Hersh CIS Pneumo Flashcards
no cell wall
causes microcytic anemia

mycoplasma pneumonia
Hyponatremia
- Legionella
Positive urinary antigens
– S. pneumo and Legionella

mycoplasma pneumonia
similar in presentation to Mycoplasma but with a hoarse voice!!!
Chlamydia pneumoniae – similar in presentation to Mycoplasma, hoarse voice!!!
Fevers, chills, cough (may be dry), dyspnea (typically with exertion)
CAP atypical pneumonia (legionelle, chlymedia, mycoplasma pneumonia)
Follows URI like sx
CAP atypical penumonia
Follows URI like sx: rhinitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis
EMPIRIC ABX FOR CAP: ambulatory
macrolide (azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin)
- EMPIRIC ABX FOR CAP in pt w/ncreased risk for drug resistance due to
- having Abx in the past 90 days
- immunosuppression
- exposure to kids
FLUOROQUINOLONE OR MACROLIDE + beta-lactam
EMPIRIC ABX FOR CAP: hospitalized patients
Hospitalized Patients – FLUROQUINOLONE
EMPIRIC ABX FOR CAP: ICU pts
- ICU
- Combo of
- FLUROLOQUINOLONE
-
antipneumococcal beta lactam
- 3rd gen cephalosporin or ampicillin sulbactam
- Add piperacillin-tazobactam, cefipime, or a “penem” for Pseudomonal coverabe
- Combo of
EMPIRIC ABX FOR CAP: ICU pts needing pseudomonal coverage
- ICU:
- FLUROLOQUINOLONE + antipneumococcal beta lactam (3rd gen cephalosporin or ampicillin sulbactam)
- Add piperacillin-tazobactam, cefipime, or a “penem” for Pseudomonal coverabe
How do you know what to do with a pt presenting with symptoms of pneumonia?
CURB65
- Confusion = 1 pt
- Blood Urea nitrogen > 20 mg/l = 1 pt
- Respiration >/= 30 breaths/min
- Blood pressure = 1 pt
- systolic < 90 mmHg
- diastolic = 60 mmHg
- Age >/= 65 = 1 pt
Score
0-1 = low risk, outpatient
2 = moderate severity: short impatient hospitalization or closely supervised outpatient tx
3-5 = severe pneumonia: hospitalization required, consider ICU admission
gram negative bacillus (pleomorphic), aerobic, flagellate: what will i grow on?
legionelle
Legionella pneumophilia – gram negative bacillus (pleomorphic), aerobic, flagellate, water lover, urinary antigen
buffered charcoal yeast extract agar
gram negative bacillus, encapsulated, pyocyanin and pyoverdine, smells like grapes, water lover, colonizer in CF and bronchiectasis.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
gram negative diplococci, encapsulated (typeable) or no capsule (non-typeable), Chocolate agar (factors V and X), smokers, immunocompromised.
Haemophilus influenzae
gram negative diplococci, encapsulated (typeable) or no capsule (non-typeable), Chocolate agar (factors V and X), smokers, immunocompromised.
gram negative DIPLOCOCCUS
fastidious, aerobic. Big time for smokers, COPD, asthmatics, malignancies. Generally exacerbates predisposing conditions and then forms a PNA
Moraxella catarrhalis
– gram negative coccobacillus, fastidious, aerobic. Big time for smokers, COPD, asthmatics, malignancies. Generally exacerbates predisposing conditions and then forms a PNA
positive Thompson test, difficulty walking, pain behind ankle
levofloxacin
MacConkey agar
What the dickens is MacConkey agar??
- Selects for G(-) bacteria, especially enteric bacteria!
Has bile salts and crystal violet in the media: these select for Gram negative bacteria only.
Also, has LACTOSE which selects for fermenters
ENCAPSULATED, gram negative, ferments lactose, grows in mucoid colonies. Bulging fissure, currant jelly sputum, immunocompromised and EtOH.
Klebsiella pneumoniae
– ENCAPSULATED, gram negative, ferments lactose, grows in mucoid colonies. Bulging fissure, currant jelly sputum, immunocompromised and EtOH.
