Images Flashcards
What is likely cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?

viral myocarditis –> cocksackie B
note the central lymphocyte aggregation and surrounding myocyte necrosis
What is possible cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?

Fungal myocarditis [aspergillus = septate hyphae branching at acute angle]
What is possible cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?
Where do you get it from? What does the black arrow point to?

Chagas disease
the arrow points to amastigotes within cytoplasm
T. cruzi transmitted by reduviid bug
What is cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?

giant cell myocarditis
arrow points to multinucleated giant cells and interstitial infiltrate
rare but fatal
What is cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?

hypersensitivity myocarditis
arrows pointing to eosinophiles
interstitial edema
What is cause of this dilated cardiomyopathy?
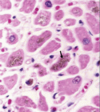
hemochromatosis
brown = cytoplasmic iron pigment
could also use prussian blue stain for iron
Which of these is hypertension and which is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?

Left is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy [HCM] = hypertrophy preferentially in interventricular septum
Right is hypertension = hypertrophy everywhere in LV
What feature of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is this?

fiber disarray
What type of cardiomyopathy? What is cause?

Restrictive cardiomyopathy due to amyloidosis
What is this? stain?

polarized congo red stain confirming amyloids
means this is likely restrictive cardiomyopathy
What is changing in these curves?

increase preload
What is changing in these curve?

Contractility
What is changing in these curves?

Changes in total peripheral resistance [TPR] = afterload
What kind of dysfunction in this figure?

Systolic dysfunction = systolic heart failure
What kind of dysfunction?

diastolic dysfunction
What kind of hypertrophy?

concentric hypertrophy
What kind of hypertrophy?

eccentric hypertrophy
What is this? What it is associated with?
step1
Aschoff body = focus of chronic inflammation with fibrinoid material and giant cells and containing anitschkow cells
sign of myocarditis in rheumatic fever
What is this? What is it associated with?
step1

anitschkow cell
asosciated with myocarditis in rheumatic fever
located usually in aschoof body


