histology images - julia Flashcards
1
Q

A
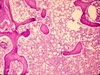
- granulomas in lung due to TB
- glassic giant cells
- ringed by lymphocytes
- sometimes focalized necrosis
- epitheliod histeocytes (activated macrophages that look like epithelial cells)
2
Q

A
- erythrobastosis fetalis
- liver
- contains lots of erythroblasts cause body is trying to make as many RBCs as possible so using every organ it can
2
Q

A
- small vessel vasculitis in lung
- type III hypersensitivity response
- usually due to drug response/reaction
- called microangitis or microvasculitis
2
Q

A
- joint of RA patient
- low magnification (middle) shows synovial hypertrophy with formation of villi
- higher magnification (right) shows subsynovial tissue containing dense lymphoid aggregate
2
Q
A
- healthy bone marrow
- not lots of cells, little fat
2
Q

A
- liver stained with congo red and viewed under polarized light in patient with amyloidosis
- amyloid is the bright yellow/green areas
2
Q

A
- metastasizing sarcoma in lymphatic vessels in lung
- not metastesized yet because not out of lymphatic vessel and established in lung tissue
- shouldn’t be cells in lymphatics
- cells in lymphatics are abnormally structured, darkly stained, pleomorphic
- center of slide is normal alveolar structure of lung
2
Q
A
- pancreatic adenoma
- occurs 6-12 months into development of cancer
- still benign cause confined to basement membrane
- cells smaller, densely packed in comparison to normal cells
- normal cells on the edge
- enlargement of previous hyperplastic nodule
3
Q

A
- colon of patient with amyloidosis
- congo red stain
- the amyloid plaque is the bright area in teh middle (which looks yellow to me but should be granny smith apple green)
- overall, congo red stains the tissue red, but if you look at it under polarized light, the dye will act as a lens if it’s attached to amyloid and will therefore reflect in the green spectrum
4
Q

A
- adenocarcinoma of lymph node
- not normal archetecture - very complex
- nuclei darkly stained
- hyperchromasia
4
Q

A
- cervix with lesion
- darkly stained, crowded nuclei all the way through the top
- no layers
- increase in mitotic figures
- atypical cells involved through the full thickness of epithelium but doesn’t invade through the basement membar so not invasive
5
Q

A
- heart with amyloidosis
- cardiac myocyte on left
- asterisk indicates amyloid fibril deposition in space between myocytes
*
6
Q

A
- acute cellular rejection in kidney
- type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- lymphocytes in renal parenchyma
- dard spots in tubules = lymphocytes infiltrating
6
Q

A
- gut (probably colon)
- can see calonic crypts and smooth muscle (muscularis mucosae)
- in middle, though, there’s a paler pink area - this is deposition of amyloid in patient with amyloidosis
- in GI tract, usually develops in and around submucosal vessles first
- therefore need adequate amounts of submucosal tissue to rule out amyloidosis using biopsy
7
Q

A
- lung of asthmatic patient
- smooth muscle hypertrophy - cells surrounded by white circles
- thickend basement membrane - should only be a thin red line
- lots of peribronchiolar inflammation
- ring aroung bronchial = chronic inflammation (includes lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, mast cells, eosinophils
7
Q

A
- pancreas in type I diabetes
7
Q

A
- uterus
- leiomyoma
- tumor cells very uniform
- On left compressed myometrium
- Large mass on the right (everything after white area) is tumor
- On higher power they’d look similar
- Very well demarkated, circumscribed
- Well differentiated because so uniform and can identify it as smooth muscle
- Can tell its benign because so well differentiated, among other things
- Also look for increase in mytotic figures – if 4 mytoses per field likely malignant (don’t need to know this)
9
Q

A
- kaposi’s sarcoma lesion in AIDS patient
- dermis has dense cellular infiltrate, narrow slit-like vascular spaces
- disorganized, haphazard, dense
9
Q

A
- normal larynx
- normal maturation
- more crowded in basal layer
- basement membrane (darker layer) intact
9
Q

