HEENT Flashcards
What is the equipment needed for a HEENT exam?
- stethoscope
- opthalmoscope
- otoscope (+/- pneumatic bulb)
- snellen or rosenbaum eye chart
- tuning fork (256 Hz vs 512 Hz)
- tongue blade
- cotton tipped applicator
- gloves, gauze
ROS Head
headache, vertigo, syncope, head trauma
ROS eyes
visual acuity changes, blurred vision, diplopia, photophobia
ROS ears
change in acuity, discharge, pain, tinnitus, recurrent ear infections
ROS nose
obstruction, discharge, epistaxis, pain
ROS Mouth
toothaches, bleeding gums, sore throat, dysphagia, hoarseness, change in taste
ROS neck
pain, stiffness, swelling/ masses
Normally the head and scapl are
normocephaic, atraumatic
inspection (face, skull, hair, scalp)
- trauma
- symmetry
- skin lesions
- scales
- hair distribution
- etc
palpation (face, skull, hair, scalp)
- Lumps
- bumps
- tenderness
- lesions
- describe regions based on underlying bone
head and scalp percussion
sinuses
head and scalp auscultation
vascular sounds
CN visual acuity
CN2
CN hearing
CN8
CN EOMs
CN3, 4, 6
CN facial expression
CN 7
CN mastication, clench
CN5 motor
CN sharp/dull face touch
CN5 sensory
CN soft palate/ uvula “Ah”
CN 9, 10
CN movement of tongue
CN12
CN head and shoulder movement
CN 11
Inspect hair for
- lice, nits
- hair loss
- quantity, distribution, texture
alopecia areata
autoimmune condition causing hair loss “patchy”
seborrheic dermatitis
- “dandruff”
- greasy
- yellowish
- scaly
- can be on scalp, nasolabial folds, eyebrows, forehead
psoriasis
- autoimmune dermatologic condition
- silvery white sharply dermarcated plaques and coarse scale
- can be quite thick, usually not associated with hair loss
tinea capitis
- fungal infection of scalp
- scaly patches or plaques with or without inflammation
- kerion- raised boggy secondarily infected fungal lesion of hair
inspect face for
- landmarks for asymetry
- lesions, rashes, swelling
- characterisitic “facies associated with disease states
acromegaly
- increase of growth hormone
- enlargement of bone and soft tissues
- elongated head with bony prominence of the forehead, nose, and lower jaw
- enlarged nose, lips, and ear soft tissues
- coarsened facial features
myxedema
- severe hypothyroidism
- dull, puffy facies
- pronounced edema around the eyes that does not pit with pressure
- dry, coarse, thinned hair and eyebrows
- dry skin
neprotic syndrome
- edematous face
- pale
- swelling first appears around eyes in the morning
- slitlike eyes with severe edema
cushings syndrome
- increased adrenal hormone
- round moon face
- red cheeks
- excessive hair growth on mustache, sideburn areas, and chin
parotid gland enlargement
- chronic bilateral
- may be associated with obesity, diabetes, cirrhosis
- swellings anterior to the ear lobes and above the angles of the jaw
- gradual unilateral enlargement suggests neoplasm
- acute enlargement seen in mumps
parkinsons
- decreased facial mobility blunts expression
- mask face
- decreased blinking
- characteristic stare
- neck and trunk flex forward
- patient peers upwards
- oily skin
- drooling
palpate bones for
tendernous
where do you palpate/ percuss
over maxillary and frontal sinuses
Temporomandibular Joint palpation
- palpate joint
- listen and feel for clicks
- check ROM
- open/close, move side to side
- palpate massetere muscles (CN5)
- clench teeth
what does the trigmeninal nerve do
- sensory
- opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
- lightly touch in all 3 areas bilaterally with Qtip
- motor
- palpate masseter muscle, clench teeth
how to test CN7
- check for facial symmetry
- wrinkle forehead “raise your eyebrows”
- squeeze eyes shut
- puff out cheeks
- smile- “show your teeth”
acromegaly
- excessive growth hormone production
- large hands and feet
- excessive facial bone growth and enlarged jaw
bells palsy
- idiopathic facial nerve paralysis causing muscle weakness on one side of face
- difficulty closing one eye
- flattened nasolabial fold
how to assess the temporal artery
palpate and ausculate for bruits
