g.i tract - prof peters Flashcards
carries food and liquid from the mouth to the stomach propelled by ……….?
peristalis
the upper and lower part of the oesophagus are bounded by what?
upper and lower oesophageal sphincters
the oesophagus is lined by what cell type
stratified squamous epithelium
the oesophagus musculature contains, striated and smooth.
what regions of the oesophagus would you find these
striated - upper thrid
smooth - remainder
what nerve innervates the oesophagus
vagus nerve CNX
what triggers the closure of the upper oesophageal sphincter
once food has entered the oesophagus
primary peristaltic wave (vagus nerve)
swallowing centre (pons and medulla)
what is the enteric nervous system
its the nervous sytsem that governs the GI system
what do the circular fibres do behind bolus during peristalsis
contract to squeeze it down to stomach

what do longitudinal fibres infront of bolus do, during peristalsis
contract to shorten distance to travel

after swallowing how many seconds later does the lower oesophageal sphincter open
2-3 seconds
prevents reflux
when would a secondary peristaltic wave occur
when sticky food becomes lodged in the oesophagus
what digest protein in the stomach
pepsin and HCl
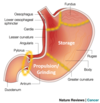
approximatley how much gastric juices is produced by the gastric glands
2 litre/day
mechanical activity occurs as two types. what are they
orad stomach
caudad stomach

for storage of ingested material in the stomach. must stomach relax or contract
relax via vagus nerve





