Glycoproteins Flashcards
What is a Glycoprotein?
a protein with covalently attached carbohydrate (saccharides); Tends to be used to refer to proteins with lower carbohydrate content, but there is a wide variability
Ubiquitionous extracellular proteins that carry out many body functions.
What is a proteoglycan?
How does their carbohydrate content compare with glycoproteins?
Glycoproteins with glycosaminoglycan chains (GAGs).
Proteoglycans tend to have a higher carbohydrate content than glycoproteins.
Where are most glycoproteins located?
Are there any exceptions?
Almost all glycoproteins are extracellular, and most extracellular proteins are glycosylated.
Yes, ;Albumin - abundant serum transport protein, is not glycosylated.
How many glycoproteins exist?
Name 5 common glycoproteins
A tremendous number of glycoproteins exist.
- *1. lectins** (carbohydrate binding proteins for cell attachment, immune response, lung surfactant, sperm-egg binding).
- *2. Ceruloplasmin** copper binding & transport.
- *3. Immunoglobulin,**
- *4. collagen,**
- *5. fibronectin**
How are sugars linked to glycoproteins?
What are common sugars that are used as building blocks of glycoproteins?
These sugars can be linked by enzymes through many of their hydroxyl groups to form oligosaccharides that are transferred to the protein in the process of glycosylation.
- Mannose
- N-acetyl Glucosamine
- Sialic Acid
Where, When, and How does glycosylation occure?
WHERE: In the lumen of the R.E.R. (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
WHEN:; As the polypeptide is being synthesized
HOW: A preassembled oligosaccharide is transferred to a an appropriate Asparagine in the sequence …[ASN-X-Ser/Thr]
What is glycosylation?
Glycosylation - the process of biosynthetically sugar coating proteins: N-linked oligosaccharides
How are oligosaccharides preassembled?
Is this process conserved throughout species?
A preassembled oligosaccharide on a dolichol carrier.
Yes

Where is the preassembles oligosaccharide transfered to?
Where and when does this happen?
The preassembled oligosaccharide is transferred to an acceptor ASN in the sequence
ASN-X-SER/THR
In the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum as the protein is being synthesized

Where does the growing peptide accept the oligosaccharide?
In the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Is the N-Linked oligosaccharide enzymatically modified before release from the rough endolasmic reticulum?
The final form of N-linked sugar is dependent on modifying enzymes that trim off sugars and add sugars so that there are a large variety of oligosaccharides possible.
Are all the N-Linked olligosaccharides initially the same?
even though all N-linked oligosaccharides are initially the same modifications change the final oligosaccharide.
Provide an example of N-Linked olligosaccharide modification
E.g. glucoses and some of the mannoses are removed, and galactose, sialic acid, and fucose can be added.
Olligosaccharides are modified by the __________ removal and addition of sugars
SEQUENTAL
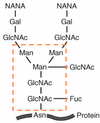
Where is the N-Glycosylated protein altered to its final form?
The Golgi gives glycosylated proteins increasingly more complex sugar modifications. The final modification being sialic acid.
Where are the sugan molecules attached to the protein?
Sugars of glycoproteins are attached to the amino acid side chain of the asparagine side chain making them N-linked olligosaccharides.
The Hydroxyl group of the sugar is linked to the N in the asparagine residue in the protein sequence.
How are glycoproteins glycosylated?
A preassembled, dolichol phosphate-oligosaccharide is transferred to asparagin (ASN or N) in a
-ASN-X-SER/THR- sequence.



