HIV Rx Flashcards
Which conditions cause Pancytopenia in HIV? (6)
Many HIV Pts Lose Cells Broadly
- •MAC
- •Histoplasmosis (Disseminated Fungal)
- •Parvovirus B19
- •CMV
- •Lymphoma
- •Medications [BAD PG] (Bactrim / AZT / Dapsone / Pyrimethamine / Ganciclovir)
What’s the normal CD4 count
800-1500
(ART should INC CD4 by 50-150 / year)
Virologic Suppression (Undetectable) is defined as what lab value?
Less than 50 HIV RNA copies
Describe the main differences between HIV2 and HIV1 (3)
HIV2 is…
- Endemic to West Africa
- Has longer Asx stage with lower viral loads and mortality
- May present as negative serology/viral load but with DEC CD4 suggestive of HIV
List the [Nucleoside/tide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTI)] (7)
ADELS TmZ
- Abavavir (ABC)
- Didanosine (ddl)
- Emtricitabine
- Lamivudine
- Stavudine
- Tenofovir
- Zidovudine (formely AZT)

NRTI MOA
Nucleoside/tide analogs lacking [3 OH group] that enter cell–>are phosphorylated–>form synthetic substrates that compete with native nucleotides–> terminate proviral DNA

NRTI Metabolism and half life
Renal Excretion with [half life=1-10 hours]
Explain how NRTI are able to be taken QD vs. BID
Intracell reservoirs of active anabolite DEC dosing frequency
NRTI SE (5)
Didanosine > Stavudine > Zidovudine
LHAMP
[Lactic Acidosis Hepatic Steatosis Syndrome]
Anemia
Myopathy
Pancreatitis
[HepB flare when discontinued]

Explain which drugs cause [Lactic Acidosis Hepatic Steatosis Syndrome] and why. (4)
NRTIs: Didanosine > Stavudine > Zidovudine > Tenofovir
… inhibit [DNA polymerase gamma] –> blocks mitochondria DNA synthesis –> [inhibits oxydative phosphorylation complex] activity–> INC cytosolic lactate –> [Lactic Acidosis Hepatic Steatosis Syndrome]

Which NRTIs cause [HepB Flare] when discontinued (3)
U LET these NRTIs go…there will be Hep problems!
Lamivudine (also–>Emtricitabine resistance)
Emtricitabine (also–>Lamivudine resistance)
Tenofovir
These NRTIs have Anti-HepB Activity so D/C –> HepB Flare

Abacavir Indication
Combo therapy for experienced HIV1

Abacavir SE
Hypersensitivity in [HLA-B 5701 + pts]. This is a Contraindication!!

Zidovudine Indication
Px Combo therapy for Both HIV in children/adult/prego

Zidovudine SE (2)
Anemia
[Granulocytopenia: Neutropenia]

Name the drugs contraindicated with Zidovudine (4)
Doves Really Creates Stinky Goop
Stavudine
Cotrimoxazole
Ganciclovir (BM tox)
Ribavirin (blocker)

Didanosine SE (3)
[Lactic Acidosis Hepatic Steatosis Syndrome]
Pancreatitis
Peripheral Neuropathy

Which NRTIs does Didanosine have drug-drug interactions with (3)
Stavudine - Cx
Zalcitabine - Cx
Tenofovir (INC serum Didanosine)

Which NRTIs are preferred for naive pts (2)
ET was a very naive alien
Emtricitabine
Tenofovir

Which NRTIs has DDI (drug-drug interaction) with Zalcitabine? (2)
Lem & Dal didn’t like Zal
Lamivudine
[Didanosine - Cx]

Tenofovir SE (3)
Hep B Flare
Nephrotoxic
[Lactic Acidosis Hepatic Steatosis Syndrome]

Describe the DDI between Tenofovir and Atazanavir
Tenofovir [DEC serum Atazanavir]

Name the [NonNucleotide Reverse Transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)] (5)
NO DEENR!
Delavirdine
EfaVirenz
Etravirine
Nevirapine
Rilpivirine

NNRTIs MOA
Noncompetitve inhibitors that allosterically bind to RT and induce conformational change