giant cell (tempora)l arteririts
- adults >50
- new HA
- jaw claudication
- elevated ESR
- associated condition PMR
tarsal plates of eyelids
firm strip of CT
meibomian glands of eyelids
sebaceous glands
bulbar conjunctiva of eyelids
covers anterior eyeball
palpebral conjunctiva
covers inner eyelids
visual acquity tests
snellen chart
rosenbaum pocket chart
what does 20/200 mean
pt sees at 20 ft what someone with normal vision sees at 200 ft
snellen chart screens for
myopia
distance that snellen chart tests
20 feet
myopia
impaired far vision
rosenbaum pocket chart screens for
presbyopia
presbyopia
impaired near vision
distance that rosenbaum tests at
14 inches; bedside screen
for x/y vision, the larger the denominator
the worse the vision
when examinating the lacrimal apparatus look for
excess tearing/ dryness
when examining the bulbar conjunctiva and sclera, look for
infection, inflammation, icterus
when examining the palpebral conjunctiva look for
pallor
when examining the pupils look for
- equality and pupillary reaction (direct and consensual)
- convergence
- near-far accomodation
when examining the eyes, you assess
- lacrimal apparatus
- bulbar conjunctiva and sclera
- palpebral conjunctiva
- cornea and lens
- pupils
PPERRL
Pupils Equal Round Reactive to Light
pupil inspection
size, shape, equality
miosis
excessive pupillary constriction
mydriasis
excessive pupillary dilation
ansicoria
pupils are unequal size
direct pupillary light reflex
pupil constricts on same side as light when you shine bright light in obliquely
consensual pupillary light reflex
pupil constricts in opposite eye of the one one you shine a bright light into obliquely
EOMI
extraocular muscles
EOMI testing
- tests 6 cardinal directions of gaze
- move fingers through a large H to test EOMs
- ask pt to keep head in meidline and just move eyes
- make sure H is big enough for full ROM
- watch for conjugate (parallel) movements
- pause at upward and lateral gaze to detect nystagmus
- after H pattern, pt follows finger to assess convergence with near vision
nystagums
fine rhythmic oscillation of the eyes
Near far accomodation testing
- pt focuses on object 10 cm away then an object greater than 6 feet away
- watch for pupillary constriction with near and dilation with distance
- Narrows with Near
- Dilates with Distance
corneal light reflection
shine light into pt’s eyes and note corneal light reflection
corneal light reflection tests for
conjugate gaze
extraocular movements
lateral rectus- CN6
superior oblique- CN4
all others- CN3
eyelid examination
look for
- edema
- lesions
- width of palpebral fissures
- condition and direction of the eyelashes
- adequacy with which the eyes closes
- ptosis
- incomplete closure
Ptosis seen with problem with CN
3
incomplete eye closure seen with problem with CN
7
chalazion
nontender
meibomian (sebaceous) gland obstruction/ inflammation
points inside lid
hordeolum
aka stye
tender, red infection near hair follicles of eyelashes
like pimple or boil poining on eyelid margin
which one hurts, chalazion or hordeolum?
hordeolum- it’s horrible
dacryocystitis
lacrial sac inflammation/ infection
usually secondary to blockage of nasolacrimal duct
sweling b/w base of nose and eye
orbital contact dermatitis
ex pt would be 50 yo male went camping and now returned with itchy rash on face
now developed swelling and itching around eyes, right eye more than left
periorbital/ preseptal cellulitis
example would be 32 yo with low grade fever, swelling, redness, pain and inability to open L eye
also has increased nasal congestion, facial pressure, and headache x 2 weeks prior to symptoms
no hx or trauma
entropion
eyelid inversion
more common in elderly
inward turning of the lid margin
irrititation of the conjunctiva and cornea
ectropion
eyelid eversion
margin of lower lid turns outwards
exposes palpebral conjunctiva
more common in elderly
excessive tearing can occur as puncta may not drain effectively
pingueculum
yellow trianglular nodule on the bulbar conjucntiva on either side of the iris
