GRE Math Flashcards
(45 cards)
Adjacent Squares (Addition)

Slope
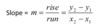
Point-Slope Form

Slope-Intercept Form
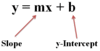
When to use estimation?
Multiple choice answers when answers are far apart
Adjacent Squares (Subtraction)

Squares of 5
- Number to be squared: 752
- Remove the 5: 75 -> 7
- Add one to the remaining digit: 7 -> 8
- Multiply the two: 7 * 8 = 56
- Put this in front of 25: 752 = 5625
Dividing by 5
- Double a number then divide by 10
- Divide by 10 then double
Doubling & Halving
- Dividing and multiplying factors by 2 to get easier factors
- You can do this multiple times
- Example
- Suppose 16 * 35
- 16 / 2 = 8
- 35 * 2 = 70
- 70 * 8 = 560
- Suppose 16 * 35
Squaring Multiples of 10
- Square the 10, square the non-10 and multiply the two
- Example: 402 = 42 * 102 = 16 * 100 = 1600
When to use doubling and halving with 5
- A factor ends in 5 (45)
- A factor is an odd multiple of 50 (150)
4 Random Number Game
- Take 4 random numbers in 0-9
- Use all of the numbers to find all numbers in 1 - 20
GRE Quantitative Question Types
- Multiple Choice
- Multiple Answer
- Number Entry
- Quantitative Comparison
Quantitative Comparison Answers
A) Quantity A is always better
B) Quantity B is always better
C) Both are always equal
D) Cannot be determined
QC Approximations
- Use estimation
- Compare parts instead of the whole
- If both columns have only numbers then D can’t be the answer
- Example
- Q(A) 32.8% of 5,929 Q(B) 41.6% of 5,041
- 33.3-% of 6000- = 2000-
- 40+% of 5000+ = 2000+
- Therefore (B)
- Q(A) 32.8% of 5,929 Q(B) 41.6% of 5,041
QC Matching Operations
- Equalities: >, <, =
- Allowable Operations
- Add to both sides
- Subtract from both sides
- Multiply or divide the same positive number
Rounding
- 0 - 4 = Round Down
- 5 - 9 = Round Up
- Only look one place to the right when rounding
- *10.49999 = 10
Quantity Increase (Percentage)
x = Q * (1 + (P% as a decimal))
x = 230 * (1 + 0.4)
x = 230 * 1.4
x = 322
Quantity Decrease (Percentage)
x = Q * (1 - (P% as a decimal))
x = 80 * (1 - 0.7)
x = 80 * (0.3)
x = 24
Find the Multiplier

Distributive Property
Multiplication distributes over addition and subtraction
Works if addition/subtraction is in the numerator, but NOT the denominator

Percent Increase Equation
Amount * (1 + Percent Decimal)
$425 increases by 30%
$425* (1 + 0.3) = $425 * 1.3 = $552.5
Percent Decrease Equation
Amount * (1 - Pecent Decimal)
$700 decreases by 25%
$700 * (1 - 0.25) = $700 * 0.75 = $525
Simple Interest
- Each payment is paid against the original principal amount.
- Not the way interest works, but is good for illustrating the general idea and estimation.
- Amount = Principle + (Principle * Percent * Repetition)
- A = P + (P*D*R)
- Example: Bob deposits $1000 in an account that yields 5% simple interest annually.
- 5% of $1000 = $50
- 1 year: $1000 + $50 = $1050.00
- 2 years: $1050 + $50 = $1100.00
- 3 years: $1100 + $50 = $1150.00
- Etc…












