histo from aaron Flashcards
1
Q

A
- Ileum
- A is Peyer’s patch, lymphatic tissue to protect against bacterial invasion.
- The structure is a villus.
2
Q

A
- Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
- Hyaline cartilage.
- Trachea.
3
Q

A
Eye. A Ganglion cells, B bipolar cells, C rods and cones.
4
Q

A
- A is simple columnar,
- B simple squamous.
- This is the cardiac sphincter.
5
Q

A
- A and B are from the thyroid.
- The whole structure A is the thyroid follicle, filled with colloid, and surrounded by simple cuboidal epithelium.
- It releases T3 and T4 that control basal metabolic rate.
- B are extrafollicular cells that secrete calcitonin to decrease calcium concentrations in the blood.
- C is the parathyroid gland, secretes parathyroid hormone to increase calcium concentrations in the blood.
6
Q

A
- Stomach,
- simple columnar,
- gastric pits with parietal, chief, and mucus neck cells.
7
Q

A
- Cardiac muscle
- in heart
- mononucleated, branched, intercalated disks.
- Intercalated disk, resists strain in heart muscle, connects muscle cells’ cytoplasm for simultaneous contraction
8
Q

A
- Testes.
- Cells of Leydig, secrete testosterone.
- Seminiferous tubule, make sperm
9
Q

A
- Kidney.
- A is Simple cuboidal epithelium with microvilli
- *note microvilli help increase reabsorption/secretion in PCT and DCT.
- B is glomerulus within Bowman’s capsule, filtration.
10
Q

A
scala vestibuli and scala tympani, perilymph. Cochlear duct, endolymph.
A is Organ of Corti
B is Basilar, C vestibular, D tectorial
11
Q

A
- Transitional epithelium in ureter, renal pelvis, or bladder,
- need in places that have liquid for expansion.
12
Q
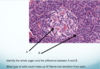
A
- Pancreas. A is islets of Langerhans (endocrine) and B is acinar cells(exocrine)
- A could be alpha or beta cells. Alpha cells secrete glucagon, beta cells insulin
13
Q

A
- Jejunum
- lack of Brunner’s glands and Peyer’s patches.
14
Q

A
- Esophagus
- A is stratified squamous epithelium,
- B is a submucosal mucus gland,
- 1st third of the esophagus is skeletal muscle,
- 2nd third is mixed,
- last third is only smooth muscle
15
Q

A
- Light staining is neurohypophysis, because of the lack of nuclei in the axons of the hypothalamic neurons that control this area, secretion is ADH and Oxytocin.
- Dark is adenohypophysis, because lots of nuclei and proteins, secrete trophic hormones like ACTH and TSH.
- Adenohypophysis is controlled by the hypothalamus through the hypophyseal portal veins.
16
Q

A
- Graafian follicle
- releases oocyte to ovarian duct.
- Estrogen and progesterone.
- 28 days.
17
Q

A
- Liver
- hepatic lobule.
- Central vein, drains to hepatic vein and then inferior vena cava.
- 3 structures are bile duct, branch of hepatic portal vein, and branch of hepatic artery.
18
Q

A
- Salivary gland, dark staining means protein rich acinar cells.
- Tubes increase in size and change epithelium as they collect more and more fluid.
- Tubes start as simple cuboidal epithelia and change to simple columnar as the tubes get bigger.
- Amylase is a classic enzyme made in the acinar cells that breaks down starch in your mouth.
19
Q

A
Lots of bacteria, so it needs lymphatic tissue to protect it.
20
Q

A
- Tongue.
- A is a taste bud on the larger papillae.
- Skeletal muscle, move your tongue voluntarily
21
Q

A
- Oocyte in the ovary.
- Zona pellucida,
- protects egg and during fertilization only allows one sperm to enter egg.
22
Q

A
- Duodenum
- A is Brunner’s glands, secrete buffer to counteract acid from stomach.
- The feature of absorption is microvilli.
23
Q

A
- A is red blood cell,
- B is lymphocyte.
- A has no nucleus, B does.
24
Q

A
sperm
25
Q

A
- Adrenal gland. A,B,C are the cortex, D is the medulla.
- A is the zona glomerulosa (aldosterone secretion).
- B is the zona fasciculata (cortisol secretion).
- C is the zona reticularis (androgen secretion).
- D secretes mainly epinephrine (some norepinephrine).