harmless
vision WNL
pterygium
medial sclera triangular thickening of bulbar conjunctiva that extends from inner canthus to cornea
may interfere with vision
scleral icterus
yellow discoloration of sclera
elevated bilirubin
jaundiced skin
xanthelasma
sharply demarcated yellow deposits of fat under the skin around eyelids
associated with hyperlipidemia
viral conjunctivitis
not usually goopy
bacterial conjunctivitis
usually goopy
types of conjunctivitis
viral, bacterial, allergic, irritant
exophthalmos
abnormal protrusion of the eyeball
seen in graves disease (thyroid dysfunction)
what causes loss to the lateral 1/3 of eyebrows
thyroid dysfunction
episcleritis
central nodule with radiation of vessels
most often associated with systemic disease
occasionally associated with autoimmune conditions
usually self limiting and benign
uveitis
aka iritis
red, painful, photophobia, no discharge
causes:
- infectious- herpes and CMV
- autoimmune/ systemic immune- sarcoidosis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, IBD (Crohns, UC)
- idiopathic
subconjunctival hemorrhage
hx of cough, straining, coumadin use (if coumadin use may be more serious and need to review labs)
asymptomatic
self limiting
if recurrent, consider bleeding disorder
hyphema
grossly visible blood in anterior chamber
usually secondary to trauma
vision threatening- refer
corneal abrasian
can be visualized with fluorescein stain
pt example- 22 yo with R eye foreign body sensation since mowing the lawn
increased photophobia, lacrimation, pain
corneal chemical burn
usually pt provids hx of liquid or gas splashed in eye
immediate and prolonged irrigation
cataract
clouding, opacity of the lens
causes painless progressive vision loss
risk factors- age, smoking, DM, corticosteroids, ETOH
opthalmoscope aperture- small
easier view through non-dilated pupil
opthalmoscope aperture- large
view through dilated pupil
opthalmoscope aperture- grid
make measurements
opthalmoscope aperture- slit
determine elevation or concavity in retina
opthalmoscope aperture- cobalt filter
for fluorescein staining to visualize corneal lesions
how to do opthalmoscopic exam
darken room
may use small or large round beam of light on scope
do not use maximum light
ask pt to try to keep both eyes open
turn disc to 0 diopters, keep index finger on dial in order to adjust focus as needed
ask pt to look over shoulder at fixed point on wall that is at eye level
R hand, R eye, Pt R eye
L hand, L eye, Pt L eye
approach pt’s eye about 15 degrees lateral to pt’s line of vision
look for red reflex first- absent red reflex= opacity of lens (cataracts, detached retina, retinoblastoma, artificial eye)
brace yourself with hand on pt’s shoulder or brow
move closer to pt’s eye almost touching their eyelashes
follow blood vessels centrall to find optic disc (nasal side of fundus)
adjust diopter dial to adjust focus
always compare findings bilaterally
note disc margins, color, size of central cup (cup: disc ration is < 1:2)
inspect vessels
inspect for hemorrhage exudate, and edema of optic disc (papilledema)
view macula, fovea
veins of the eyes are ____ and _____ than arteries
larger and darker
eye artery to vein ratio is
2:3
how do you view the macula/ fovea
pt looks directly into the the light (temporal)
what is the macula/ fovea responsible for
central vision
pan optic
larger
increases distance b/w pt and clinician
clinician my use the same eye to examine both of the pt’s eyes
most clinicial settings do not have
hyptertensive vascular changes- copper wire
vessels get full and tortuous with increased light reflex
coppery luster
hyptertensive vascular changes- silver wire
vessel wall becomes too opaque and blood cannot be seen
hyptertensive vascular changes- AV nicking
artery-vein nicking
appearance of breaks in vein when artery and vein cross
hypertensive retinopathy- cotton wool patches
aka soft exudates
white, gray, ovoid lesions with irregular (soft) borders
caused by infarcted nerve fibers
also seen in DM
hyptertensive retinopathy- hemorrhages