IS gram negative, but not a lactose fermenter. Additionally, SEVERE pt presentation: fever, headache, weakness, chest pain, dyspnea, pulmonary hemorrhages (bloody sputum)
Yersinia pestis – IS gram negative, but not a lactose fermenter. Additionally, SEVERE pt presentation: fever, headache, weakness, chest pain, dyspnea, pulmonary hemorrhages (bloody sputum)
Fast Fermenters
Fast Fermenters: “Lactose? OH-KEE!!!!”
KEE: Klebsiella, E. coli, Enterobacter
Slow Fermenters:
CS
Citrobacter, Serratia
atypical, no cell wall, extracellular, bullous myringitis, cold agglutinins, scattered pulmonary infiltrates (if anything), younger pts, generally self-limiting, dry cough
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – atypical, no cell wall, obligate intracellular, bullous myringitis, cold agglutinins, scattered pulmonary infiltrates (if anything), younger pts, generally self-limiting, dry cough
gram positive diplococci, encapsulated, alpha hemolytic, optochin sensitive, urinary antigen, lobar PNA, MOST COMMON CAUSE OF CAP (and meningitis). Sick patients: fevers, chills, cough, rust colored sputum, dyspnea, and weakness.
Streptococcus pneumoniae – gram positive diplococci, encapsulated, alpha hemolytic, optochin sensitive, urinary antigen, lobar PNA, MOST COMMON CAUSE OF CAP (and meningitis). Sick patients: fevers, chills, cough, rust colored sputum, dyspnea, and weakness.
gram negative, non-lactose fermenter, buffered yeast charcoal medial, lover of water systems, hyponatremia, relative bradycardia, can affect multiple people at same time
Legionella pneumoniae – gram negative, non-lactose fermenter, buffered yeast charcoal medial, lover of water systems, hyponatremia, relative bradycardia, can affect multiple people at same time
gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive, known to follow viral pneumonia, necrotizing, pulmonary hemorrhages, salmon colored sputum.
Staphylococcus aureus
– gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive, known to follow viral pneumonia, necrotizing, pulmonary hemorrhages, salmon colored sputum.
encapsulated gram negative, lactose fermenter, mucoid colonies, currant jelly sputum….
Klebsiella pneumoniae – encapsulated gram negative, lactose fermenter, mucoid colonies, currant jelly sputum….you can fill in the rest!
vaccination against capsular polysaccharide antigens of 23 strains
Pneumovax – against capsular polysaccharide antigens of 23 strains
vaccination protective against 13 strains
Prevnar 13
Prevnar 13 – protective against 13 strains
who gets the pneumococcal vaccine? what are C/I? when is it administered?
Age ≥65, immunocompromised, asplenic patients, pts 2-64 for risk factors
Contraindications: serious allergic reaction to previous vaccination (anaphylaxis)
**Hold off on vaccination until your patient’s are better!!!
Gram (-) encapsulated organism that produces pyocyanin
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
G+ diplococci (lancet shaped), rust colored sputum, lobar PNA
Streptococcus pneumoniae – G+ diplococci (lancet shaped), rust colored, lobar PNA
no cell wall, extracellular, bullous myringitis, anemia, cold agglutinins, younger adults
Mycoplasma pneumoniae - no cell wall, extracellular, bullous myringitis, anemia, cold agglutinins, younger adults
gram negative rod, CF, bronchiectasis, green (pyocyanin and pyoverdine), grape smelling, encapsulated, biofilms (alginate)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa – gram negative rod, CF, bronchiectasis, green (pyocyanin and pyoverdine), grape smelling, encapsulated, biofilms (alginate)
a gram negative coccobacillus that grows on chocolate agar
Haemophilus influenza
non-enveloped, dsDNA, icosahedral virus.
Common cold
viral keratoconjunctivits
conjunctivitis
pharyngitis
Can cause overlapping symptoms.
Viral Cx standard, can use direct assay or enzyme immunoassay.
Adenovirus – non-enveloped, dsDNA, icosahedral virus. Common cold, viral keratoconjunctivits, conjunctivitis, pharyngitis. Can cause overlapping symptoms. Viral Cx standard, can use direct assay or enzyme immunoassay.
Sx: fevers, chills, myalgias, HA, nasal stuffies, coryza, nonproductive cough. Fever >38C, LAD. diffuse pneumonitis and hypoxemia. Leukopenia.
