Histology of the Liver & Pancreas Flashcards
What are the primary functions of the liver?
- metabolism
- glucose regulation, storage as glyogen
- lipid metabolism - synthesis of cholesterol, triglycerides, phospholipids
- absorption of fats
- bile secretion into the gallbladder
- protein synthesis
- plasma proteins, lipoproteins
- storage
- iron, some vitamins
- detoxification
- peptide hormines, steroids, catecholamines, toxins/drugs, alcohol
What are the features of hepatocytes?
- prominent RER, Golgi complexes, and secratory vesicles involved in protein synthesis
- prominent SER for metabolism of fat and steroids
- many mitochondria
- often more than one nucleus

The lifespan of a hepatocyte is
~150 days
Hepatocytes are organised into
lobules, with portal triads around the edge and a central vein in the middle
Hepatocytes are supported by
reticular fibres of collagen types I & III
What is in the portal triads?
- branch of hepatic artery
- branch of hepatic portal vein
- bile duct
- lymphatic

What is a central vein?
- centre of lobules
- convergence of sinusoids (capillaries)
- carries blood to the hepatic vein and out of the liver

What are sinusoids?
- capillary network arising from hepatic vein and artery
- surround rows of hepatocytes
- blood flows from sinusoids to central vein (middle of lobule)
- carry 20% oxy and 80% deoxygenated blood

What are the features of sinusoids?
- two-way communciation between hepatocytes and bloodstream
- larger than other capillaries
- discontinuous lining
-
space of Disse - gap between endothelium and adjacent hepatocyte
- microvilli on surface of sinusoidal endothelium (lumen of sinusoid)
- Kupfer cells - macrophages on inner walls of sinusoids

What is the classic lobule model?
- centre is central vein
- triads in periphery
- focus on direction of blood flow from each of the triads into the central vein

What is the portal lobule model?
- centre is portal triad
- central veins in periphery
- focuses on direction of bile flow from the central vein toward the portal triad

What is the acinar lobule model?
-
physiological context where different zones have different oxygenation and metabolic function
- Zone 1 is high in O2, high in toxins, high in nutrients (near portal triad)
- Zone 3 is low in O2, low in toxins, low in metabolites (near central veins)

Bile salts are synthesized from
cholesterol
Bile is synthesized by
hepatocytes
Bile salts allow for the absorption of
fats and fat-soluble vitamins
Bile salts are reabsorbed in the
small intestine (ileum)
What are bile pigments?
breakdown products of haemoglobin, etc.
What is the function of canaliculi?
collects bile from hepatocytes
carries it to bile ducts in the portal triads

What percentage of water and salts is resorbed in the gallbladder?
90%
What is the function of cholecystokinin?
- release into blood stimulated by fat in the duodenum
- CCK causes the gallbladder to contract, and the sphincter of Oddi to relax
- bile is released into the duodenum

The gallbladder is lined by what cell type?
simple columnar epithelium - absorptive
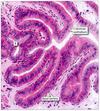
What is the exocrine function of the pancreas?
- release of pancreatic fluid
- contains enzymes for digestion: proteases, lipases, amylases, nucleases
- and bicarbonate ions (neutralize stomach acid)

What is the structure of the exocrine pancreas?
- basal region w/high density of RER (dark purple)
- lumenal region w/numerous zymogen granules containing inactive digestive enzymes (light pink)
- not two types of cell
What is the structure of pancreatic exocrine glands?
- pancreatic glands from from acini
- the lumenal portion of the acinus stains pink (contains proenzymes)
- faces tubule that drains acinus
- the basal portion of the acinus stains blue/purple (contains +RER)
- faces outside pancreatic gland

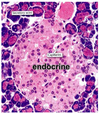
What is the function of the endocrine pancreas?
- comprise only 1-2% of total pancreas volume
- 1m clusters of hormone-secreting cells called islets of Langerhans
- secrete insulin and glucagon for glucose and energy metabolism into rich vascular supply
- stain paler than surrounding exocrine zones