caused by microaneurysms
diabetic retinopathy
hemorrhages can be seen along with hard exudates
hard (well defined borders) exudates are cream/ yellow and appear bright common with DM and HTN
neovasculation
neovascularization
development of new blood vessels arising from the disc and extending to the margins
caused by abnormal permeability and vascular occlusion
more numerous and torturous
glaucoma with cupping
increased pressure within eye resulting in abnormal cupping (backward depression of disc)
represents optic nerve damage
normal up to disc ratio is < 1:2, but in glaucoma the ratio is > 1:2 because of intraocular pressure
may have an abnormal anterior chamber depth on exam
detached retina
curtain like shadow over vision
flashes, floaters, risk of vision loss
papilledema
optic disc swelling caused by increased intracranial pressure
pt may have severe HA, nausea, vomiting
macular degeneration
observed in the last step of eye exam, normal would have reflection of light
with degeneration there is decreased reflection
degeneration is due to build up of dusen (cellular debris)
Specialized vision tests
visual field
cover-uncover
anterior chamber
corneal reflex
lid eversion
How to check visual fields
provide sit at same level of pt to ensure similar visual fields
pt closes one eye and looks at providers nose
examiner closes opposite eye to mimic pts visual fiedl
examiner places handto periphery of visual field, checks each eye individually and tests all 4 quadrants
“while looking at my nose, how many fingers am I holding up?”
next provider moves wiggling fingers slowly from periphery (in each quadrant) centrally
“while looking at my nose, please say now when you can see my wiggling fingers”
check all 4 quadrants and each eye individually
then perform the wiggling finger technique, moving fingers peripherally to centrally in each quadrant and pt says “now” when they see the fingers
normally what i see on the nasal side
hits the opposite (temporal) side of the retina and stays on the same side
normally what i see on the temporal side
hits the opposite (nasal) side of the retina and crosses at the optic chiasm
visual field defects- horizontal defect
occlusion of a branch of the cenral retinal artery may cause a horzontal (altitudinal) defect. Shown is the lower field defect associated with occlusion of the superior branch of this artery.
visual field defects- blind eye
defect at the optic nerve before the optic chiasm (neither the nasal or temporal sight will make it to the brain)
visual field defects- lesion at the optic chiasm
causes defect in both temporal fields (bitemporal hemianopsia)
ex Pituitary tumor
visual field defects- lesion on optic tract behind chiasm
produces defects on opposite side
defets on R optic tract causes L homonymous hemianopsia
defect on L optic tract causes R homonymous hemianopsia
ex: stroke, tumor
cover- uncover test will test for
muscle imbalance not otherwise seen in general eye exam
you occlude each eye in alternating fashion and observe for change in fixation of the uncovered eye. Also assess for movement of the covered eye after cover is moved
when do you do the cover-uncover test
when you see an abnormeal corneal light reflection
striabismus
misalignment of the eyes
deviation of the eyes from their normally conjugate position
can be congenital or acquired
one of the most common eye problems in children (4% of children under 6)
check visual acquity if strabismus is detected and refer
esotropia
eye turns in medially
a type of strabismus
light will be displaced laterally on affected eye
exotropia
eye turns out laterally
a type of strabismus
light will be displaced medially on affected eye
hypertrophia
eye turns up
a type of strabismus
hypotropia
eye turns down
a type of strabismus
anterior chamber depth tests for
increased intraocular pressure
ex glaucoma
how to do anterior chamber depth test
shine light from temporal side of patient’s eye (towards nose)
look for shadow on the medial aspect of the iris
“crescent shadow”