NNRTIs metabolism and half life
NNRTI: [Rapidly absorbed and Liver metabolized]
Half life = (Delavirdine 2-11) to (EfaVirenz 40-55)

NNRTI Indication
HIV1
Can NNRTI be used as monotherapy? Why or why not?
NO! Rapid resistance development

What are the advantages and disadvantages (2) of NNRTI?
Advantage: Using NNRTI saves [Protease Inhibitors] for later
Disadvantage: Resistance and [Heavy influence on CYP450]
General NNRTI SE
Common DDI (heavy influence on CYP450)

EfaVirenz Indication
Initial HIV1 tx

EfaVirenz Contraindication
[1st Trimester preggo] or [Women planning to conceive]

EfaVirenz causes Birth and Transient CNS Defects
EfaVirenz DDI (2)
CYP3A4 inducer
- DEC serum Methadone
- DEC exposure to [Protease Inhibitors]

Nevirapine Indication
Combination HIV1; alternative to EfaVirenz in
[Naive women with pretx CD4<250]
and
[Men<400]

Nevirapine Contraindication (2). What happens as a result?
- [Women with pretx Greater than 250 CD4]
or
- [Men Greater than 400 CD4]
These pts given Nevirapine –> Severe Hepatotoxicitiy

Which DDI does Nevirapine have (2)
CYP3A4 inducer –>
DEC serum methadone
DEC exposure to Protease Inhibitors

Name the [Protease Inhibitors] (8)
INDRAFTS
- Indinavir
- NeLFinavir
- Darunavir
- Ritonavir
- Atazanavir
- Fosamprenavir
- Tipranavir
- Saquinavir

[Protease Inhibitors] MOA
INDRAFTS inhibit [HIV aspartyl protease] –> Blocks Proteolytic processing necessary for packaging & assembly –> Blocks maturation

[Protease Inhibitor] General Characteristics (4)
PPPProtease Inhibitors!
- [Poor PO bioavailability sometimes enhanced with fatty meals]
- hePatic CYP metabolism
- P-glycoprotein substrates
- Plasma protein bound
Describe the effectiveness of [Protease Inhibitors] to DEC Viral load
HIGHLY Effective when used as combo therapy

[Protease Inhibitors (PTI)] SE (6)
Many PTIs Don’t NNeglect Lipids
- Metabolic Syndrome
- NVD and [Nephrolithiasis w/Indinavir]
- Paresthesia
- [Lipodystrophy-Chronic use]
- [DDIs-(Q W SPERMS)]

Name the DDIs [Protease Inhibitors] have and why there is an interaction (7)
[Protease Inhibitors] Qlash’s With SPERMS!
Quinidine - CYP3A4 substrate
Warfarin - CYP3A4 substrate
St.John Wart - strong inducer of CYP3A4
Phenobarbital-strong inducer of CYP3A4
Ergotamine - CYP3A4 substrate
Rifampin - strong inducer of CYP3A4 **
Midazolam - CYP3A4 substrate
SAL statins (Sim/Ator/Lovastatin)-substrates

Ritonavir Indication
Both HIV (1 and 2)

Ritonavir SE
Paresthesias

Explain why Ritonavir is often co-prescribed with other Protease inhibitors? Which HIV strain is this most useful for?
Ritonavir (RTV) is a PI that potently inhibits CYP3A4 –> enhances/boost exposure of other PIs –> Reduced dosing frequency/INC efficacy.
HIV2 benefits most from this

Other than Ritonavir, name an alternative boosting agent
Cobicistat (used in Stribild) - has no HIV reduction activity

How should you manage an HIV+ pt with Hypercholesterolemia on ART
Switch them from PTIs (if they’re on it) –> NRTIs
Remember that PTIs inhibits CYP3A4
Raltegravir MOA
Binds/Inhibits Mg+ cofactors required for strand transfer during viral integration

How can HIV develop resistance to Raltegravir
Mutations altering orientation of Mg+ co-factors –> Resistance of INTIs
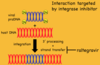
Raltegravir Indication
Combo therapy [Raltegravir + PTI + NRTI]
for naive AND experienced pts