A
- gastric adenocarcinoma (ulcerated)
- bottom left is normal
- above that have an irregular boarder that’s not circumscribed
- overgrowth of glandular structure and complex archetecture implies invasive
10
Q

A
- glomeruli filled with amyloid in patient with amyloidosis
- bit more subtle
- can see aggregates in mysangium though
- agregates are the smooth light pink areas
10
Q

A
- pulmonary hamartoma
- mass of normal lung elements that are fully differentiated but not where they should be and not functional
- popcorn calcification
11
Q

A
- invasive pannus in patient with RA
- I’m assuming that this is in a joint…
11
Q

A
- ulceration tumor at illiocecal junction
- top has normal mucosa, normal polarity
- bottom has lost polaritiy
- glandular structure in submucosa - shouldn’t be there - invasive
12

* liver stained with congo red in patient with amyloidosis
* the amyloid is stained dark red here
* this is under normal light (not polarized, where the amyloid would be green)
* should be able to tell that this is liver
* amyloid depostied around blood vessel walls, in sinusoids
13

* graft atherosclerosis
* chronic graft rejection secondary to extensive damage to endotehlium and artery wall
14

* GI biopsy in patient with amyloidosis
* all he said about it was that it was "distorted as the devil"
15

* rhabdomyosarcoma in skeletal muscle
* bottom of image has normal skeletal muscle
* top has sarcoma
* cells don't look like skeletal muscle anymore - overgrown, darkly stained, nuclear size much bigger, not normal archetecture of tissue
16

* heart from patient with amyloidosis
* balnd cellular pinkish stuff = amyloid deposits
* can tell it's not collagen because there's not a lot of fibroblasts (but should use congo red stain to be sure)
17

* granuloma in lymph nodes
* due to type IV hypersensitivity reaction
* giant cells
* sarcoidosis
18

* interstitial pneumonitis (inflammation of lung) in RA
19

* pancreas
* adenocarcinoma invading duodenal muscularis
* glandular archetecture on right, but doesn't have normal archetecture
* invading into muscular layer - should only be in mucosal layer
20

* rheumatic fever vegitations on mitral valve
* chordae tendinae get sticky, shorten, fuse together
* eventually get deformation of the valve
* vegitations form on the flow surface of the valve
21

* chronic graft rejection in kidney
* scarred parenchyma
* occluded vessel
* wouldn't know it's kidney
* focal damage to vessel wall
* lumen so compromised by repeated and longstanding damage there's no lumen left
22

* low grade squamous cell carcinoma
23

* osteosarcoma in bone
* hyperchromatic cells
* mytotic figure in center implies increased mitosis
* pleomorphic
25

* lung
* CMV infection in AIDS patient
* characteristic intranuclear inclusion
* might see in advanced AIDS
27

* inflammatory phase of vasculitis
* type III hypersensitivity
* muscullar blood vessel
* internal elastic lamina is the dark pink squiggly line
* thrombus formation in lumen
* on left side of blood vessel, smooth muscle layer gone
* in small/medium arteries called polyarteritis nerdosa
28
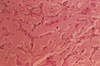
* liver failure due to amyloidosis
* heavy amyloid infiltration (pale pink amorphous material)
* don't need to be able to tell that this was liver - it's too distorted at this point
* not much blood getting in, and sinusoids totally filled with amyloid
29

* stepwise progression of colon dysplasia to adenocarcinoma
* dysplasia on left
* in middle is benign adenoma
* on right is malignat tumor mass invading muscle
* have normal epi on left
30

* necrotic phase of vasculitis
* type III hypersensitivity reaction
* can see a few smooth muscle cells in the bottom right corner of the vessel
* lots of neutrophils and nuclear debris present beyond what would be the endothelium
* thrombosis in vessel lumen
* this thrombosis will lead to ischemia, blood vessel wall destruction will lead to hemorrhage
* in small/medium arteries called polyarteritis nerdosa
30

* biopsy of small intestine from patient with amyloidosis
* can see extensive infiltration by amyloid = homogenous pink hyaline substance
31

* bone marrow after chemo
* lots of empty space cause cells have been killed
32
best diagnosis of this abnormal growth?