corneal light reflection tests for
ocular alignment
corneal reflex tests
CN5 sensory and CN7 motor
how to do corneal reflex test
gently touch the edge of the cornea with a rolled cooton and observe for response blink
what is this?

alopecia areata
what is this?

seborrheic dermatitis
what is this?

psoriasis
what is this?
tinea capitis

what is this?

acromegaly
what is this?

bells palsy
what are the arrows

green- pupil
gray- medial canthus
blue- limbus- where the bulbar conjunctiva merges with cornea
orange- lateral canthus
what are the arrows

green- lacrimal gland
black- lacrimal sac with puncta
blue- nasolacrimal duct
what is this?

chalazion- nontender
what is this?

hordeolum- painful
what is this?

dacrycocytis
aka lacrimal sac inflammation
what is this?

orbital contact dermatitis
what is this?

periorbital/ preseptal cellulitis
what is this?

entropion
what is this?

ectropion
what is this?
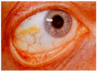
pingueculum
what is this?

pterygium
what is this?

scleral icterus
what is this?

xanthelasma
what is this?

viral conjunctivitis
what is this?

bacterial conjunctivitis
what is this?

exophthalmos
what is this?

episcleritis
what is this?

uveitis aka iritis
painful
what is this?

subconjunctival hemorrhage
what is this?

hyphema
what is this?

corneal abrasion with fluorescein stain
what is this?

corneal chemical burn
what is this?

eye puncture
what is this?

cataract
what is this?

hemorrhages- hypertensive retinopathy
what is this?

hypetertensive retinopathy
what is this?

creamy exudates in diabetic retinopathy
what is this?

a normal fundus
what is this?

fundus with neovascularization from diabetic retinopathy
the one on the left is a normal fundus, what is the one on the right

fundus with cupping from glaucoma
abnormal optic nerve
what is this?

detached retina
what is this?

papilledema
what is this?

macular degeneration
what is this?

blind right eye- right optic nerve lesion
what is this?

bitemporal hemianopsia- optic chiasm lesion
what is this?

left homonymous hemianopsia
right optic tract lesion
what is this?

crescent shadow from abnormal intraocular pressure
we inspect the ear for
deformities, lesions
we palpate the ear
the pinna, the tragus, and the mastoid for tenderness
example- otitis externa causes pain when there is movement of the helix and tragus
the length of the external auditory canal is
24 mm ending in the tympanic membrane
gouty tophi
deposit of uric acid crystals that occurs aftery years of chronically elevated uric acid
what is this?

gouty tophi
basal cell carcinoma
raised nodule with central telangiectasia
squamous cell carcinoma
crusted border with central ulceration and bleeding
what is this?

basal cell carcinoma
what is this?

squamous cell carcinoma
how do you do a gross hearing test
rub fingers together by each ear
if hearing is reduced you need to distinguish between conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss
conductive loss
problme conducting sound waves (EAC, TM or middle ear)
abnormality is usually visible
sensorineural hearing loss
disorder of the inner ear
cochlear nerve impairs transmission of nerve impulse to the brain
problem is not visible
specialized tuning fork test- weber
tests for
lateralization
specialized tuning fork test- rinne
tests for
compares air conduction to bone conduction
air conduction
sound transmitted through the air (EAC –> TM –> middle ear) into cochlea
bone conduction
sound transmitted through vibrations in bone
bypass external and middle ear
vibration of the SKULL stimulates the inner ear directly
normally which is greater, air or bone conduction?
AC
with conductive hearing loss which is greater, air or bone conduction
BC
with sensorineural hearing loss, which is greater, air or bone conduction
air
how to do a weber test
- place the vibrating tuning fork on top of the pt’s head and ask where they hear the sound, L, R, or both
- normally they should hear sound in both ears equally
- unilateral conductive loss- the sound lateralizes (is heard best) to the impaired (bad) ear
- ex: otitis media, perforation, cerumen, otoscerlosis
- unilateral sensorineural loss- the sounds lateralizes (is heard best) to the good ear because the bad ear cannot trasmit the impulse.
- there is no signal transduced by the cochlea on the affected side
- caused by damage to the inner ear
- ex: presbycusis (age related hearing loss), noise exposure, head trauma
weber test sound lateralizes to impaired ear
conductive hearing loss
weber test sound lateralizes to good ear
sensorineural loss
damage to inner ear causes
sensorineural loss
how to do a rinne test
place tip of vibrating tuning fork on mastoid bone
ask pt if they can hear it, have them tell you when the sound stops
move tuning fork in front of ear, ask if they can still hear it
if they CAN then AC > BC, therefore a normal test
in a rinne test, normal is
AC > BC
in a rinne test, with BC > AC, you would have
unilateral conductive loss
the sound hear through bone is longer than through air
in the impaired ear BC > AC but in the good ear AC> BC
in a rinne test with AC > BC, you would have
a normal result OR unilateral sensorineural loss
unilateral sensoriuneural loss the sound is heard longer through air because AC and BC are reduced equally and the normal pattern prevails
AC > BC in both ears
where is the loss? if it lateralizes (sound is heard best) to the damaged ear it is
conductive loss
where is the loss? if it lateralizes (sound is heard best) to the good ear it is
sensorineural loss
how to do an otoscope exam of the ear
brace yourself with 1 or 2 fingers against patients head
pull auricle (pinna) upward and back and insert otoscope slightly down and forward
in infants pull auricle down and back
inspect EAC for cerumen, lesions, foreign body, d/c
inspect tympanic membrane for redness, retraction, bulging, perforations, scarring
the middle ear anatomy
air filled, there is a cone of light (light reflection) located in the anterior inferior quadrant of the tympanic membrane
bony landmarks- malleus and umbo (visible)
pneumatic otoscopy is used to test
tympanic membrane (TM) mobility
see if there is serous OM or TM perforations
how to do pneumatic otoscopy
speculum large enough for a snug fit
gently squeeze bulb to send a puff of air against the TM- normally the TM would move inwards, if no movement then thre is effusion
tympanosclerosis
chalky white patch of scarring on the TM
caused by recurrent otitis media or hx of tubes or previous perforation
what is this

