growth hormone Flashcards
where is the growth hormone produced
anterior pituitary
which anterior pituitary cell type produces growth hormone
somatotroph
growth hormone circulates freely or bound?
bound to GH-binding protein
describe the function of GHRH and somatostatin (hormones produces by hypothalamus)
- GHRH: acts on somatotrophs to induce synthesis and release of GH
- Gs mediated
- somatostatin: acts on somatotrophs to inhibit GH secretion
- Gi mediated
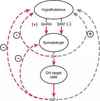
How do GHRH and somatostatin reach the anterior pituitary?
reaches the somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary through the portal veins

what is the direct effect of growth hormone? Indirect effect?
- direct effect: maintaining plasma glucose
- Indirect effect: growth
glycogen synthesis
conversion of glucose to glycogen, the storage form of glucose
oxidation
using something for fuel, e.g. converting glucose to ATP
glycogenolysis
breakdown of stored glycogen to yield glucose
gluconeogenesis
synthesis of new glucose, conversion of amino acids to glucose
how does GH effect metabolism
- increase lipolysis in adipose tissue
- increase gluconeogenesis in liver
- increase amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in muscle
growth hormone is a protein anabolic hormone. what does this mean
stimulate protein synthesis, muscle growth, and insulin.
describe how GH has a glucose sparing effect
- decreases glucose uptake and use by muscle, liver and adipocytes
- increases liver glucose output by gluconeogenesis
- net effect = increase in glucose
GH is a lipolytic hormone. Describe this
- activates triglyceride breakdown and increases free fatty acid release in adipose tissue
the indirect effects of GH are carried out by what
- growth caried out by liver generated insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1)
- structurally related to proinsulin
what is Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) actions on growth
- increase in linaer bone growth
- action on growth plates of long bones
- increase amino acid uptake and protein and collagen synthesis -> promotes hyperplasia and hypertrophy of organs
The pubertal peak rate of growth corresponds to the peak serum concentrations of
IGF-1
release of GH follows what type of rhythm
-
diurnal (sleep-wake) rhythm
- GH levels remain low during day
- with sleep: sharp rise at onset, then steady drop throughout sleep time (70% of total secretion)
- due to pulsatile release of GHRH
how is GH regulated via IGF
- IGF acts on the hypothalamus to stimulate somatostatin release and inhibit GHRH release -> inhibits GH release from anterior pituitary
- IGF has a negative feedback loop with anterior pituitary

how is GHRH regulated
GHRH inhibits its own release at the hypothalamus
how is growth hormone regulated
- inhibits its own secretion from the anterior pituitary
- may also stimulate somatostatin release at the hypothalamus