dysplasia
34

* SLE in the skin
* top image = liquefactive degeneration of the basal layer of the epidermis and edema at the dermoepidermal junction
* bottom image is an immunoflorscent stain for IgG - can see IgG deposits along dermoepidermal junction
35

* mostly normal pancreatic tissue
* the area in the middle though (slightly lighter) is a focal hyperplasia
* occurs at 1-2 months stage into development of cancer
* mass of abnormal cells with large nuclei, chromatin
36

* ultrastructure of amyloid in heart
* amyloid characterized by non-branching fibrils that are 7 to 10 nm wide
* no matter where deposited or what type of fibers are being made, will get fibrilar strands of processed protein
* forms very insoluble, dense masses between cells
37

* normal lymph node
38

* heart with rheumatic fever
* aschoff giant cell in top left = small with only 5-6 nuclei, not lots of cytoplasm
* anitschkow monocyte in bottom middle = chromatin looks like caterpillar
39

* pancreas in type I diabetes
40

* aschoff body in heart due to rheumatic fever
* where the inflammation in the muscle is
* note no bacteria
42

* tricuspid valve in systemic lupus erythematosis
* darker areas are vegetations
* these consist of sterile fibrin-platelet aggregates
* no inflammation in these vegetations!
43

* kidney with post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
* lots of neutrophils
* basement membrane tends to look a little thicker (he said not to worry about it if you don't see it though)
43

* vasculitis in RA
45

* myocarditis in SLE
46

* bronchus
* dysplasia
* no secreting cells
* darkly stained cells have taken over the entire epidermis
* no layers anymore
* don't appear to be proper cilia anymore
47
what abnormality accounts for the abnormal cell? (star shaped thing in middle)

extra centrosomes
48

* necrotic phase of vasculitis
* type III hypersensitivity
* hard to even know this was a blood vessel - totally necrotic
* in small/medium arteries called polyarteritis nerdosa
49

* squamous cell carcinoma of larynx
* maligant, invasive
* islands of squamous epithelium invading into submucosa (areas surrounded by dark blue line at bottom of picture)
* this is relatively well differentated for a tumor, but has an invasive growth pattern
51

* brain in AIDS patient with toxoplasmosis
* can see intracellular and extracellular tachyziotes of toxoplasma gondii
52

* kidney with post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
* the dark areas that are sort of in a diagonal line running from the bottom left to top right are aggregates of complexes (involving IgG) present just beyond the basement membrane
* these will attract neutrophils
53

* cardiac biopsy in patient with amyloidosis
* the pale pinkish material that seems more homogenous than the rest of the tissue is deposition of amyloid
* the darker pink is cardiac myocytes
55

* borderline papillary cycstic neoplasm of the ovary
* both cycstic neoplasm and a papillary neoplasm
* the islands of projections make it papillary
* borderline so has malignant potential but don't see definitive invasion
56

* normal glomerulus
* note thin-walled capillaries
58

* lung with goodpasture's
* have hemorrhage in alveoli
* can still see defined alveoli
60

* acute cellular rejection
* blood vessel
* type IV hypersensitivity response
* damage to walls
* endothelium almost totally destroyed
* occlusion of lumen - filled with recipient T cells and macrophages
62

* granuloma in lung due to TB
* classic giant cells
* epithelioid histocytes (activated macrophages resembling epithelial cells)
* this is a typical TB granuloma
62

* neoplasm of skeletal muscle
* has cells with both myoid differentiation and anaplastic cells
* can tell that the ones with the green arrow are probably skeletal muscle
* but most of the rest is anaplastic - can't tell what type of cells they are
* would use immunomarkers to confirm diagnosis
* from a mesenchymal tumor
63

* kidney with goodpasture's disease
* linear basement membrane staining with immunoflorescence due to IgG binding in glomerulus
* tubules have a different kind of basement membrane (different type of type IV collegen) so doesn't stain
65

* high grade carcinoma
* hard to tell it was squamous
* have necrosis at bottom (the dark pink surrounded by white)
* abnormal mitosis in middle
* pleoporphism = large purple cell in top left
66

