IBD Immunology Flashcards
NB! what is a characteritic that really sets UC and CD apart
CD- rectum spared (40%)
UC - rectum always involved
what are the key concepts of IBD
chronic relapsing idiopathic inflammation of GI tract
genetics and immune mechanisms play imp role
irreversible impairment of GI structure and function –> increased intestinal permeability bc impaired formation of tight jxns
hygiene hypothesis- -> increased incidence of IBD
What is the role of commensal bacteria in IBD
cause inflam rxn –> self-sustained mucosal inflam
bacterial components cross the mucosal barrier and induce innate and adaptive responses
both cellular and humoral immune responses to a variety of antigens in IBD
persistent & inappropriate perturbation of highly regulated interaxn btn immune system and commensal bacteria of normal microbiome causes dysbiosis and mucosal inflam
What are the aberrant responses that are genetically determined
disrupt barrier fxn- UC
dysfxn of the microbe sensing - CD
changes in immunoregulation in both disorders
what are the respective lab tests for CD and UC
CD = (+) ASCA
UC = pANCA test (+)
what is the role of environmental factors in IBD
= initiate and reactivate dz
environmental factors imp bc low cordance rate in identical twins
genetics - influence luminal microbiota
what is gut microbiota & what is its role in the host
=symbiotic & reciprocal interaxn w/ host cells - make complex & regulated ecosystem
fxnal roles =
- protection: against invasion/colonization
- facilitation: digestion & abs
- immunological surveillance signals
what is the role of microbiota in IBD
develops in high bacterial concentration
surgical diversion of fecal stream –> prevent intestinal inflamm - IF reestablish –> recurrence!
ABx and probiotics = beneficial effects on IBD
circulating Abs against fecal Ag detected ; lymphocytes show reactivity to these
what phyla make up the gut microbiome
Bacteroidetes
Firmicutes
wht dysbiosis occurs in CD
increase Firmicutes (majority) and Actinobacteria
decrease bacteroidetes
What is the dysbiosis that occurs in UC
increased Proteobacteria
decreased Bacteroidetes
how do we know that intestinal microbiota may be imp for IBD pathogenesis
spontaneous colitis doesnt occur in mutant mouse strains when kept in a germ free environment
BUT it develops rapidly when mice are colonized by commensal bacteria
GFM colonized w/ intestinal microbiota from IBD donors show exacerbated dz
____________________________________________
Babies born from IBD women –> lower bacterial diversity & altered composition [maternal IBD = main predictor of diversity of infant microbiota]
GFM injected w/ IBD mother & infant ==> stools show sig altered adaptive immune system of intestines in GFM
what can cause dysbiosis & lead to dysregulation of the immune system and inflam in genetically susceptible host
host genetics
maternal transfer & early colonization
ABx & meds
infxn
inflam
stress
hygiene
age
how doe diet control the microbiota diversity
High fiber: increases all besides proteobacteria (decreases)
High protein: increases all except actinobacteria (dysbosis bc increase proteobacteria!)
High carb: increases all except Proteobacteria
High fat: decreases all except actinobacteria (dysbosis bc decrease in bacteriodetes & firmicutes)
what is the role of infxn in IBD
no specific organisms conclusively linked to development
gastroenteritis, such as Salmonella and campylobacter, possible etiology of IBD
prevalence of IBD is inversely related to prevalence of helminth colonization (imp immunoregulators)
what are the roles of genetic factors in IBD
Asia & Africa: UC is 10x less** & CD if **very uncommon
risk increase w/ 1st degree relative
greater concordance rate in monozygotic vs dizygotic
NB! over 200 SMPs associated w/ predisposition ( NOT mutations )
NB! all genes encode for immunoinflam components
what is the IBD-1 gene
in chromosome 16q12
contains CARD15/NOD2 genes = CAspase Recruitment Domain family member 15 also known as Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain 2 gene)
what are the fxns and characteristics of CARD15/NOD2
expressed in macrophages/DCs
defects in CD (17-27%)
ppl homozygous for susceptible variant (SNPs) have > 20x increased risk for CD
= intracellular PRR and recognizes MDP, a peptidoglycan constituent of both gram (+) & (-) ==> triggers activation of NF-kB
What is the possible mechanism for mutations of CARD15/NOD2 that cause CD
- *Defective functions of macrophages**–> persistent intracell infxn & stimulate T cells
- *Defective epithelial-cell responses** –> loss of barrier fxn & increased exposure to mucosal microflora
- *Defective conditioning of APCs**–> inappropriate activation of APCs & disrupte the homeostatic balance of effectors and regulatory cells
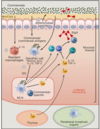
how does normal microbiota maintain homeostasis
colonization of the GI w/ beneficial bacteria –> induce development of GALT
maintains the basal levels of Th17 & Th1 in lamina propria
increased barrier fxn (maintain permeability)
pathobionts suppressed by commensal bacteria via Treg & IL-10

what is the role of SCFAs in the GI system
produced by commensal bacteria
anti-inflam properties in macrophages, DCs, CD4+ T cells, and intestinal epithelial cells
GPR43 is the receptor for SCFAs that induces Treg cells and IL-10 production
induce IgA and mucus secretion into lumen
promotes epithelial barrier integrity & prevent pathogen colonization
what happens whtn the GI tract is colonized by segmented filamentous bacteria
(Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium spp)
= induce Treg cells in the lamina propria
and maintain basal level activation of Th17 - imp for the integrity of the epithelial border
how does the microbiota induce host immune tolerance to commensal bacteria
microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMP)
polysac signaling (PSA)
indirectly through production of SCFAs
potentially by expression of intestinal Alkaline phosphatase (IAP), which detoxifies luminal LPS
describe the “mucosal firewall”
primary barrier limiting contact btn microbiota & host tissue = mucus
epithelial cells –> make antimicrobial peptides –> also limit exposure to commensal microbiota
tissure resident macrophages - quickly eliminated translocating commensals
DC can capture commensal Ags that traffic to the mLN from lamina propria –> Ag presentation –> differentiation of Treg, Th17 and IgA producing B cells
combo of mucus, DC, IgA and T cells = firewall - limit passage & exposure of commensals to the gut associated lymphoid tissue