Image questions Flashcards
(68 cards)
50 yom with chest pain for 24 hours: (a fib/ventricular tachycardia/ventricular bigeminy)

ventricular bigeminy: a ventricular premature beat follows each normal beat
55 yom with 4 hours of crushing chest pain. (anterior wall MI/inferior wall MI/anteroseptal MI/RV MI/L lateral wall MI)

inferior wall MI.
The electrocardiogram shows the early hyperacute injury phase of inferior wall myocardial infarction. This is reflected by the marked slope elevation of the ST segments, and the increased amplitude of the T waves in Standard leads II and III, and lead aVF. Reciprocal ST segment depression occurs in Standard leads I, lead AVL and leads V 4 to V6.
lipid deposition and smooth muscle cell hyperplasia (accumulation in intima)

atherosclerosis
two findings

atherosclerosis and thrombus
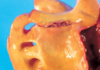
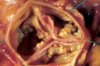
dissecting aorta
medium sized arteries, smoking history

Buerger disease (thromboangiitis obliterans)
what vessel does syphilitic aneurysm typically affect

ascending aorta (vasa vasorum)
xanthomas in which disease

familial cholesterolemia (foamy macrophages, ApoE involved, lacks LDL receptor)
filarial worm infestation causing obstruction of what

lymph nodes (elephantiasis)
biopsy of skin lesion in 25yow patient with proteinuria, recent hx of Hep B infection, P-ANCA, elevated erythrocyte sed rate
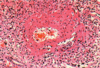
polyaderitis nodosa (medium sized and smaller muscular arteries, fibrinoid necrosis)
AIDS patient with multiple purple-colored skin nodules on hands and feet. What virus is implicated
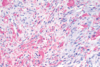
HHV 8 (Kaposi sarcoma)
70yow with throbbing unilateral headache and vision problems, mandibular pain
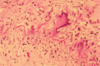
Giant cell arteritis

cavernous hemangioma
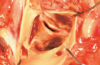
thoracic aorta with aldehyde fuchsin stain

cystic medial necrosis (dissecting aneurysm). focal loss of elastic and muscle fibers in the aortic media leads to cystic spaces filled with pools of metachromatic myxoid material

aneurysm
coronary artery section in pt with familial hypercholesterolemia. what’s in it?

platelets and RBCs + fibrin = thrombus (at an early age)
fever, skin rash, mucosal inflammation, lymph node enlargement. usually self limited but may involve coronary arteries and lead to aneurysm
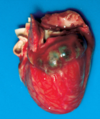
Kawasaki
renal biopsy. (papillary necrosis/polyarteritis nodosa/monckeberg medial sclerosis/hyaline ateriolosclerosis)

hyaline ateriolosclerosis

varicose veins
excessive collagen deposition in the skin, subintimal fibromuscular thickening, renal biopsy. what is the disease

scleroderma
infant heart. (cardiac amyloidosis/endocardial fibroelastosis/hypoplastic left heart syndrome)

endocardial fibroelastosis (fibroelastotic thickening of the endocardium of the left ventricle, may also affect valves)
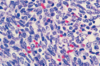
left main coronary artery 2 days after an MI. what histologic changes are present?
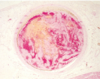
two days after MI: heart muscle will show myofiber necrosis, edema, and focal hemorrhage. this artery shows necrosis of cardiac myocytes and infiltrates of neutrophils
35 yom with MI, L main coronary artery two days later. what underlying disease does the patient have?

familial hypercholesterolemia
ruptured myocardial wall causes what

cardiac tamponade