TM perforation
what is this?

tympanosclerosis
what is this?

bulging erythematous TM consistent with acute otitis media
what is this?

foreign bodies in the ear
what is this?

serous effusion with air bubbles
usually caused by viral URI or barotrauma
eustachian tube dysfunction often involved
symptoms include- fullness in ear, popping in ear
what is this?

myringotomy tube
usually remains in ear for 6-12 months
usually falls out on own
used for: repeat bouts of OM, persistent effusion, hearing loss
what is this?

bullous myringitis
painful hemorrhagic vesicles
+/- hearing loss during infection
what is this?

otitis externa
infection of the EAC
notice the drainage and edema of the canal
tenderness and movement of the tragus and pinna
what do the turbinates do
clean, humidify and warm air
what is the meatus
groove below each turbinate
what does the inferior meatus drain
nasolacrimal duct
what does the middle meatus drain
the paranasal sinuses
we inspect and palpate the external nose/ nasal bridge
to evaluate for asymmetry, deformities, tenderness
how do you test for nasal patency
ask pt to occlude one nostril and sniff
how to do a nasal speculum exam
gently insert speculum into nose
avoid touching septum and turbinates
use light source
inspect internal nasal septum, mucosa, turbniates
look for septal deviation or perforation, inflammation, polyps, d/c
to transilluminate frontal sinus, place the light
below the brow and look for glow (normal)
to transilluminate the maxillary sinus place the light
agains the cheek bone below the eye and look for glow on the hard palate (normal)
what is this

septal deviation
symptoms- nasal obstruction, headache, change in smell
see spurs and crests
what is this?

septal perforation
seen with trauma, infection, cocaine, s/p surgery
symptoms- crusting, epistaxis
small lesions may whistle
what is this?

nasal polyps
soft, translucent growths
can cause nasal obstruction
anosmia
what is this?

foreign body
what is this?

septal hematomas
seen following trauma
more common in peds pts
symptoms- increased nasal obstruction, pain, tenderness
PE: soft, tender, swelling
must rule out septal hematomal in all nasal trauma and document
what is this?

epsitaxis
highly vascular region of the anteroinferior nasal septum
90% of all epistaxis occur in the kiesselbachs plexus/ area
why do you get these?

rhinitis and sinusitis
why would you have swollen, pale, blue, boggy turbinates
allergic rhinitis (AR)
also would have shiners and eye Sxs
why would you have erythematous turbinates
sinusitis and URI
also drainage- mucoid vs. clear vs. purulent
why would have you tendernous to palpation of sinuses
sinusitis
anatomy of the mouth and pharynx
lips, tongue, buccal mucosa, 32 adult teeth, gingiva, tonsils, anterior/posterior pillars, hard & soft palate, uvula, whartons duct (drains submandibular gland), stensons duct (drains parotid gland)
how to examine oropharynx
inspect lips, teeth, gingivae, buccal mucosa, floor of mouth, hard & soft palates, tongue, tonsils, pillars, and posterior orpharynx for color, symmetry, lesions
inspect palate and uvula
CN 9 and 10- ask pt to say “Ah”, gag reflex, consider wetting tongue blade if pt has a sensitive gag reflex
palpation- bimanually
examine salivary glands
palpate for masses
parotid- stensons duct- buccal mucosa lateral to molars
submandibular- whartons ducts- floor of mouth under tongue
ask pt to stick out tongue and move it side to side; assesses function of CN__
12
bimanual exam of oropharynx
palapate oropharynx with gloved hand
palpate wall of mouth between internal and external fingers (what bimanual means)
feel floor of mouth, tongue for masses, induration
how to extend lateral margins of tongue
wearing gloves, use gause to grasp the tip of tongue
what is this?

