Glycolysis Flashcards
Main GLUT Transporters
-
GLUT 2:
- Found in hepatocytes and pancreatic cells
- Higher Km (15 mM)
- Liver will pick up glucose for storage proportional to its concentration in the blood (first-order kinetics)
- ß-islet cells of pancreas, along with glucokinase, serve as the glucose sensor for insulin release
-
GLUT 4:
- Found in myocytes and adipocytes
- Insulin stimulates movement of GLUT 4 transporters to membrane by exocytosis
- Lower Km (5 mM); at high glucose concentration, transporters permit only a constant rate of glucose influx because they will be saturated (zero-order kinetics)
Action and Regulation of Hexokinase and Glucokinase
- phosphorylate glucose to form G6P and prevent it from leaving the cell
-
Hexokinase is widely distributed in the tissues and is inhibited by its own product, G6P
- Lower Km
-
Glucokinase is found only in liver cells and pancreatic ß- islet cells
- in the liver, glucokinase is induced by insulin
- _g_lucokinase acts as the glucose sensor with GLUT 2 in pancreatic cells
- Higher Km

Action and Regulation of PFK-1 and PFK-2
-
PFK-1:
- rate-limiting enzyme and main control point in glycolysis
- phosphorylates F6P to F 1,6-BP using ATP
- inhibited by ATP and citrate
- activated by AMP and F 2,6-BP (overrides inactivation by ATP to allow glycolysis to continue to metabolites can be used elsewhere)
-
__PFK-2:
- converts F6P to F 2,6-BP, which activates PFK-1
- found mostly in the liver (see above role or F 2,6-BP; this is crucial in the liver to allow metabolites of continued glycolysis to be redirected)
- activated by insulin
- inhibited by glucagon

Action and Regulation of GAP Dehydrogenase
- catalyzes oxidation and phosphorylation of GAP to 1,3-BPG
- reduces NAD+ to NADH

Action and Regulation of 3-Phosphoglycerate Kinase
- transfer high-energy phosphate from 1,3-BPG to ADP, forming ATP and 3PG
- (substrate-level phosphorylation)

Action and Regulation of Pyruvate Kinase
- last enzyme in aerobic glycolysis
- catalyzes substrate-level phosphorylation of ADP using higher-energy substrate PEP
- activated by F 1,6-BP from PFK-1 reaction (feed-forward activation)

Glycolysis Step 1

Glycolysis Step 2

Glycolysis Step 3

Glycolysis Step 4

Glycolysis Step 5

Glycolysis Step 6

Glycolysis Step 7

Glycolysis Step 8

Glycolysis Step 9

Glycolysis Step 10

PDH Complex Reaction
- converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- irreversible
- inhibited by acetyl-CoA
- PDH in the liver is activated by insulin, but PDH in the nervous system is resistant to hormones
- (high insulin signals to the liver that the individual is in a well-fed state and should not only burn glucose for energy but shift the fatty acid equilibrium toward production and storage, rather than oxidation)
- Equation:
- pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA → acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2
- Required Coenzymes:
- TPP, lipoic acid, CoA, FAD, NAD+

Fermentation
- occurs in the absence of oxygen
- Mammalian Cells: pyruvate → lactate
- Yeast Cells: pyruvate → ethanol
-
Enzyme: lactate dehydrogenase
- oxidizes NADH to NAD+, regenerating the coenzyme needed for the GAP dehydrogenase reaction

Diagram: Full Process of Glycolysis
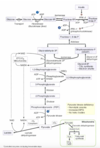
Important Intermediates of Glycolysis
-
DHAP:
- used in hepatic and adipose tissue for triacylglycerol synthesis
- DHAP is formed from F 1,6-BP and can be isomerized to glycerol 3-phosphate, which can then be converted to glycerol
-
1,3-BPG and PEP:
- high energy intermediates used to generate ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation
- generate only ATP gained in anaerobic respiration
Irreversible Enzymes in Glycolysis
Step 1: Glucokinase/Hexokinase
Step 3: PFK-1
Step 10: Pyruvate Kinase
Glycolysis in Erythrocytes and 2,3-BPG
- anaerobic glycolysis is the only pathway for ATP production in RBCs
- RBCs have bisphosphoglycerate mutase, which produces 2,3-BPG from 1,3-BPG
- 2,3-BPG bind allosterically to the ß-chains of HbA and decreases its affinity for oxygen: this allows for greater unloading of oxygen in tissues while still allowing for 100% saturation in the lungs
- 2,3-BPG does not bind well to fetal hemoglobin (HbF) = HbF has a higher affinity for oxygen, allowing transplacental passage of oxygen from mother to fetus
Galactose Metabolism
- lactose is hydrolyzed to galactose and glucose by lactase; galactose reaches the liver via the hepatic portal vein (as is typical of other monosaccharides)
- Steps:
- galactose is phosphorylated by galactokinase to form galactose 1-P
- galactose 1-P is converted to glucose 1-P by galactose 1-P uridyltransferase and an epimerase

Fructose Metabolism
- sucrose is hydrolyzed by sucrase to glucose and fructose
- fructose is absorbed in the hepatic portal vein (with other monosaccharides)
- Steps:
- fructokinase in the liver phosphorylates fructose to fructose 1-P
- fructose 1-P is cleaved into glyceraldehyde and DHAP by aldolase B
- Steps:


