Glycolysis II Flashcards
What are the last five intermediates of glycolysis?
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
- 3-phosphoglycerate
- Phosphoglycerate
- Phosphoenolpyruvate
- Pyruvate
The last five steps of glycolysis are sometimes called the “_________________ _____________” phase.
Energy payoff
The sixth step of glycolysis converts glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to ________________________________________________ via __________ __________________________________.
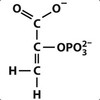
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
GAP dehydrogenase
What is the mechanism for GAP dehydrogenase?
Redox reaction
As a redox reaction, step 6 of glycolysis requires what cofactor?
NAD+
What amino acid residue acts as a nucleophile in GAP dehydrogenase?
Cysteine
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the formation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate?
GAP dehydrogenase
What is the mechanism for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GAP) dehydrogenase?
- The cysteine residue in the enzyme acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon at C1
- This attack ultimately kicks out a hydride, which then attacks the NAD+ molecule
- The enzyme is covalently bound to the molecule; an inorganic phosphate attacks the carbonyl carbon at C1, expelling the enzyme
- 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is formed

In addition to being a redox reaction, the sixth step of glycolysis - the formation of 1,3BPG - also involves what type of catalysis?
Covalent catalysis
The sixth step of glycolysis requires the cofactor NAD+ and what other molecule to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate?
Inorganic phosphate
What is the seventh step of glycolysis?
The formation of 3-phosphoglycerate from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate via phosphoglycerate kinase
Is the sixth step of glycolysis reversible?
Yes
- The cysteine residue in the enzyme acts as a nucleophile, attacking the C1 of carbonyl and expelling inorganic phosphate
- The lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in NADH move and expel a hydride ion, which attacks the enzyme-transition state intermediate carbonyl and ultimately “kicks out” the enzyme
- Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate has been reformed

What position does glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase prefer on NADH: the proR or the proS?
ProS
What enzyme catalyzes the seventh step of glycolysis - the formation of 3-phosphoglycerate from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate?
Phosphoglycerate kinase
What type of phosphorylation does the seventh step of glycolysis catalyze?
Substrate-level phosphorylation of ADP to ATP
What is the mechanism of phosphoglycerate kinase?
Phosphoryl transfer - nucleophilic attack of the acyl phosphate on 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by the oxygen atom on ADP’s beta phosphate group

Phosphoglycerate kinase is named for its reverse direction. What is the mechanism for the reverse?

The eighth step of glycolysis converts 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate. What enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
Phosphoglycerate mutase
Phosphoglycerate mutase requires a phosphorylated amino acid residue in its active site to function. What amino acid residue is it?
Histidine
What is the mechanism for the eighth step of glycolysis catalyzed by phosphoglycerate mutase?
A phosphoryl shift
- A deprotonated histidine residue abstracts a proton from the hydroxyl group on C2
- An oxygen atom acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic phosphorus on the phosphohistidine residue
- The dephosphorylated histidine then attacks the phosphate group on C3, restoring its phosphorylated status, and oxygen picks up a proton from the other protonated histidine residue

What intermediate produced in the eighth step of glycolysis is also important in regulating hemoglobin?
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate
The ninth step of glycolysis forms the high-energy compound ______________________.
Phosphoenolpyruvate
The formation of phosphoenolpyruvate is catalyzed by what enzyme?
Enolase
What is the mechanism of action for enolase?
Dehydration and general-acid catalysis