A. Orthomyxovirus – 8 segmented (-)ssRNA, Hemagluttinin and Neuriminadase spikes. Sx: fevers, chills, myalgias, HA, nasal stuffies, coryza, nonproductive cough. Fever >38C, LAD. Can cause diffuse pneumonitis and hypoxemia. Leukopenia is common. Rapid Flu is suboptimal. PCR is preferred. ***REYE SYNDROME – don’t give ASA to kids!
ssRNA. Fever, cough, dyspnea, GI sx (diarrhea, ab pain). Fecal-oral transmission. Travel to ME, esp Saudia Arabia. Thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia/cytosis, transaminitis. SEVERE – ARDS presentation.
C. MERS – Coronavirus, ssRNA. Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome. Fever, cough, dyspnea, GI sx (diarrhea, ab pain). Fecal-oral transmission. Travel to ME, esp Saudia Arabia. Thrombocytopenia, lymphopenia/cytosis, transaminitis. SEVERE – ARDS presentation.
Travel to China, Hong Kong, Taiwan. Initial flu-like sx and can progress rapidly to ARDS. Cough, difficulty breathing, severe hypoxia.
SARS – Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Coronavirus. Travel to China, Hong Kong, Taiwan. Initial flu-like sx and can progress rapidly to ARDS. Cough, difficulty breathing, severe hypoxia.
similar to orthomyxo, history of exposure to dead or sick poultry. Fever (prolonged), cough, dyspnea. RT-PCR. Start with OSELTAMIVIR (same for prophylaxis after exposure)
H5N1
– similar to orthomyxo, history of exposure to dead or sick poultry. Fever (prolonged), cough, dyspnea. RT-PCR. Start with OSELTAMIVIR (same for prophylaxis after exposure)
gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive, necrotizing PNA, golden colony growth, follows flu.
S. aureus – gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive, necrotizing PNA, golden colony growth, follows flu.
- Histoplasmosis
- microconidia found in caves with bat/bird droppings.
- Dimorphic yeast in body, fungi in natural environment.
- Narrow-based budding.
- Mild PNA unless immunocompromised, chronic course.
- Most resolve on their own.
- Prevalent in: Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River Valleys. Lesions calcify on CXR (coin lesion)

- Histoplasmosis –
- microconidia found in caves with bat/bird droppings.
- Dimorphic yeast in body, fungi in natural environment.
- Narrow-based budding.
- Mild PNA unless immunocompromised, chronic course.
- Most resolve on their own.
- ***Prevalent in: Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River Valleys. Lesions calcify on CXR (coin lesion)

Coccidioidomycosis (C. immitis – Valley Fever) – chronic PNA, fungi spherule with endospores, dimorphic, prevalent in Southwest (CA, NM, AZ, San Juaquin River Valley).
Some will develop painful erythematous nodular lesions – ERYTHEMA NODOSUM. Self-limiting

a fungus caused this on a patient in the southwest

Coccidioidomycosis (C. immitis – Valley Fever)
– chronic PNA, fungi spherule with endospores, dimorphic, prevalent in Southwest (CA, NM, AZ, San Juaquin River Valley). Some will develop painful erythematous nodular lesions
– ERYTHEMA NODOSUM. Self-limiting
chronic PNA, soil with decomposing matter (leaves, wood), BROAD BASED BUDDING YEAST.
Can cause SKIN, BONE, and NEURO changes.
Blastomycosis (Blastomyces dermatitidis) – chronic PNA, soil with decomposing matter (leaves, wood), BROAD BASED BUDDING YEAST. Can cause SKIN, BONE, and NEURO changes.

Blastomycosis (Blastomyces dermatitidis) – chronic PNA, soil with decomposing matter (leaves, wood), BROAD BASED BUDDING YEAST. Can cause SKIN, BONE, and NEURO changes.
FLU PREVENTION: who, vaccine, C/I
recommended that all persons over the age of 6 months of age be vaccinated!
