High yield Flashcards
(12 cards)
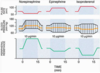
Label the agents for A-C

A) Norepinephrine
B) Epinephrine
C) Isoproterenol
What are the effects of epinephrine on skeletal muscle, mediated by which receptors?
- Causes muscle tremor (β2)
- Increases K+ uptake by skeletal muscle (β2) = promotes HYPOkalemia and decreased K+ excretion by kidneys
What are the effects of epinephrine on blood glucose, fatty acid levels and renin?
- Elevates blood glucose levels –> enhances liver glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (β2)
- Increases free fatty levels in blood
- Increases renin release (β1)
What are the major effects of norepinephrine?
- Potent cardiac stimulant BUT reduces HR
- Potent vasoconstrictor
- Increases peripheral vascular resistance and BP; decreases pulse rate

What are the adrenergic receptor types found in the vascular beds of the skin vessels/mucous membranes, skeletal muscle, renal, and cerebral?
- Skin vessels and mucous membranes (α1)
- Skeletal muscle (α1 and β2)
- Renal, cerebral (D1 and α1)
Clonidine acts on which receptors and produces what effects?
- SELECTIVE α2 agonist
- Central effect on α2 receptors in the lower brainstem area –> decrease sympathetic outflow, reduction in BP, BRADYCARDIA
*Guy holding claw weapons w/ 2 lit candles!
Which adrenergic receptors are activated at low doses vs. high doses of Dopamine?
What are the effects?
- At low doses β1 receptors are activated (cardiac activation)
- At high doses α1 receptors are activated (pressor effects)
*Remember D-B-A*
Tyramine is found where?
What is the MOA when administered parenterally and how is it metabolized?
- Found in cheese, cured meats, and smoked/pickled fish
- Releases stored NE from presynaptic adrenergic terminals (if administered parenterally)
- Metabolized by MAO in liver (may lead to increased BP in pt’s taking MAO inhibitors)
What is the MOA of Metyrosine?
Inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase; prevents conversion of tyrosine –> L-DOPA
What is the MOA of Guanethidine?
Prevents storage, depletes NE
Which 2 drugs are used in the treatment of chronic urinary retention associated with BPH?
Which receptor do they target?
- Tamsulosin and Silodosin (α1 selective antagonists)
- Greater selectivity for α1A = most important α receptor subtype mediating prostate smooth muscle contraction
How does the (-) isomer of Dobutamine differ from the (+) isomer in its effects on α1 receptors?
- Dobutamine is a selective β1 agonist
- Has some α1 activity: the (-) isomer is an agonist at these receptors and the (+) isomer is an α1 antagonist