Raltegravir SE (3)
Nausea
Diarrhea
HA

Raltegravir half life and dosage
9 hours (take BID after high fat meal)

Raltegravir is the main ____ inhibitor. What’s unique about Elvitegravir?
Raltegravir is the main Integrase inhibitor.
Elvitegravir = short half life unboosted and is the only approved INTI that is a CYP substrate. Only in Combo pill (Stribild)

Raltegravir is the main ____ inhibitor. What’s unique about Dolutegravir?
Raltegravir is the main Integrase inhibitor.
Dolutegravir = LONGEST INTI half life but is in development as microparticle injectable formulation, with half life of 3-7 weeks total

Enfuvirtide MOA
Binds to [surface Gp41] –>Blocks confirmation required for fusion

Enfuvirtide Dosage and Indication
Injected BID as combo therapy in [Refractory experienced pts]

Which HIV strain is Enfuvirtide not active against and why?
HIV2; Mutation of binding site at [HR1 of Gp41]

Enfuvirtide SE
Hypersensitivity at injection site. Cx in pts with known Hypersensitivity

Maraviroc MOA
slowly and reversibly blocks [Human CCR5] interaction with [HIV Gp120] –> prevents [Tropic HIV1] attachment

Maraviroc Indication
Combo therapy in [Refractory experienced pt with tropic HIV1]

Why is a Trofile assay required when using Maraviroc? (2)
mutation in the [HIV Gp120-CCR5 amino acid binding sequence]
or
Emergence of CXCR4 tropic HIV
both lead to Maraviroc Resistance

Maraviroc Contraindications (3)
Rifampin
Ritonavir
Liver Failure (use cautiously)

Describe the 3 major complications of treating TB in [HIV ART pts]
Give RifaButin to HIV TB pts
- Co-admin of RifaButin (preferred TB tx in HIV pts) with ART still requires monitoring/dose adjustment
- Rifampin DEC efficacy of [ALL PTIs and NNRTIs] except EfaVirenz
- Rifamycin is a potent CYP Inducer

Combination ART Tx for Naive patients (2)
[1 NNRTI (EfaVirenz > Nevirapine)] + [2 NRTI (E + T)]
OR
[1 PTI (A+R) vs. (D+R) vs. (F+ RBID)] + [2 NRTI (E+T)]
PTI boosed with RTV

In using Combo ART for naive pts, which PTI can…
A: not be used in pts with high dose PPI
B: Not used in combo with tenofovir or [Didanosine/lamivudine]
A: A + R
B: Unboosted Atazanavir

List the Dual NRTI options for [Combination ART tx in naive pts] (1 preferred and 3 Alternataive)

Definition of Viral Suppression Failure (3)
- HIV RNA > 400 after 24 weeks of ART
- HIV RNA > 50 after 48 weeks of ART
- Virologic Rebound (repeated detection of HIV RNA above undetectable even after once being suppressed)
What is IAS-USA?
HIV education organization that keeps updates on Drug Resistance Mutations in HIV1
List the 3 Combination Therapies in HIV pts that are NOT recommended? Rationale for each?

What is the exception to using Non-recommended [Triple NRTI regimens] (2)
Z + A + L
or
Z + L + T
in pts that have worst options

Why shouldn’t you use
PTI [Atazanavir + Indinavir]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
NRTI [Didanosine + Stavudine]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
[Double NNRTI combination tx]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
NRTI [Emtricitabine + Lamivudine]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
[Etravirine + Unboosted PTI]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
[Etravirine + (boosted ATV vs. FPV vs. TPV)]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
[Etravirine + (boosted ATV vs. FPV vs. TPV)]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
NRTI [Stavudine + Zidovudine]?
Any exception?

Why shouldn’t you use
PTI [Unboosted Darunavir + Saquinaivr + Tipranavir]?
Any exception?

Definition of [Functional Cure] in HIV. Example?
Preventing virus from inducing immune deficiency. CCR5 Zinc Fingers?
Definition of [Sterilizing Cure] in HIV. Example?
Complete Elimination of Virus
Berlin Pt with stem cell transplant


