Helminth Flashcards
Nematodes
Roundworms - GI helminths
Cestodes
Tapeworms, tissue dwelling heminths
Trematodes
Flukes - tissue dwelling
Pathology of heminths

Nematode life cycle
adult worms in intestine –> feces –> leave in eggs –> ingested eggs –> young larvae mature to adults and live in guy

trichuris trichirua
nematode
whipworm - whip part is buried in mucosa of colon and rectum
light infections - asymp
heavy infections - colitis, chronic diarrhea, prolapsed rectum occasionally
trichuris trichiura transmission, control, treatment
control:
- proper fecal disposal
- avoid contamination of food with soil that contains infectious eggs
treatment: albendazole, mebendazole
enterobius vermicularis
pinworm!
nematode
scotchtape test - kids
wash bedding and clothes, handwashing and baths and clip fingernails
treatment: albendazole, pyrantel pamoate
hookworm
nematode - hook-like shape
infect small intestines - mult bleeding sites after hookworms detach and move to another site in the gut - more blood loss
anemia - eggs in stool!
hookworm transmission
adult worms in the intestine
can ingest eggs OR larvae hatch in soil and can penetrate intact skin and enter blood stream, pass through lungs to get to intestine!
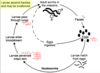
hookworm diagnosis and treatment
diagnosis: anemia,
eggs in stool - microscopy
treatment: albendazole, pyrantel, mebendazole, oral iron and folic acid for anemia
Ascaris lumbricoides
8-12 inches long
SMALL BOWEL
pneumonitis during lung stage, hypersensitization –> astham
eosinophilia! especially early
possibly obstruction of intestine (kinds) or pancreatic ducts (adults)
diagnosis and treatment of ascaris lumbricoides
passage of adult worms via anus or mouth
passage of eggs (warty surface in stool)
treat:
mebendazole, albendazole, pyrantel (pregnant women)
ancylostoma canium and a braziliense
larve in humans are inappropriate host - don’t have proper enviornental cues - no normal hookworm life cycle
nematodes
“wander” through epidermis - inflammatorytracks
eggs passed in dog/cat feces, larvae develop in sandy soil and pentrate intact skin
CLM
cutaneous larva migrans
in humans by mistake - wander through epidermis and leave inflamatory tracts
treat w thiabendazole or ivermectin
toxcara canis and t. cani
nematodes
ascaris-like infections of puppies and kittens
visceral larva migrams - larva in human brain, liver,eye from contact in soil
misdaignosed as Rb!
CLM, VLM, OLM treatment
albendazole, mebendazole, ivermectin
prednisone - when lkill parasites in tissues - strong immune response! need corticosteroids
strongyloidasis
smallest intestinal nemotode
small bowel
simialr to human hookworms except:
AUTOINFECTION: larvae emerge rapidly from eggs deposited by adults high in gut - some develop to become infective larvae in gut and reinvade as pass down
HYPERINFECTION: continued cycling between gut and lungs and may lead to multiplication of parasites, disseminated infection
larvae (not eggs) passed in stool - diagnosis by motile larvae
strongyloides pathology
cycling of worms between gut and lung - longstanding infection
acute: inflammation and ulceration of small bowel mucosa, eosinophilia
long standing infections - sub clinical symptosm
increase in infection after immunosuppression
worms leave gut and travel through body - disseminated infection!! medical emergency, spread bacteria from gut all over body, sepsis
strongyloides diagnosis and treatment
eosinophila, pulmonary symptoms (wheezing)
larvae in stool - rare because may reinvade gut as move down
may need mult stool samples
may be found in duodenal secretions
serology
treat: ivermectin or albendazole, antibac, antiviral for disseminated larvae
filariasis
nematodes
live in lumen of afferent lymph vessels 0 inflammation, accumulation of lymph - elephantitis
filaririasis lifecycle/transmission
- mosquito takes blood meal - larvae enter skin
- adults in lymphatics
- adults make filariae that migrate into lymph and blood
- mosquito takes a blood meal and ingests microfilariiae, replicate in mosquito

IL-10
induced by helminth infections, inhibits immune mediated pathology
tmodulated response - tolerant/suppressed - subclinical infection
loiasis
filiaris, nematode
migrates through eye - response is more dangerous than carrying






