Hit to Lead and Lead to Drug optimization Flashcards
Hit
A small molecule which exhibits the desired pharmacology towards the target (TDD) or phenotype (PDD)
Lead
- Novel structure that exerts disease modifying effects (typically in an animal model) that has a defines SAR and plausible optimisation path towards the drug
- patentable
Drug/ candiate
product of the optimisation effort that will be progressed towards clinical and pre-clinical development
TPP
Description of the new drug asset and how it addresses an unmet clinical need
Drug Selection Matrix
A detailed description (matrix) of the clinical and pre-clinical endpoints that a candidate directed to the TPP must satisfy
Drug Assay Cascade
A series of experiments/assays that have been stratified to enable a stage wise progression from a hit to lead and lead to a candidate that fulfils stipulated requirements of the DSM
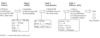
Stage 1
Potency: EC50 < 100 nm
Sel > 50 fold
Log P, D MW, TPSA etc
LE > 0.4
LipE > 4
LELP < 8
Stage 2
ADME
- Solubility Sw > 30 uM
- Permeability Papp > 4e-6 cm/s
- Microsomal stab HLM t/12 > 120 mins
Stage 3
Toxicokinetics
Rodent PK, Repeat dose tox, cytotoxicity
- Oral BA > 20% , T1/2 > 4h, Cmax 10xIC50
- NOAEL > 300 mg/ kg
- Cytotox > 30 uM
Stage 4
- Efficacy
- Off target
- Cyp inhibition
- Chromosomal Tox
- Stability studies
SAR guided optimization
(w/ functional groups and their issue)

Increasing potency
Potency needs to be considered as a function of molecular weight, as increasing MW results in promiscuity and solubility issues
Potency should be increased via the addition of the minimum number of C,N, and O
Diversity Space
- Proteome of a binding site which needs to be filled by binding elements
- Combinations and permutations of binding elements seperated by an amount of space. Seperated by bonds i.e. 2-50 A.
- A modestly sized library is required for a protein binding site required with 2 binding sites
- Three binding elements induces an additional dimension and thereby a much larger divesity space is created
SAR guided optimization of potency
- Functional groups roles in roles are examined and can be changed to determine their contribution towards binding
- general focus is to define a chemical class with a tractable SAR relationship, develope new IP, develop suitable ADME and PK parameters from early proof of concept experiments in cellular and animal models
Ways in which to modify hits
- Modify the periphery, functionalize so groups can easily be attatched
- Modify the core
Chemical Modifications which can be used to improve potency
- Increasing SP3 content- improves selectivity (but adds chirality) and solubility
- Cyclisization, conformational lock: Pharmacophores are held into place
Steric Bias i.e. adding a methyl group to select for the more potent conformer
Systematic exposure
Desires: 10-20 h which aproximates 3-7 hours in rat ans 2-4 in mouse
Improving permeability
- Remove ionic groups/modulate pKa
- Reduce PSA
- Increase LogP (only if very low)
- Retain solubility
Short Half-Life
- Verify Clearance: metabolism or transport: renal/liver/other
- Determine metabolite ID via LCMS
- Biosteric replacement
- Reduce LogP
Testing Solubility
Kinetic Solubility: Concentration at which a drug (added as DSMO) solution begins to ppt from aq buffer solution (pH = 6.5)
Testing Permeability
Note: Papp-BA/Papp-AB > 2 => PGP substrate

Phase 1 enzymes
- CYP-p450
- FMO
- MOA
- Esterases and amidases
- Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Phase 2 enzymes:
- UGT
- ST
- Acetyl- Transferase
- Gluthathione-S-Transferase
Aromatic Oxidation
Remedy: Replace H with F (bioistere) or CH with N

Methy and Alkyl group oxidation
Remedy: Flouro-bioestere or deuterium

Ester/Amide hydolrysis

Dealkylation

Vd
Increasing Vd will increase (T1/2)
Anionic drugs: Show high plasma protein binding, are confined to body water
Neutral drugs: Show even distribution: moderate Vd, increases with lipophilicity
Basic Cationic Drugs: Show high tissue binding: High Vd > 8 L/kg
To improve Vd, acid/anions can be replaced with higher pKa biosteres