squamous cell carcinoma
when doing an oral exam, look for sores that dont heal and newly formed lesions
consider risk factors
what is this?

angular cheilitis
irritation, fissuring of the skin at the corners of the mouth associated with ill fitting dentures, vitamin deficiency, and excessive salivation
what is this?

oral candidas (thrush)
white patches or plaques on the tongue or bucacl mucosa
uncommon among healthy adults
can brush away
what is this?

leukolplakia
potentially premalignant
differentiated by thrush by inability to remove white area
referral for biopsy recommended
what is this?

oral carcinoma
through physical exam is necessary
majority of oral cancer is SCC
what is this?

torus palatinus
benign, midline mass of the palate
what is this

gingivitis
causes changes to the gums
- redness
- bleeding
- edema
- tenderness
what is this?

gingival hyperplasia
can be caused by medication such as dilantin (phytoin), cyclosporine, Ca channel blockers
can also be caused by poor dental hygiene and pregnany
what is this?

tonsillar hypertrophy
numerous tonsilar crypts
what is this?

hairy tongue
benign condition
defect in desquamation of papillae
many causes- Abx, tea, coffee, tobacco use
what is this?

fissured tongue
multiple small grooves on the dorsum of tongue
benighn
increasing incidence with advanced age
what is this?

geographic tongue
dorsum of tongue shows smooth areas void of papillae
benign
what is this?

bilateral exudative tonsilitis
could be caused by Group A strep OR mononucleosis (Epstein Barr virus)- determine diagnosis by strep screen/ culture and mono screen
strep A

ex pt: worsening sore throat x 2 days, fever of 102, n/v, 3 friends with similar Sxs, no cough, nasal congestion, fatigue
bilateral exudative tonsilitis and cervical LAD
diagnosed determined by pos strep screen/ culture
mononucleosis

ex pt- sore throat x 5 days, fever 101, fatigue, tender anterior and posterior cervical LAD
bilateral exudative tonsilitis
slight splenomegaly
diagnosed by negative strep screen, positive mono screen
what is this?

peritonsillar abscess
unilateral peritonsillar swelling and shifted uvula
infections spreads into the peritonsillar space
drooling
hot potato voice
very sore
anatomy of neck

how to examine the neck
inspect while observing the patient swallowing
look for symmetry, masses, scars, nodes, tracheal position, thyroid
evaluate ROM- flexion, extension, rotation, lateral bending
evaluate motor function of CN 11 and strength
how to evaluate motor fxn of CN11 and strength
lateral rotation of neck against resistance
shoulder shrugging against resistance
examination of the trachea
inspect for deviation from midline- deviation may suggest mediastinal mass/ pneumothorax
palpate and assess mobility
label these lymph nodes

how to examine lymph nodes
use pads of your index and middle fingers
neck should be relaxed
can examine one side or both sides at once
note size, shape, consistency, mobility or tenderness of nodes
shotty (small, mobile, nontender) nodes are common in children
supraclavicular LN may suggest metastasis from lung or GI cancer
how to do a carotid artery exam
auscultate each carotid, listening for “bruits” (signs of turbid arterial blood flow… whooshing)
palpate the carotid arteries using gentle pressure and only one side at a time
examine the thyroid
inspect for enlargement, asymmetry from the front
from the posterior or anterior, place fingers below cricoid cartilage on each side of the neck
palpate the isthmus and each lobe
ask pt to swallow, feel for gland rising beneath fingers, note size, shape, and consistency
note any masses, nodules, or tenderness
goiter
an enlarged thyroid aka thyromegaly
can be present in multiple forms of thyroid dysfunction
remember to palpate the thyroid while pt swallows
what do you do if they have an enlarged thyroid?
auscultate
listen over the lateral lobes to detect a bruit
bruits may be present in hyperthyroidism or toxic multinodal goiter
tracheal deviation
trachea shifts to one side or other because of goiter pnueumothorax, or tumor
what is this?

JVD- jugular venous distension
caused by cardiac and pulmonary dx
blood flows backwards from right atrium into the jugular veins