Inactivated influenza virus
Contraindications: previous allergic reaction, egg allergy (there are alternatives), Guillan-Barre within 6 weeks of previous flu vax.
microconidia found in caves with bat/bird droppings. Dimorphic – yeast in body, fungi in natural environment. Narrow-based budding. Mild PNA unless immunocompromised, chronic course. Most resolve on their own. ***Prevalent in: Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River Valleys. Lesions calcify on CXR (coin lesion)
Histoplasmosis – microconidia found in caves with bat/bird droppings. Dimorphic – yeast in body, fungi in natural environment. Narrow-based budding. Mild PNA unless immunocompromised, chronic course. Most resolve on their own. ***Prevalent in: Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River Valleys. Lesions calcify on CXR (coin lesion)
chronic PNA, fungi spherule with endospores, dimorphic, prevalent in Southwest (CA, NM, AZ, San Juaquin River Valley). Some will develop painful erythematous nodular lesions – ERYTHEMA NODOSUM. Self-limiting
Coccidioidomycosis (C. immitis – Valley Fever) – chronic PNA, fungi spherule with endospores, dimorphic, prevalent in Southwest (CA, NM, AZ, San Juaquin River Valley). Some will develop painful erythematous nodular lesions – ERYTHEMA NODOSUM. Self-limiting
chronic PNA, soil with decomposing matter (leaves, wood), BROAD BASED BUDDING YEAST. Can cause SKIN, BONE, and NEURO changes.
Blastomycosis (Blastomyces dermatitidis) – chronic PNA, soil with decomposing matter (leaves, wood), BROAD BASED BUDDING YEAST. Can cause SKIN, BONE, and NEURO changes.
Culture results from sputum, blood, and urine demonstrate a Gram-negative, aerobic, catalase positive, bacillus that flourishes on BC agar. The organism does not ferment lactose…
Burkholderia cepacia –
G(-) bacillus
catalase positive, non-lactose fermenter.
Grows on BC agar (has crystal violet and bile salts – colonies are pearly gray).
Also colonizes CF pts (or with bronchiectasis) and is found on hospital equipment and irrigation systems.
VERY HARD TO TREAT, MULTI-ABX resistant
G(-) bacillus, oxidase positive, catalase positive, aerobic, pyocyanin/pyoverdine, non-lactose fermenter.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa – G(-) bacillus, oxidase positive, catalase positive, aerobic, pyocyanin/pyoverdine, non-lactose fermenter.
Gram (-) bacillus, encapsulated, anaerobic, EtoH, currant jelly sputum, mucoid colonies, bulging fissure, lobar or necrotizing.
Klebsiella pneumoniae – Gram (-) bacillus, encapsulated, anaerobic, EtoH, currant jelly sputum, mucoid colonies, bulging fissure, lobar or necrotizing.
Gram (-) coccobacillus, chocolate agar, encapsulated
Haemophilus influenza – Gram (-) coccobacillus, chocolate agar, encapsulated
gram (-) bacillus, lactose fermenter, oxidase negative, anaerobic. Opportunistic, mechanical ventilaltion. Coliform bacteria. MOTILE!!!
Enterobacter- gram (-) bacillus, lactose fermenter, oxidase negative, anaerobic. Opportunistic, mechanical ventilaltion. Coliform bacteria. MOTILE!!!
… exposure to infected rodents via urine, feces, saliva. Prodromal phase mimics many flu-like syndromes. Rapidly progresses to Hanta CP (cardiopulm) syndrome with RESPIRATORY Distress. Look for clues in History!!!
Labs: Thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, elevated LDH, pulmonary infiltrates B/L
Bunyavirus – HANTAVIRUS.
Zoonotic, exposure to infected rodents via urine, feces, saliva. Prodromal phase mimics many flu-like syndromes. Rapidly progresses to Hanta CP (cardiopulm) syndrome with RESPIRATORY Distress. Look for clues in History!!! Labs: Thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis, elevated LDH, pulmonary infiltrates B/L
ABRUPT high fever, HA, myalgias. Fevers and sx last through duration of illness. May have mild PNA or rapidly progress to respiratory distress. Hepatitis with no jaundice, acute endocarditis, maculopapular rash. Leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia.
Coxiella burnetti –
obligate intracellular. Small, gram-negative. Has ENDOSPORE ABRUPT high fever, HA, myalgias. Fevers and sx last through duration of illness. May have mild PNA or rapidly progress to respiratory distress. Hepatitis with no jaundice, can cause acute endocarditis, maculopapular rash. Leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia. Think shepherds, farmers, cattle birthers.
flu symptoms, rapid antigen detection, 8 segmented RNA.
