Biology Memorization Flashcards
1
Q
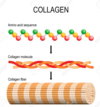
Structural Proteins: Collagen
A
- trihelical fiber (three left-handed helices woven together to form secondary right-handed helix)
- makes up most of ECM of connective tissues
- found throughout body, provides strength and flexibility
2
Q
Structual Proteins: Elastin
A
- component of ECM of connective tissue
- stretches and recoils like a spring to restore original shape of the tissue

3
Q
Structural Proteins: Keratin
A
- intermediate filament proteins found in epithelial cells
- contribute to mechanical integrity of the cell and function as regulatory proteins
- primary protein in hair/nails
4
Q
Structural Proteins: Actin
A
- makes up microfilaments and thin filaments in myofibrils
- most abundant protein in eukaryotic cells
-
polar: positive and negative sides
- polarity allows motor proteins to travel unidirectionally along actin filaments
5
Q
Structual Proteins: Tubulin
A
- makes up microtubules
- polar: negative end usually adjacent to nucleus, positive end in periphery of the cell
6
Q
Motor Proteins: Myosin
A
- primary motor protein that interacts with actin
- thick filament in myofibrils
- can be involved in cellular transport
- each myosin subunit has a single head and neck; movement of the neck is responsible for the power stroke in sarcomere contractions
7
Q
Motor Proteins: Kinesins and Dyneins
A
- motor proteins associated with microtubules
- have two heads, at least one of which remains attached to tubulin at all times
-
Kinesins:
- play key role in aligning chromosomes during metaphase and depolymerizing microtubules during anaphase of mitosis
- bring vesicles toward the positive end of cell during vesicular transport
-
Dyneins:
- involved sliding movement of cilia and flagella
- bring vesicles toward negative end of cell during vesicular transport
8
Q
CAMs: Cadherins
A
- glycoproteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell adhesion
- hold similar cell types together
9
Q
CAMs: Integrins
A
- group of proteins with 2 membrane-spanning chains called alpha and beta
- chains are important for binding to and communication with ECM
- play role in cell signaling
- impact cell function by promoting cell division, apoptosis, etc.
- part of clotting
- WBC migration
10
Q
CAMs: Selectins
A
- bind to carbohydrate molecules that project from other cell surfaces
- weakest bonds of CAMs
- expressed on WBCs and endothelial cells
- play an important role in host defense: inflammation and WBC migration
11
Q
Cytoskeletal Components: Microtubules
A
- hollow polymers of tubulin
- radiate throughout cell, providing primary pathways along which motor proteins carry vesicles
- cilia and flagella are composed of microtubules
- microtubules are organized by centrioles in the centrosome; during mitosis, centrioles mirgrate to opposite poles of the dividing cell and organize the mitotic spindle; microtubules emanating from centrioles attach to the chromosomes via kinetochores and pull the sister chromatids apart
12
Q
Cytoskeletal Components: Microfilaments
A
- made up of actin polymers organized into bundles and networks
- resistant to compression and fracture = protection for cell
- actin filaments can use ATP to generate force for movement by interaction with myosin (muscle contraction)
- Cytokinesis: microfilaments organize as a ringe at the site of division in cytokinesis
13
Q
Cytoskeletal Components: Intermediate Filaments
A
- diverse group; includes: keratin, desmin, vimentin, and lamins
- involved in cell-cell adhesion or maintenance of integrity of cytoskeleton
- can withstand great tension, increasing structural rigidity of the cell
- intermediate filaments help anchor organelles, including the nucleus
14
Q
A
15
Q
A


