Grey Matter Flashcards
(57 cards)
Difference between endocrine and nervous system
nervous system: acts faster
targets specific parts/cells
has a short lasting effect
electrical impulses sent
Endocrine system: slower but long-lasting
affects through chemical control
What is a phytochrome Which phytochrome in plants is active?
Phytochrome absorbs and detects light Pfr is active in plants
What converts Pr to Pfr what converts Pfr to Pr
When red light is absorbed by Pr it is converted to Pfr When far-red light is absorbed by Pfr it is converted to Pr
Benefits of plant responses to light
ensures that flowering happens at the right time so same species flower at the same time and they flower when insects are available since length of days varies short days in winter and long days in summer
Which phytochrome stimulates flowering?
Low levels of Pfr
explain role of neurotransmitters
comes from pre-synaptic neurone diffuses across synaptic gap affects post-synaptic neurone
special structure in sensory neurone
cell body in middle
how structure of neurone helps conduct impulses
Schwann cell convers axon Schwann cell contains myelin which provides insulation So Action potential only occurs at nodes of ranvier (gaps between schwann cells) undergoes saltatory conduction and jumps from node to node
how does structure of axon membrane help with impulses
phospholipids restrict ion movement proteins span membrane sodium potassium pump punmps ions across membrane protein gates allow for diffusion of ions
advantages of having mylelinated neurone
myelin sheath provides electrical insulation except at nodes of ranvier where neurone is exposed because nodes are site of sodium-gated channel proteins these open when impulse arrives causing depolarisation of nodes impulse jumps from node to node this is known as saltatory conduction only occurs between Schwann cells this is faster than non-myelinated neurones
Why are neurones not affected by a second stimulus that occurs to quickly
they are still undergoing action potential neurone hasn’t reached resting potential Sodium ion gates are closed
what are the events leading to depolarisation of membrane
depolarisation of adjacent membrane this changes PD across membrane opens sodium gates and sodium ions move into axon
Which type of neurone is found in the central nervous system
Relay neurone
direction of impulse in sensory neurone direction of impulse in motor neurone
away from receptor towards effector
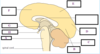
What is A?
What is B?
What is C?
What is D?

A- nucleus
B- Cytoplasm
C- Myelin Sheath
D- Axon
How is an action potential generated?
Stimulus occurs
This causes Na+ voltage gated channels to open
Allowing Na+ to diffuse into axon down concentration gradient
More Na+ channels are stimulated to open (positive feedback)
Axon PD becomes positive due to increase of Na+ in axon and is depolarised and AP generated
Wave of depolarisation is passed through axon
Sodium ion gates then close and K+ channels open
K+ permeablility increases
K+ diffuse out down the electrochemical gradient
it repolarises the axon, making it more negative
Hyperpolarisation occurs and K+ channels are closed
Sodium-potassium pump returns axon to resting potential
Events that occur at synapse
Impulse arrives at synaptic knob
Ca2+ channels in pre-synaptic membrane open
Ca2+ diffuse into synaptic knob
Synaptic vesicles containng neurotransmitters move towards pre-synaptic membrane
Vesicles fuse with membrane ad neurotransmitter is released into synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter diffuse across synaptic cleft and
attach to specific protein receptors
on post-synaptic membrane
Na+gated-channels on post-synaptic membrane open
Na+ diffuse in to post-synaptic neurone
PD across mombrane changes and it is depolarised
AP generatedin post-synaptic membrane
Could be spatial or temporal summation
Enzyme breaks down neurotransmitter and it is reabsorned through pre-synaptic membrane
So there is no prolonged stimulation of post-synaptic membrane
Difference between spatial and temporary summation
Spatial is when potentials from many pre-synaptic neurones cause post-synaptic neurone to reach threshold potential
Temporal is when a single presynaptic neurone fires many times in succession causing postsynpatic neurone to reach threshold potential
Describe structure and role of choroid
It is at back of eye, contains black pigment which absorbs all light
Where are Rod Cells found?
Where do neurones of the optic nerve begin?
Which direction is light moving in?

C
A
from bottom to top

What happens when light hits eye
Rhodopsin is bleached
retinal changes shape
and rhodopsin splits into opsin and retinal
The cell that links a rod cell to snesory neurone is
bipolar neurone