Growth factor signaling, receptors and non-receptor tyrosine kinases Flashcards
True or False
___ The general structure of receptor tyrosine kinases is monomers, and when a signal comes in it will remain as a monomer.
___ Growth factors receptors can dimerize constitutively in absence of a ligand.
___ Binding to ligands stabilizes dimer and leads to allosteric changes in receptor structure needed for receptor activation and signaling.
___ Tyrosine kinases receptors have a single-pass transmembrane domain, large extracellular domain, tyrosine-kinase domain is intracellular, and ligand-induced is the main source of activation.
False, receptor tyrosine kinase is a monomer but when the signal binds it will dimerize the structure.
False, It can but it occurs at a very low frequency.
True
True
Mutations in enzyme coupled receptors that lead to overexpression or overactivity are associated with and appear to be the primary basis of _______________.
Types of mutations in enzymes-coupled receptors:
In TM domains that caused receptors to dimerizes in the absence of ligand, and convert receptors from being ligand-induced dimers to constitutive dimer
In/near the catalytic domain that converts receptors from having ligand-induced enzyme activity to constitutive enzyme activity
Ovexpression of the receptor
numerous cancer
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) __________________ enhances RTK catalytic acitivty via conformational chnages in active site, autophosphohation and active other proteins.
Transautophosphorylation
Fill in the blanks for Transautophosphorylation
Inactive RTKs, which are monomers, get activated (and become a dimer) by a signal protein causing _________________________.
Phosphorylation on tyrosine residues outside of the active site generates ___________________________.
_____________________ relay siganl downstream
Activating phosphorylation site within the active site
binding sites for other proteins
Activated signaling proteins

Fill in the blanks
RTK Transautiphosylation creates binding sites for a variety of ___________containing proteins
Related but distinct ___________ on different proteins confer specificity for binding to different P-Tyr residues on RTKs
SH2 domains

Fill in the blanks
_____________ Interactions Mediating SH2: P-Tyr Binding
SH2 performs ____________ between having high enough binding affinity for neighboring amino acid sequences to ensure specificity and having binding dependent on the phosphorylation state of the tyrosine
Non-covalent
balancing acts
Why does the SH2 domain have two separate sites?
One binding site for neighboring amino acid side chains
and the other is for phosphotyrosine
Drosophila Eye Development Pathway
Fill in the blanks
________ binds to the Sev RTK
_____________(Drk) will bind to _____________(Sos) which will activate a _____________ a form of GPCR.
Cause downstream signals which lead to expression in the R7 cell
Boss
adaptor protein
Ras-GEF
Ras protein

True or False
Parallele RTK-Based Signaling Pathways Regulating Fly Eye Development and Human Cell Proliferation
True

The ______________ is similar to heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits:
Activated by GDP to GTP exchange triggered by upstream GEF
Undergoes local conformational change in guanine nucleotide-binding site depending on whether GDP or GTP is bound
Local changes at the guanine nucleotide-binding sites are allosterically coupled to changes in the switch region
Self-contained GTPase activity
Localized on the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane by covalent lipid modification
Activated by receptor-based signaling pathways
Ras family of monomeric G proteins
True or False
Most frequent Ras GOF mutations in cancer
Common Mutations to change Gly12 to any amino acid converts proto-oncogene Ras to oncogenic Ras due to 90% inhibition of GTPase
Due to lack of activation of GTPase activity by GAPs (broken brake)
Can also get Ras GOF mutation in which GTP for GDP exchange occurs in absence of GEF
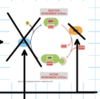
True
True or False
LOF mutations in Ras-GAPs
Neurofibromatosis gene NF1 encodes a tumor suppressor RAS-GAP, eliminating GAP will eliminate GTPase activity
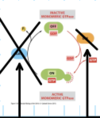
True
True or False
__ Heterotrimeric G proteins alpha subunits have a critical Arg in the GTPase domain supplied by the switch I region.
__The critical Arg is also in Ras and does not need a trans by Arg787 from GAP (a protein)
__ Ras signaling has a set of protein kinases that carry out the phosphorylation reaction that changes the cell phenotype
True
False, Ras is lacking this residue. Ras need GAP protein for the GTPase activity
True
What domains do the 8 non-receptor tyrosine kinases have?
SH1 –> Tyrosine kinase catalytic domain
SH2 –> as seen in the RTK
SH3 –> Bind Proline-rich sequences
Where is Src located and how are they there?
Can these Src associate with receptors that have no function?
Can they be activated through diverse signaling pathways? Which one is the major one?
They are anchor to the inner face of plasma membranes which are covalently attached
Yes
yes, a major one being through protein tyrosine phosphtase
True or False
__ 90-95% of Src in cells is maintained in a state of phosphorylated at Y527. Maintained in inhibited/restrained state: SH2 and SH3 domains participate in an inhibitory intramolecular interaction
__The latch is formed between SH3 domain binding to P-tyr527
__The clamp is formed by the SH2 domain binding to the backside of the kinase domain
___The switch is when Tyr-416 interferes with the active site when unphosphorylated.
True
False, the latch is formed between SH2 binding to P-tyr527
False, the clamp is formed by the SH3 domain
True
_________- Dephosphorylation of P-tyr527 by a protein tyrosine phosphatase leads to loss of intramolecular P-Tyr:SH2 interaction
Primary mechanism
Unlatching
True or False
Unclamping Could also occur via competition for SH3 domain binding by another protein, changes intramolecular interaction to intermolecular
Switching: intramolecular autophosphorylation of Tyr416, change in a structure near active site leading to enhanced catalytic activity. Similar to what occurs with trans autophosphorylation in RTKs Tyr416 could also be phosphorylated in an intermolecular manner by another TK
True
V-Src: Mutant present in Rous sarcoma virus is missing _______, cant form the latch, tyrosine will always be unwound which would lead to unregulatory activation of Src
Tyrosine residue



