagen)
93
Q

A
- hyaline = clear
- influenza pneumonia
- not a cellular infiltrate filling up airspaces - hyaline
- interferes with normal oxygenation
- can be end product of viral action and all kinds of toxic things including high levels of O2
95
Q

A
- bowel biopsy at high power
- CMV cells = enlarged cells with very dark staining nucli and sometimes can see nuclear inclusion = owl’s eye cells
96
Q

A
- trachea with HSV infection
- mucosal epithelium has been lost
- cells where it has been maintained have cytopathic effect due to virus
- inclusion bodies indicate herpes (look at darker spot in the middle of the white circle in the middle of the image)
97
Q

A
- gelatinous appearance of cryptococcus in meninges in brain
- viscous so can block CSF circulation => hydrocephalous
98
Q

A
- pancreas in patient with pancreatitis
100
Q

A
- kidney with CMV infection
- owl eye cells
101
Q

A
- cryptococcus in epidermis
- yeast = on right, white areas with dot in middle
- not much morphologic inflammation
102
Q

A
- malaria in spleen (left) and liver (right)
- brown stuff is phagocytized breakdown products of Hb = characteristic of chronic malaria
104
Q
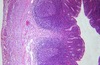
A
- normal appendix
- lots of lymphocytes
105
Q

A
- kidney infection
- with CMV - can see dark large cells but most of kidney looks normal at this magnification
106
Q
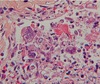
A
- HSV in lung or trachea
- big red inclusions
107
Q

A
- skin wound in the process of scar formation
- reepitheilalized
- will become focus of scar
- vascularity and cellularity will decrease over time - this about 1-2 months old
108
Q

A
- lung
- CMV pneumonia
- great big cells with very dark nuclear staining = CMV infected cells
- sometimes can actually see rim of nucleus with inclusion within it
109
Q

A
- pyelonephritis
- lots of PMNs
- glomerulus/structure visible
- glomerulus not really involved
110
Q

A
- yeast stained with mucicarmine stain - dyes capsules bright pink
- brain
- diagnostic characteristic of crytpococcus
111
Q

A
- candida albicans invading epithelium
- yeast-like oval forms, some with tubular structures
112
Q

A
- heart 4-7 days after MI
- early myocardial granulation tissue
- still inflammatory cells and macrophages
- lots more background ECM
- fribroblasts prominent, large, active
- lots of capillaries formed
- stage will persist for weeks
114
Q

A
- kidney with CMV infection
- see cytomegalic cells in the collecting tubules (epi cells)
115
Q

A
- skin biopsy - low power
- of a lesion
- purple at the top are the squamous epithelium
- can see hair follicles and vessels
- brown stuff is india ink (not important - just used to help the pathologists remember the orientation of the sample)
- there’s reduced acute inflammation with bacterial pathogen in this - reduced because the patient has low neutrophil count
116
Q

A
- phagocytized yeast in lung nuclei
- macrophages
- little lighter dots in cytoplasm = yeasts
- halo around yeasts = polysaccharide capsule
117
Q

A
- lung with HSV infection
- thickend alveolar walls, but alveolar spaces still open
- lots of lymphocytes in walls - indicates that you’re probably looking at something viral rather than bacterial
118
Q

A
- heart 4-8 weeks after MI
- maturing granulation tissue
- inflammatory cells virutally all gone
- ECM no longer watery, begining to organize
- blood vessels far more defined


