How the body responds to infection Flashcards
What is primary immunity
Immunity produced by the first exposure to the pathogen
What is adaptive immunity ?
Occurs when re-exposed to the same microbe ; it is a more improved secondary response
Adaptive immunity is generated by ____
Lymphocytes
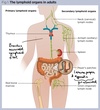
What are the secondary lymphoid tissues?
Tonsils
Lymph nodes (cervical, axillary and inguinal)
Adenoids
Bronchus associated lymphoid tissue
Spleen
Peyer’s patches
Lamina propria
Appendix
Function of lymphoid organs
Production of RBCs , WBCs and platelets
Removal of damaged RBCs
Maturation of immune cells
Trapping foreign material
What are the primary lymphoid organs
Majority of immune cells originate in these organs
Red bone marrow and thymus
What is lymphocyte recirculation
Refers to the continuous transport of large numbers of naive lymphocytes between the blood and lymphatic organs ; allows constant surveillance of the whole body for infection
Describe innate immunity
Acts as a general response to many types of pathogens
Quickly activated
remains the same on repeated exposure to the same microbe
moderate effficiency - unlikely to provide full protection against highly virulent pathogens
works by recognising PAMPs and PRRs
What are PAMPs
give 2 examples
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
they distinguish pathogens from cells from our own body
bacterial lipopolysaccharides and viral double stranded RNA
What are PRRs
give an example
Pattern recognition receptors that are widely expressed in many cells involved in the innate immune response
they bind to PAMPs
E.g. toll like receptors
Describe adaptive/acquired immunity
Involves T and B lymphocytes
more slowly activated
improves on repeated exposure to same pathogen
highly efficient
specific response adapted to individual microbes
recognition of antigens specific to each type of pathogen
antigens recognised by antigen-specific receptors clonally expressed by lymphocytes
Stages of a primary infection
1) epithelial barrier
2) immediate innate local response via complement proteins and macrophages
3) early induced response (innate/inflammatory)
inflammatory mediators produced by complement macrophages and mast cells
these attract leukocytes and serum proteins (more complement)
4) later adaptive response
antigen carriage by dendritic cells/diffused in lymphoid tissue to activate specific T and B cells
Antibody produced and recirculated back to the site of infection
Which WBC are responsible for furthering the immune response in intra-cellular vesicular infection
Helper T cells
Which components of the immune system are involved in intracellular cytosolic infection (most viral infections)
Interferon proteins
natural killer cells
cytotoxic T cells
What are the different types of diseases that come under immunopathology ?
Immunodeficiency
allergy
autoimmunity
transplant rejection
lymphoproliferative disease