* immunoflorescent stain of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
* granular "lumpy-bumpy" basement membrane staining due to IgG-antigen deposits
* non-linear localization of glomeruli
* aggregated antibody
68

* lung with goodpasture's
* immunoflorescent stain for IgG
* binds to type IV collagen in alveolar wall basement membranes
69

* multiple hyperplastic nodules in pancreas
* occurs 4-6 months into development of cancer
70

* invasive ductal carcinoma in breast tissue
* has ductal structure, but haphazardly
71

* subcuteaneous rheumatoid nodule in RA patient
* area of necrosis surrounded by palisade of macrophages and scattered chronic inflammatory cells
73

* acute graft rejection (type IV hypersensitivity response)
* in parenchyma
* stained for surface antigens of T cells
* this type of reaction is almost exclusively t cells
74
which feature best characterizes the dysplastic epithelium? (actinic keratosis)

loss of polarity
75

* joint in RA patient
* synovitis (inflammation of synovial membrane)
76

* hepatic amyloidosis
* sinusoids distended
* hepatocytes pushed out of the way
* moderate amyloid infiltration
77

* cerebral amyloid angiopathy
* reddish material around blood vessels is amyloid deposits
* probably a congo red stain
78

* acinar cell carcinoma in pancreas
* occurs after 1-2 years
* irregular nuclei
* clumped chromatin
* mitosis and some atypical mitosis (usually don't see any mitosis in the pancreas)
80
most likely diagnosis?

melanoma
82

* tonsil with benign squamous papilloma
* Circumscribed lesion = benign neoplasia
* Bottom is what normal squamous cell epithelium should look like
* Section from top is from tumor – papillary archetecture
* Dark blue line at bottom is basement membrane – can see that it’s intact so no invasion into surrounding tissue
* Well differnetiated, no invasion, so features of benign
83
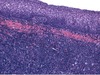
* normal tonsil
84

* lung with pneumocystis carinii infection in AIDS patient
* giemsa stain
* this type of infection won't occur until T lymphocyte count gets below 200
85

* normal pseudostratified cells in bronchus
* dividing stem cells
* mixture of cell populations
* cilia
86

* colonic adenocarcinoma invading muscularis layer
* look at arrangement of nuclei - don't have polarity
* very complex and crowded and highly nuclear cells
* hyperchromasia
* pleomorphism
87

* antibody-mediated blood vessel damage
* type IV hypersensitivity (graft rejection)
* blood vessel has been killed
* endothelial cells basically all dead
* wall damaged
* example of donor blood vessel killed by host antibodies
88

* fish-mouth deformation of aortic valve due to rhemuatic fever
* edges of valve should be three leaflets
* here they've fused together and there's only a narrow appeture
89

* congo red stain of CNS parenchyma
* patient with amyloidosis
* vessels are a little bit thickened
* not imaged with polarized light, so the amyloid appears dark red rather than green
90
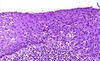
* cervix with dysplasia
* on the left, neraly normal cervix
* on left CIN 1
* on right CIN 3 - can see the atypical cells higher up in the layer
91
what cytologic feature best defines this lesion as malignant?

pleomorphism
92

* bone marrow in patient with multiple myeloma
* note the abundance of plasma cells - identifiable by their clock-face nuclei and perinuclear hoff
93

* kidney with post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
* note neutrophils in glomerular tufts
* lots of neutrophils
* basement membrane a bit thicker than it should be
94

* example of amyloid stained by congo red and examined under polarized light
96

* glomeruli filled with amyloid in patient with amyloidosis
* can see that the regular glomerular elements are totally pushed aside in some of these glomeruli
97
this cancer has not yet acquired which malignant capacity?

angiogenesis
98
best diagnosis?

well differentiated SCC
99

* lymph node in patient with AIDS
* mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection
* lots of acid-fast bacilli (cord-like accumulations) within histiocytes
100
populations of cells give evidence of?

clonal progression
101
nucleus indicated by arrow illustrates which malignant cytologic feature?

hyperchromasia
102

* normal cervix
* can see normal maturation
* basal layer is more crowded
* all nuclei are similar


