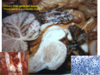
Gliomas Flashcards
What are th types of gliomas?
Astrocytomas (WHO Grades I/IV)-most common
Oligodendrogliomas (Grade II)
Ependymomas (Grade II)
Choroid plexus papillomas (Grade I)
Colloid cysts (nonneoplastic lesions)-just lesions
Where can astrocytomas be found?
Cerebral
cerebellar
What is 80% of adult brain tumors?
Astrocytomas
What are the grades for the types of astrocytomas?
Well differentiated (gradeII)
Anapestic astrocytoma (grade III)
Glioblastoma (grade IV)-patients die within a year
What causes Well differentiated defuse astrocytoma (grade II)?
Inactivation of p53, overexpression of PDGF-A
What are the types of Glioblastomas?
2º from a low-grade tumor: younger patients
de novo tumors: older patients
What are the causes of 2º from a low-grade tumor?
P53 mutation, isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation, & PDGFR-A overexpression
What are causes of De nova tumors?
Mutation of PTEN (tumor suppressor) & amplification of EGFR
What are characteristics of a Well differentiated defuse astrocytoma (grade II)?
are poorly defined, gray, infiltrative tumors that expand and distort the invaded brain
–Inactivation of p53, overexpression of PDGF-A
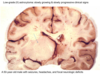
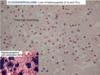
What does low grade (II) astrocytomas histological appearance?
increase in glial cellularity
background of fibrillary appearance
–Inactivation of p53, overexpression of PDGF-A
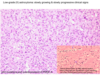
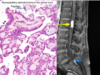
What are glioblastomas characterized by?
Ring enhancement
very poor prognosis
rapidly growing

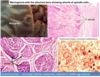
What are the characteristics of glioblostomas histologically?
shows high cellularity, numerous mitotic figures, pleomorphism of cells and their nuclei areas of necrosis, proliferation of blood vessels and their endothelium.

What is the most common tumor for children under 10?
Cerebellar (pilocytic) astrocytoma: good prognosis if excised completely
slow growing
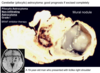
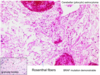
Wha type of fibers does a low grade cerebellar polycytic astrocytoma have for histological identification?
Rosenthal fibers
What are the usual locations of Oligodendrogloma?
Cerebral hemispheres