Orthomyxovirus – flu symptoms, rapid antigen detection, 8 segmented RNA.
fevers, HA, Aseptic meningitis (possible meningeal signs), severe myalgias.
Hepatitis with jaundice,
enal failure with nephritis, subconjunctival hemorrhage.
Rodents, cattle, horses, sheep goats – watch out for aborted animals
Leptospirosis – spirochete. HIGH fevers, HA, Aseptic meningitis (possible meningeal signs), severe myalgias. Hepatitis with jaundice, renal failure with nephritis, subconjunctival hemorrhage. Rodents, cattle, horses, sheep goats – watch out for aborted animals!
gram negative, intracellular, endospore. HIGH fevers (don’t relent), HA, myalgias. Mild PNA or respiratory distress. Hepatitis with NO jaundice!
Leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia.
Coxiella burnetti – gram negative, intracellular, endospore. HIGH fevers (don’t relent), HA, myalgias. Mild PNA or respiratory distress. Hepatitis with NO jaundice! Leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia. Shepherds, cattle birthers, etc
gram negative aerobic
abrupt onset of nonspecific sx: fevers, chills, HA, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Ulceroglandular ds – most common.
Single lesion at a tick bite site with a central eschar with assc.
Adenopathy.-pleural effusions with different opacification patterns.
Francisella tularensis –
gram negative aerobic. abrupt onset of nonspecific sx: fevers, chills, HA, abdominal pain, diarrhea. Ulceroglandular ds – most common. Single lesion at a tick bite site with a central eschar with assc. Adenopathy. Pulmonary tularemia - pleural effusions with different opacification patterns. See next slide.
no cell wall
abrupt HA, dry cough, myalgias, dyspnea.
CXR – indistinguishable from many bacterial and viral PNA.
Can have epistaxis and splenomegaly.
Chlamydia psittacosis
– obligate intracellular, gram negative, no cell wall. Reservoir – birds. Can see with pet shop owners and vets, ducks, turkeys. Obtain – inhaled bird feather dust, infected feces. Sx: abrupt HA, dry cough, myalgias, dyspnea. CXR – indistinguishable from many bacterial and viral PNA. Can have epistaxis and splenomegaly. History is paramount!
obligate intracellular, no cell wall, EB (infectious aspect!!) and RB, follows URI, HOARSNESS.
Chlamydia pneumoniae – obligate intracellular, no cell wall, EB (infectious aspect!!) and RB, follows URI, HOARSNESS.
no cell wall, bullous myringitis, cold agglutinins, generally follows URI.
Mycoplasma pneumoniae – no cell wall, bullous myringitis, cold agglutinins, generally follows URI.
generally ELEVATED in bacterial infections
Procalcitonin = generally ELEVATED in bacterial infections
Neutropenic and Cystic Fibrosis
Neutropenic and Cystic Fibrosis – Pseudomonas
Asplenic
Asplenic (susceptible to encapsulated organisms) – Klebsiella, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Nisseria sp,
Smokers, COPD
Smokers, COPD – Moraxella, H. influenzae
Alcoholics
Alcoholics – Klebsiella
S/P influenza –
S/P influenza – S. aureus
Bird handlers
Bird handlers – C. psittaci
Animal breeders (incl. vets)
Animal breeders (incl. vets) – Coxiella burnetti (Q fever)
Hunters, Rabbit Exposure, Lawn Care
Hunters, Rabbit Exposure, Lawn Care – Francisella tularensis
Sputum characteristics: Rust colored
Rust colored: S. pnuemoniae
Sputum characteristics: Salmon colored
Salmon colored: S. aureus
Currant jelly colored sputum
Currant jelly colored: K. pneumoniae
Possibly green tinged sputum
Possibly green tinged: P. aeruginosa
Foul-smelling sputum
Foul-smelling: anaerobes
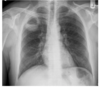
abscess: CAVITATION WITH AIR FLUID LEVEL
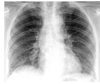
interstitial pneumonia

lobar pneumonia


